|
Dorcopsoides
''Dorcopsoides'' is a genus of extinct species of kangaroo from the Pliocene of Australia.. Description ''Dorcopsoides'' was described in 1967 from the well-preserved lower jaw, skull fragments and occipital found in the Upper Miocene Alcoota Fossil Beds north-east of Alice Springs in the Northern Territory. It was part of the Alcoota local fauna, which also included zygomaturine diprotodonts, a type of mihirung (''Ilbandornis''), a crocodile (''Baru'') and the giant thylacine, ''Thylacinus potens''. It was about the size of a gray and black four-eyed opossum. The generic name (''Dorcopsoides'') indicates a resemblance to forest wallabies (''Dorcopsis'') now living in New Guinea and neighboring islands. References Prehistoric macropods Pliocene marsupials Miocene marsupials Miocene mammals of Australia Pliocene mammals of Australia Prehistoric marsupial genera {{Diprotodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baru
''Baru'', sometimes referred to as the cleaver-headed crocodile, is an extinct genus of Australian mekosuchine crocodilian. Its fossils have been found from various Late Oligocene and Miocene localities from across the Northern Territory and Queensland, indicating that ''Baru'' was a common genus during the late Paleogene and early Neogene. Three species are recognized, ''B. darrowi'', ''B. iylwenpeny'', and ''B. wickeni''. ''Baru'' was a large and powerful mekosuchine with an incredibly deep and robust skull and long teeth with compressed crowns that in the case of ''Baru darrowi'' are furthermore adorned with minute serrations. At a length of around , it was among the largest crocodilians native to Australia at the time and the largest predator of its ecosystem. With dorsally oriented nostrils and eyes and a poor range of head movement, as well as its fossils being associated with freshwater environments, ''Baru'' is generally interpreted to have been a semi-aquatic ambush hunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Mammals Of Australia
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Marsupials
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Macropods
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorcopsis
''Dorcopsis'' is a genus of marsupial in the family Macropodidae Macropodidae is a Family (biology), family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, Wallaby, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing .... The members of the genus are found on the island of New Guinea. Species The genus contains the following species: * Black dorcopsis (''Dorcopsis atrata'') * White-striped dorcopsis (''Dorcopsis hageni'') * Gray dorcopsis (''Dorcopsis luctuosa'') * Brown dorcopsis (''Dorcopsis muelleri'') References Macropods Marsupial genera Taxa named by Salomon Müller Taxa named by Hermann Schlegel Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Diprotodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
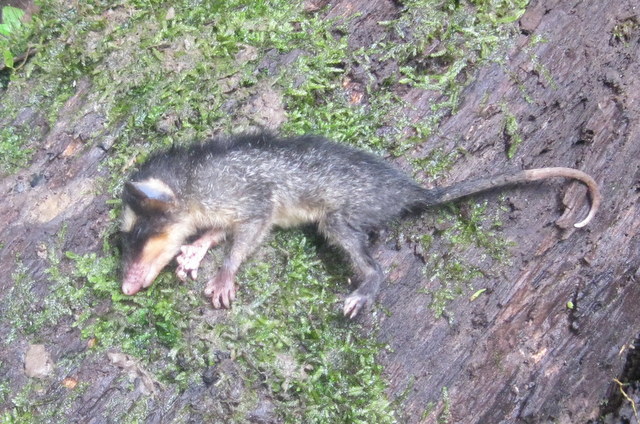
Gray And Black Four-eyed Opossum
The nine species in the genus ''Philander'', commonly known as gray and black four-eyed opossums, are members of the order Didelphimorphia. Mature females have a well-developed marsupium. The tail appears to be hairless except for the proximal (closest to the body) 5 or 6 cm, which has a few long hairs. The tail is slightly longer than the head-and-body length, and it is black for the proximal one half to two thirds of its length. The genus is closely related to ''Didelphis'' but the species of ''Philander'' are smaller than those of ''Didelphis''. The genus formerly included ''Metachirus nudicaudatus'', but this species lacks a pouch and so is now considered a separate genus. The common name comes from the white spots above the eyes, which can appear from a distance to be another set of eyes. Species *'' Philander andersoni'' - Anderson's four-eyed opossum *'' Philander canus'' - Common four-eyed opossum *'' Philander deltae'' - Deltaic four-eyed opossum *'' Philander m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylacinus Potens
''Thylacinus potens'' ("powerful pouched animal") was the largest species of the family Thylacinidae, originally known from a single poorly preserved fossil discovered by Michael O. Woodburne in 1967 in a Late Miocene locality near Alice Springs, Northern Territory. It preceded the most recent species of thylacine by 4–6 million years, and was 5% bigger, was more robust and had a shorter, broader skull. Its size is estimated to be similar to that of a grey wolf; the head and body together were around 5 feet long, and its teeth were less adapted for shearing compared to those of the now-extinct thylacine. Taxonomy The description of the species was published in 1967, the author Michael O. Woodburne distinguishing the new thylacine with the epithet ''potens'' for what he interpreted as a "powerful" predator. The evidence for the species emerged from geological and palaeontological research into the fossil fauna of the Alcoota site. Description A larger species of ''Thylacinus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilbandornis
''Ilbandornis'' was a genus of ostrich-sized dromornithid, a clade known casually as "demon ducks" because they are most closely related to the water fowl clade anseriformes. It was far more lightly built than other members of the family, indicating a more cursorial lifestyle; it was a fast runner. The majority of researchers consider Dromornithids to be herbivorous; this is borne out by molecular analysis of the gastroliths and eggshells of both ''Ilbandornis'' and the related ''Genyornis''. While ''Ilbandornis'' and ''Genyornis'' have skulls of similar size to emus, other Dromornithids such as '' Dromornis'' have far more robust skulls with large beaks; these were previously considered an adaptation for carnivory, but their blunt edges and lack of hooked tip indicate that the species were herbivorous. It is therefore likely that the differences in skull shape are due to differences in diet. Ilbandornis went extinct sometime in the Miocene epoch. Taxonomy Two species named by Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |