|
Djenné-Djenno
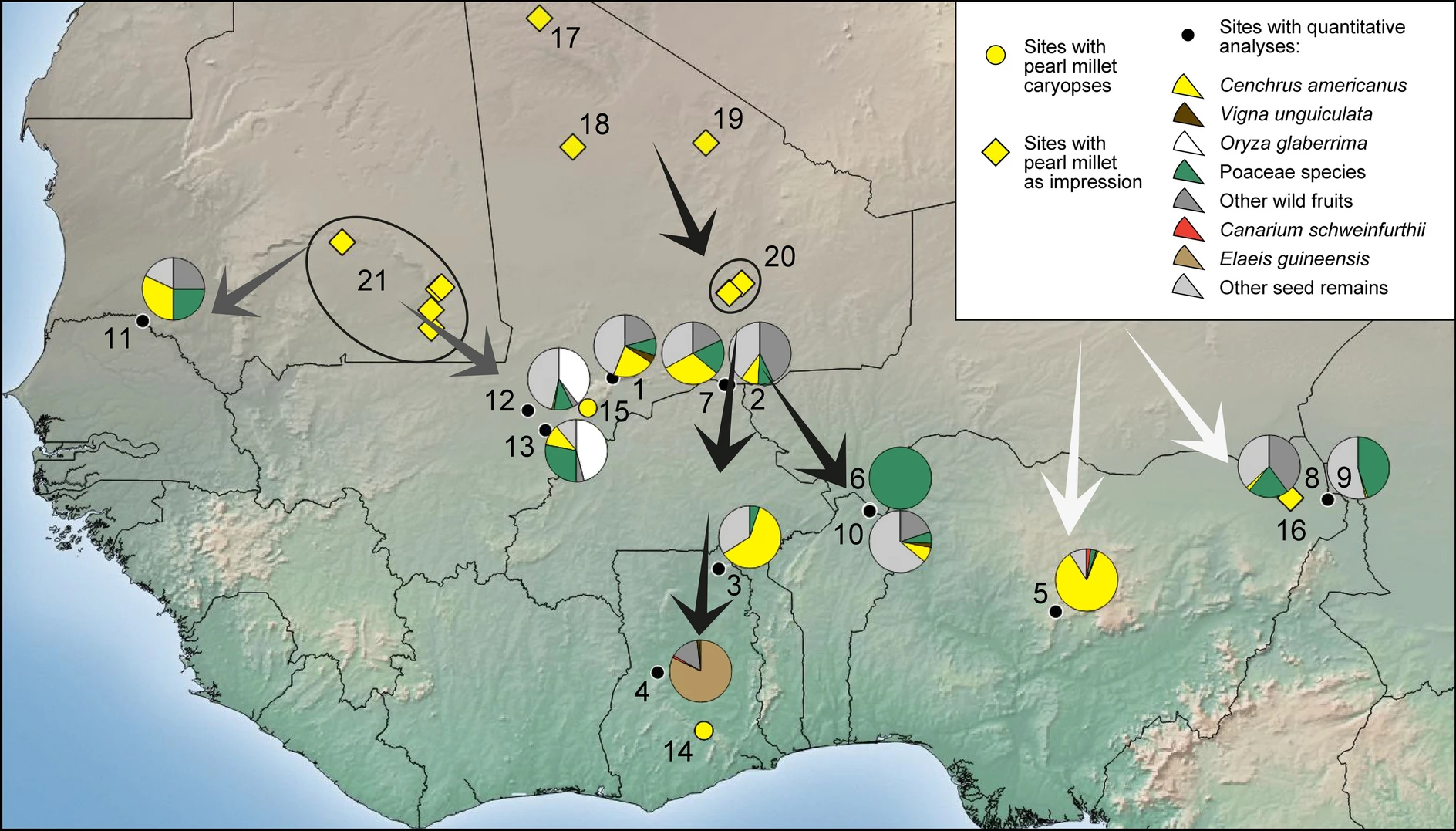
Djenné-Djenno (also Jenne-Jeno; ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Niger River Valley in the country of Mali. Literally translated to "ancient Djenné", it is the original site of both Djenné and Mali and is considered to be among the oldest urbanized centers and the best-known archaeological sites in West Africa. This archaeological site is located about from the modern town, and is believed to have been involved in long distance trade and possibly the domestication of African rice. The site is believed to exceed in area; however this is yet to be confirmed with extensive survey work. With the help of archaeological excavations mainly by Roderick and Susan McIntosh, the site is known to have been occupied from 250 BC to 900 AD. Previously, scholars did not believe that advanced trade networks and complex societies developed in West Africa until traders started coming from the north. However, sites such as Djenné-Djenno disprove this, as these tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandé Peoples
The Mandé peoples are a linguistic grouping of those African nations who speak Mande languages. The various Mandé-speaking nations are concentrated in the western regions of West Africa. The Mandinka or Malinke, a western Mandé nation, are credited with the founding one of the largest West African empires. Other large Mandé-speaking nations include the Soninke and Susu, as well as smaller ones such as the Ligbi, Vai, and Bissa. Mandé-speaking peoples inhabit various environments, from coastal rainforests to the sparse Sahel, and have a wide range of cuisines, cultures, and beliefs. After migrating from the Central Sahara, Mandé-speaking peoples established Tichitt culture in the Western Saharan region of Mauritania, which had Dhar Tichitt as its primary regional center and possibly the Malian Lakes Region as its secondary regional center. Subsequently, toward the end of the Mauritanian Tichitt culture, Mandé-speaking peoples began to spread and established M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan McIntosh
Susan McIntosh is an American anthropologist and archaeologist and has been the Herbert S. Autrey Professor of Anthropology at Rice University since 2012. She is known for her work at Djenné-Djenno in Mali and for her advocacy against looting of cultural artifacts. Education McIntosh began her undergraduate studies at Wellesley College and received her BA in anthropology from the University of Pennsylvania in 1973. After graduate studies at the University of Cambridge and University of California, Santa Barbara she received her MA and PhD, respectively. Her doctoral dissertation was based on field work at Djenné-Djenno in Mali. Career McIntosh is the Herbert S. Autrey Professor of Anthropology and interim dean of the School of Social Sciences at Rice University, where she has taught since 1981. She has co-authored or edited archaeological monographs on field work 19802018 at the sites of Djenné-Djenno (Mali), Sincu Bara (Senegal), and Cubalel (Senegal). In 1999 President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djenné
Djenné (; also known as Djénné, Jenné, and Jenne) is a Songhai people, Songhai town and Communes of Mali, urban commune in the Inland Niger Delta region of central Mali. The town is the administrative centre of the Djenné Cercle, one of the eight subdivisions of the Mopti Region. The commune includes ten of the surrounding villages and in 2009 had a population of 32,944. The history of Djenné is closely linked with that of Timbuktu. Between the 15th and 17th centuries much of the trans-Saharan trade in goods such as salt, gold, and slaves that moved in and out of Timbuktu passed through Djenné. Both towns became centres of Islamic scholarship. Djenné's prosperity depended on this trade and when the Portugal, Portuguese established trading posts on the African coast, the importance of the trans-Saharan trade and thus of Djenné declined. The town is famous for its distinctive adobe architecture, most notably the Great Mosque of Djenné, Great Mosque which was built in 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dia, Mali
Dia (''Jà'') is a small town and seat of the commune of Diaka in the Cercle of Ténenkou in the Mopti Region of southern-central Mali. It is situated at the western edge of the Inland Delta floodplain, and is watered by the Diaka, one of the Niger River's major distributaries and the only permanent watercourse in the region. Tigemaxo and also some Fulfulde are spoken in Dia. The three-settlement mound complex of Dia, located at the western edge of the Inland Niger Delta of Mali, is known for rich oral and written resources, and predates the much better-known cities of nearby Djenne and Timbuktu. According to Levtzion, the Diakhanke "remember Dia in Massina as the town of their ancestor, Suware, a great marabout, and a saint." This vast site thus offers the possibility of studying the beginning of urbanization in this part of Africa and the structure of an early West African city. Favorable climate and water supply have favored human settlement for centuries, and the history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhar Tichitt
Dhar Tichitt is a line of sandstone cliffs located in the southwestern region of the Sahara Desert in Mauritania that boasts a series of eponymous Neolithic archaeological sites. It is one of several in the area belonging to the Tichitt culture, including Dhar Tichitt, Dhar Walata, Dhar Néma, and Dhar Tagant. Dhar Tichitt, which includes Dakhlet el Atrouss, may have served as the primary regional center for a hierarchical social structure within the Tichitt Tradition. The cliffs of Dhar Tichitt were inhabited by pastoralists and farmers between 4000 BP and 2300 BP, or between 2000 BCE and 300 BCE. Dhar Tichitt is one of the oldest known archaeological occupation sites in West Africa. About 500 settlements littered the region in the former savannah of the Sahara. In addition to herding livestock (cattle, sheep, goats), its inhabitants hunted, fished, collected wild grain, and grew bulrush millet. The inhabitants and creators of these settlements during these periods are thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire (), also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadu, was an ancient western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali. It is uncertain among historians when Ghana's ruling dynasty began. The first identifiable mention of the imperial dynasty in written records was made by Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī in 830. Further information about the empire was provided by the accounts of Cordoban scholar al-Bakri when he wrote about the region in the 11th century. After centuries of prosperity, the empire began its decline in the second millennium, and would finally become a vassal state of the rising Mali Empire at some point in the 13th century. Despite its collapse, the empire's influence can be felt in the establishment of numerous urban centers throughout its former territory. In 1957, the British colony of the Gold Coast, under the leadership of Kwame Nkrumah named itself Ghana upon independence. Etymology The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive River delta, delta, known as the Niger Delta, into the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile and the Congo River. Its main tributary is the Benue River. Etymology The Niger has different names in the different languages of the region: * Fula language, Fula: ''Maayo Jaaliba'' * Manding languages, Manding: ''Jeliba'' or ''Joliba'' "great river" * Tuareg languages, Tuareg: ''Eġərəw n-Igərǝwăn'' "river of rivers" * Songhay languages, Songhay: ''Isa'' "the river" * Zarma language, Zarma: ''Isa Beeri'' "great river" * Hausa language, Hausa: ''Kwara'' *Nupe language, Nupe: ''Èdù'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom Overseas Territories, United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at around million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male.United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017). World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, custom data acquired via webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; ; Koyra Chiini: ; ) is an ancient city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. It is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali, having a population of 32,460 in the 2018 census. Archaeological evidence suggests prehistoric settlements in the region, predating the city's Islamic scholarly and trade prominence in the medieval period. Timbuktu began as a seasonal settlement and became permanent early in the 12th century. After a shift in trading routes, particularly after the visit by Mansa Musa around 1325, Timbuktu flourished, due to its strategic location, from the trade in salt, gold, and ivory. It gradually expanded as an important Islamic city on the Saharan trade route and attracted many scholars and traders before it became part of the Mali Empire early in the 14th century. In the first half of the 15th century, the Tuareg people took control for a short period, until the expanding Songhai Empire absorbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krannert Art Museum
The Krannert Art Museum (KAM) is a fine art museum located at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in Champaign, Illinois, United States. It has of space devoted to all periods of art, dating from ancient Egypt to contemporary photographyThe museum's collectionof more than 11,000 objects can be accessed online and includes specializations in 20th-century art, Asian art, and pre-Columbian art, particularly works from the Andes. In addition to collection galleries, the museum features 6 to 10 special exhibitions each year from national and international museum collections as well as exhibitions of art by contemporary artists, faculty and graduate and undergraduate students . History The museum was designed by architect Ambrose Richardson and opened in 1961. An addition to the museum was completed in 1988. This addition, the Kinkead Pavilion, was the creation of Larry Booth and Associates. The building incorporates contemporary Egyptian art decorative elements in an over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its south. Of the fifty U.S. states, Illinois has the List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, fifth-largest gross domestic product (GDP), the List of U.S. states and territories by population, sixth-largest population, and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 25th-most land area. Its capital city is Springfield, Illinois, Springfield in the center of the state, and the state's largest city is Chicago in the northeast. Present-day Illinois was inhabited by Indigenous peoples of the Americas#History, Indigenous cultures for thousands of years. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi and Illinois River, Illinois rivers in the 17th century Illinois Country, as part of their sprawling colony of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indianapolis Museum Of Art
The Indianapolis Museum of Art (IMA) is an encyclopedic art museum located at Newfields, a campus that also houses Lilly House, The Virginia B. Fairbanks Art & Nature Park, the Garden at Newfields and more. It is located at the corner of North Michigan Road and West 38th Street, about three miles north of downtown Indianapolis, northwest of Crown Hill Cemetery. There are exhibitions, classes, tours, and events, many of which change seasonally. The entire campus and organization was previously referred to as the Indianapolis Museum of Art, but in 2017 the campus and organization were renamed "Newfields" as part of a rebranding campaign. The "Indianapolis Museum of Art" now specifically refers to the main art museum building that acts as the cornerstone of the campus, as well as the legal name of the organization doing business as Newfields. The Indianapolis Museum of Art is the ninth oldest and eighth largest encyclopedic art museum in the United States. The permanent collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |