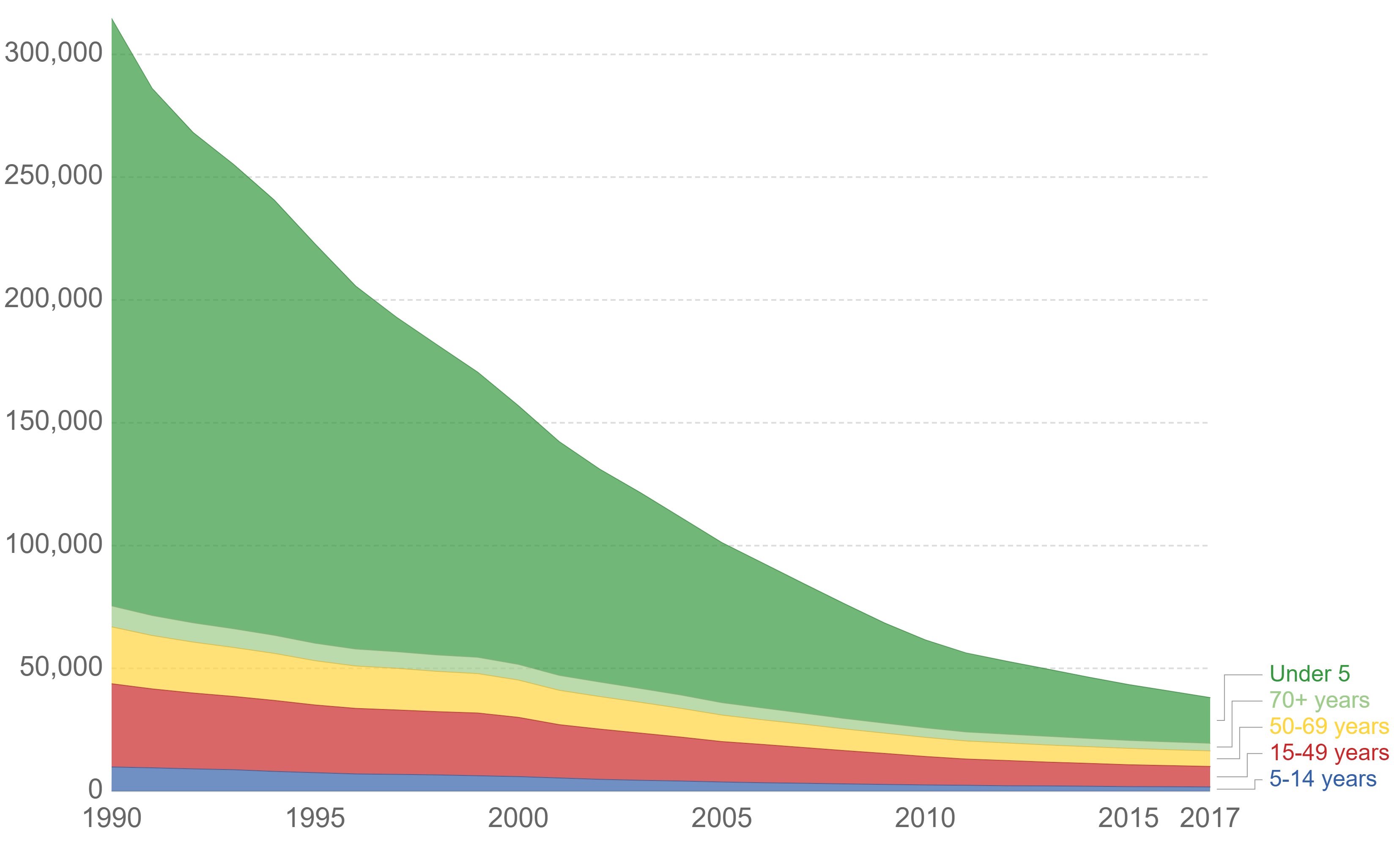
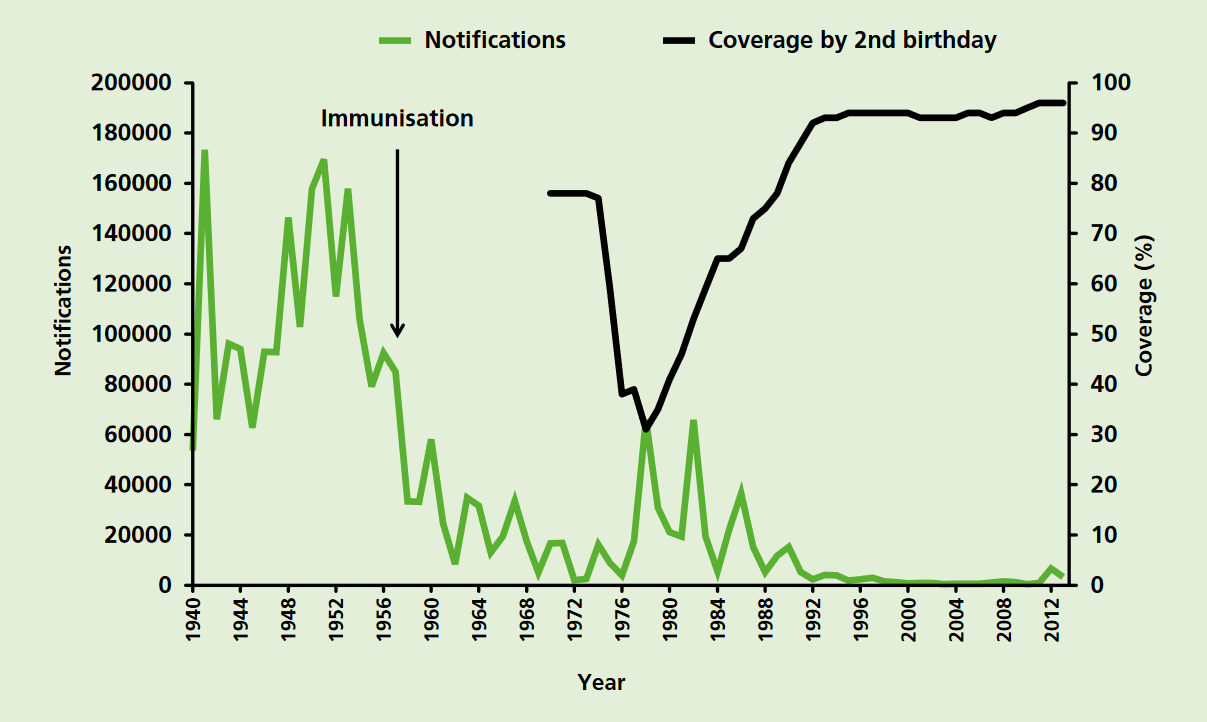
|
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacteria, bacterium ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild Course (medicine), clinical course, but in some outbreaks, the mortality rate approaches 10%. Signs and symptoms may vary from mild to severe, and usually start two to five days after exposure. Symptoms often develop gradually, beginning with a sore throat and fever. In severe cases, a grey or white patch develops in the throat, which can block the airway, and create a barking cough similar to what is observed in croup. The neck may also swell, in part due to the enlargement of the facial lymph nodes. Diphtheria can also involve the skin, eyes, or genitals, and can cause complications, including myocarditis (which in itself can result in an cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rate), peripheral neuropathy, inflammation of nerves (which can result in paralysis), proteinuria, kidney problems, and bleeding problems due to thrombocytopenia, low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium Diphtheriae
''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' is a Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. It is also known as the Klebs–Löffler bacillus because it was discovered in 1884 by German bacteriologists Edwin Klebs (1834–1912) and Friedrich Löffler (1852–1915). These bacteria are usually harmless, unless they are infected by a bacteriophage carrying a gene which gives rise to a microbial toxin, toxin. This toxin causes the disease. Diphtheria is caused by the adhesion and infiltration of the bacteria into the mucosal layers of the body, primarily affecting the respiratory tract and causing the subsequent release of an exotoxin. The toxin has a localized effect on skin lesions, as well as a metastatic, proteolytic effects on other organ systems in severe infections. Originally a major cause of childhood mortality, diphtheria has been almost entirely eradicated due to the vigorous administration of the diphtheria vaccination in the 1910s. Diphtheria is no longer transmitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphtheria Vaccine
Diphtheria vaccine is a toxoid vaccine against diphtheria, an illness caused by ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Its use has resulted in a more than 90% decrease in number of cases globally between 1980 and 2000. The first dose is recommended at six weeks of age with two additional doses four weeks apart, after which it is about 95% effective during childhood. Three further doses are recommended during childhood. It is unclear if further doses later in life are needed. The diphtheria vaccine is very safe. Significant side effects are rare. Pain may occur at the injection site. A bump may form at the site of injection that lasts a few weeks. The vaccine is safe in both pregnancy and among those who have a poor immune function. The diphtheria vaccine is delivered in several combinations. Some combinations (Td and DT vaccines) include tetanus vaccine, others (known as DPT vaccine or DTaP vaccine depending on the pertussis antigen used) comes with the tetanus and pertussis va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanus Vaccine
Tetanus vaccine, also known as tetanus toxoid (TT), is a toxoid vaccine used to prevent tetanus. During childhood, five doses are recommended, with a sixth given during adolescence. After three doses, almost everyone is initially immune, but additional doses every ten years are recommended to maintain immunity. A booster shot should be given within 48 hours of an injury to people whose immunization is out of date. Confirming that pregnant women are up to date on tetanus immunization during each pregnancy can prevent both maternal and neonatal tetanus. The vaccine is very safe, including during pregnancy and in those with HIV/AIDS. Redness and pain at the site of injection occur in between 25% and 85% of people. Fever, feeling tired, and minor muscle pain occurs in less than 10% of people. Anaphylaxis, Severe allergic reactions occur in fewer than one in 100,000 people. A number of vaccine combinations include the tetanus vaccine, such as DTaP and Tdap, which contain diph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertussis Vaccine
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effective. The effectiveness of the vaccines appears to decrease by between 2 and 10% per year after vaccination, with a more rapid decrease with the acellular vaccines. The vaccine is only available in combination with tetanus and diphtheria vaccines (DPT vaccine). Pertussis vaccine is estimated to have saved over 500,000 lives in 2002. Vaccinating the mother during pregnancy may protect the baby. The World Health Organization and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend all children be vaccinated for pertussis and that it be included in Vaccination schedule, routine vaccinations. Three doses starting at six weeks of age are typically recommended in young children. Additional doses may be given to older children and adults. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croup
Croup ( ), also known as croupy cough, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "barking/brassy" cough, inspiratory stridor, and a hoarseness, hoarse voice. Fever and runny nose may also be present. These symptoms may be mild, moderate, or severe. It often starts or is worse at night and normally lasts one to two days. Croup can be caused by a number of viruses including parainfluenza and influenza virus. Rarely is it due to a bacterial infection. Croup is typically diagnosed based on signs and symptoms after potentially more severe causes, such as epiglottitis or an airway foreign body, have been ruled out. Further investigations, such as blood tests, X-rays and cultures, are usually not needed. Many cases of croup are preventable by immunization for influenza and diphtheria. Most cases of croup are mild and the patie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropathies affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerve fibers result in different symptoms. More than one type of fiber may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, excessive alcohol consumption, immune system disease, celiac disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fomite
A fomite () or fomes () is any inanimate object that, when contaminated with or exposed to infectious agents (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses or fungi), can transfer disease to a new host. Transfer of pathogens by fomites A fomite is any inanimate object (also called passive vector) that, when contaminated with or exposed to infectious agents (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses or fungi), can transfer disease to a new host. Contamination can occur when one of these objects comes into contact with bodily secretions, like nasal fluid, vomit or feces from toilet plume. Many common objects can sustain a pathogen until a person comes in contact with the pathogen, increasing the chance of infection. The likely objects are different in a hospital environment than at home or in a workplace. Fomites such as splinters, barbed wire or farmyard surfaces, including soil, feeding troughs or barn beams, have been implicated as sources of virus. Hospital fomites For humans, common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy (although this symptom may also be caused by other conditions). Severe proteinuria can cause nephrotic syndrome in which there is worsening swelling of the body. Signs and symptoms Proteinuria often causes no symptoms and it may only be discovered incidentally. Foamy urine is considered a cardinal sign of proteinuria, but only a third of people with foamy urine have proteinuria as the underlying cause. It may also be caused by bilirubin in the urine ( bilirubinuria), retrograde ejaculation, pneumaturia (air bubbles in the urine) due to a fistula, or drugs such as pyridium. Causes There are three main mechanisms to cause proteinuria: * Due to disease in the glomerulus * Because of increased quantity of proteins in serum (overflo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care units, intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μL) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μL. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood – thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually asymptomatic, has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonsil
The tonsils ( ) are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil (or pharyngeal tonsil), two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system. When used unqualified, the term most commonly refers specifically to the palatine tonsils, which are two lymphoid organs situated at either side of the back of the human throat. The palatine tonsils and the adenoid tonsil are organs consisting of lymphoepithelial tissue located near the oropharynx and nasopharynx (parts of the throat). Structure Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils. Development The palatine tonsils tend to reach their largest size in puberty, and they gradually undergo atrophy thereafter. However, they are largest relative to the diameter of the throat in youn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |