|
Dip
Dip or DIP, may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''The Dip'', the tenth published book by Seth Godin * Dip (album), ''Dip'' (album), a 2007 studio album by Scottish musician Aidan Moffat * "Dip", a single by Danny Brown from his 2013 album ''Old (Danny Brown album), Old'' * Dip (song), "Dip" (song), a 2018 song by Tyga * Dip (TV series), ''Dip'' (TV series), an online 201 Turkish TV series * Death in Paradise (TV series), a 2011 British-French TV series Exercise * Dip, a brief swim; for example skinny dipping * Dip (dance move), a partner dance move * Dip (exercise), a type of strength training exercise ** Dip bar, a piece of fitness equipment Organisations * DIP Research (Distributed Information Processing), a defunct company which designed the Atari Portfolio * Revolutionary Workers' Party (Turkey) Places * Dezhou East railway station (China Railway telegraph code) * Diapaga Airport (IATA airport code), Burkina Faso * Dubai Investments Park, United Arab Emirates Science and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Dip
''The Dip: A Little Book That Teaches You When to Quit (and When to Stick)'' (2007) is the tenth published book by former dot com executive Seth Godin. It is a 76 page book that illustrates the concept of "the dip"—a temporary setback that can be overcome with persistence—and how to recognize if you are within one worth pushing through or one where you should quit. Background The rough idea for ''The Dip'' first materialized on Godin's blog.The Dip: A New Book Coming From Seth Godin on ''800-CEO-READ''. January 22, 2007. On an entry titled "The four curves of want and get," Godin shows four curves representing patterns of adoption. ''Seth's Blog''. June 24, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deletion/insertion Polymorphism
Indel (insertion-deletion) is a molecular biology term for an insertion or deletion of bases in the genome of an organism. Indels ≥ 50 bases in length are classified as structural variants. In coding regions of the genome, unless the length of an indel is a multiple of 3, it will produce a frameshift mutation. For example, a common microindel which results in a frameshift causes Bloom syndrome in the Jewish or Japanese population. Indels can be contrasted with a point mutation. An indel inserts or deletes nucleotides from a sequence, while a point mutation is a form of substitution that ''replaces'' one of the nucleotides without changing the overall number in the DNA. Indels can also be contrasted with Tandem Base Mutations (TBM), which may result from fundamentally different mechanisms. A TBM is defined as a substitution at adjacent nucleotides (primarily substitutions at two adjacent nucleotides, but substitutions at three adjacent nucleotides have been observed). Indels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Dip
A voltage sag (U.S. English) or voltage dip (British English) is a short-duration reduction in the voltage of an electric power distribution system. It can be caused by high current demand such as inrush current (starting of electric motors, transformers, heaters, power supplies) or fault current ( overload or short circuit) elsewhere on the system. Voltage sags are defined by their magnitude or depth, and duration. A voltage sag happens when the RMS voltage decreases between 10 and 90 percent of nominal voltage for one-half cycle to one minute. Some references define the duration of a sag for a period of 0.5 cycle to a few seconds, and a longer duration of low voltage would be called a ''sustained sag''. The definition of voltage sag can be found in IEEE 1159, 3.1.73 as "A variation of the RMS value of the voltage from nominal voltage for a time greater than 0.5 cycles of the power frequency but less than or equal to 1 minute. Usually further described using a modifier indicating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIP DRAM
In computing, a memory module or RAM stick is a printed circuit board on which memory integrated circuits are mounted. Memory modules permit easy installation and replacement in electronic systems, especially computers such as personal computers, workstations, and servers. The first memory modules were proprietary designs that were specific to a model of computer from a specific manufacturer. Later, memory modules were standardized by organizations such as JEDEC and could be used in any system designed to use them. Distinguishing characteristics of computer memory modules include voltage, capacity, speed (i.e., bit rate), and form factor. Overview Types of memory module include: * TransFlash Memory Module * SIMM, a single in-line memory module * DIMM, dual in-line memory module ** Rambus memory modules are a subset of DIMMs, but are normally referred to as RIMMs ** SO-DIMM, small outline DIMM, a smaller version of the DIMM, used in laptops * Compression Attached Memory Modu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
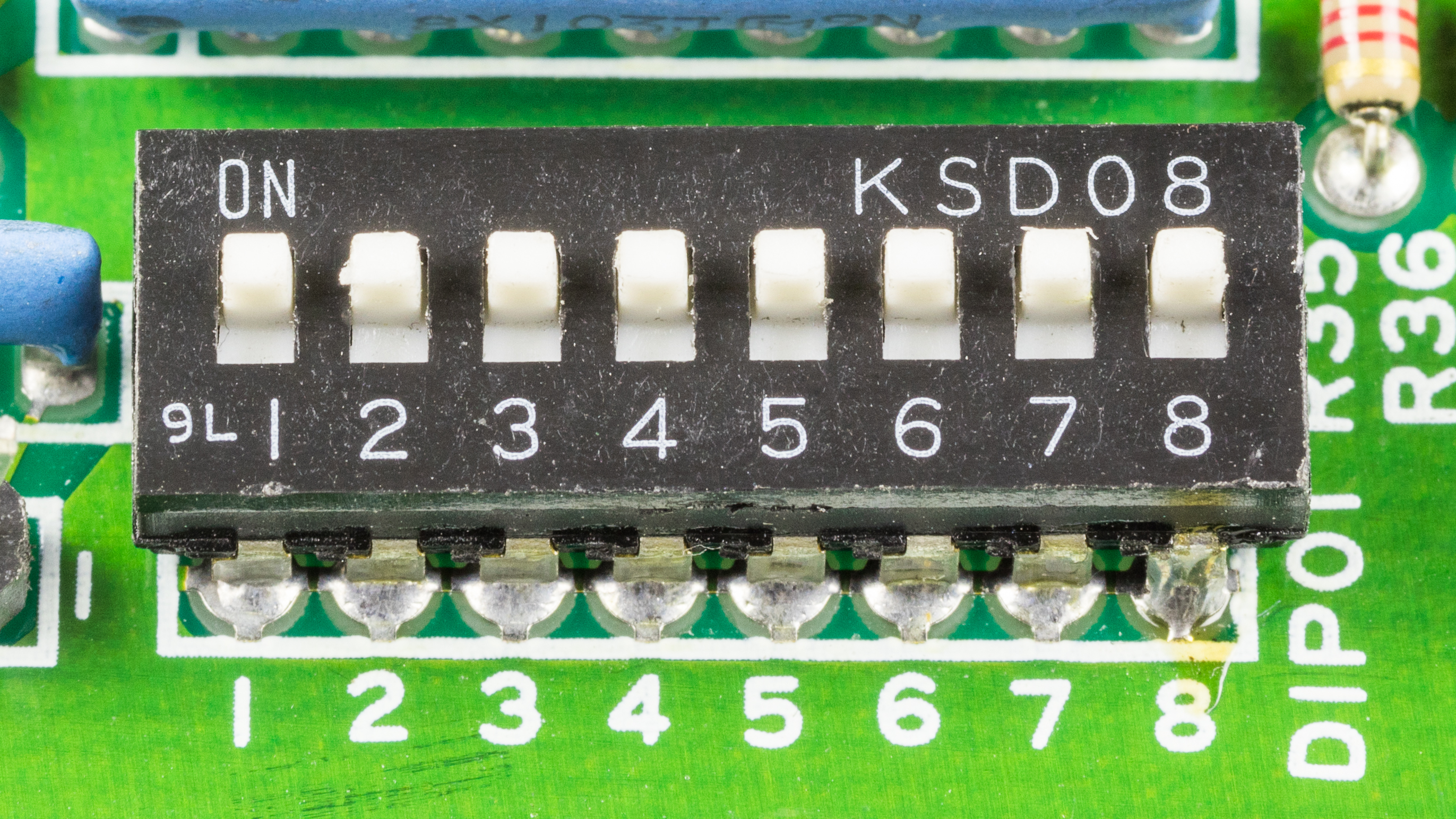
DIP Switch
A DIP switch is a manual electric switch that is packaged with others in a group in a standard dual in-line package (DIP). The term may refer to each individual switch, or to the unit as a whole. This type of switch is designed to be used on a printed circuit board along with other electronics, electronic components and is commonly used to customize the behavior of an electronic device for specific situations. DIP switches are an alternative to jumper (computing), jumper blocks. Their main advantages are that they are quicker to change and there are no parts to lose. History US patent 3621157, filed in 1970 by Pierre Schwab,U.S. Patent 3621157. "Miniature switch with multiple cam-operated switch contacts", filed June 1, 1970. is the earliest known DIP switch patent, which discloses a rotary style DIP switch. US patent 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual In-line Package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL) is an Semiconductor package, electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole technology, through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (PCB) or inserted in a socket. The dual-inline format was invented by Don Forbes, Rex Rice and Bryant Rogers at Fairchild Semiconductor, Fairchild R&D in 1964, when the restricted number of leads available on circular transistor-style packages became a limitation in the use of integrated circuits. Increasingly complex circuits required more signal and power supply leads (as observed in Rent's rule); eventually microprocessors and similar complex devices required more leads than could be put on a DIP package, leading to development of higher-density chip carriers. Furthermore, square and rectangular packages made it easier to route printed-circuit traces beneath the packages. A DIP is usually refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Document Image Processing
Document imaging is an information technology category for systems capable of replicating documents commonly used in business. Document imaging systems can take many forms including microfilm, on demand printers, facsimile machines, copiers, multifunction printers, document scanners, computer output microfilm (COM) and archive writers. Document Imaging means the conversion of paper files (of any size or description) or microfilm / fiche to digital images. Transitioning to digital in the legal sector The UK have been working slowly over the last decade to transition to digital processes. In 2013, the government launched an online claims portal to help keep track of and manage claims efficiently and quickly. Created to deal with claims of up to £25,000, the portal applies to organisations on the receiving end of employer liability and public liability claims. On May 31, 2021, a new separate system was launched called Official Injury Claim. This service deals with motor accidents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Information Processing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers. The components of a distributed system communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to microservices to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. Distributed systems cost significantly more than monolithic architectures, primarily due to increased needs for additional hardware, servers, gateways, firewalls, new subnets, proxies, and so on. Also, distributed systems are prone to fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Virtual Server
Linux Virtual Server (LVS) is load balancing software for Linux kernel–based operating systems. LVS is a free and open-source project started by Wensong Zhang in May 1998, subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2. The mission of the project is to build a high-performance and highly available server for Linux using clustering technology, which provides good scalability, reliability and serviceability. Overview The major work of the LVS project is now to develop advanced IP load balancing software (IPVS), application-level load balancing software (KTCPVS), and cluster management components. * IPVS: an advanced IP load balancing software implemented inside the Linux kernel. The IP Virtual Server code is merged into versions 2.4.x and newer of the Linux kernel mainline. * KTCPVS: implements application-level load balancing inside the Linux kernel, still under development. LVS can be used for building highly scalable and highly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Image Processing
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allows a much wider range of algorithms to be applied to the input data and can avoid problems such as the build-up of Noise (signal processing), noise and distortion during processing. Since images are defined over two dimensions (perhaps more), digital image processing may be modeled in the form of Multidimensional system, multidimensional systems. The generation and development of digital image processing are mainly affected by three factors: first, the development of computers; second, the development of mathematics (especially the creation and improvement of discrete mathematics, discrete mathematics theory); and third, the demand for a wide range of applications in environment, agriculture, military, industry and medical science has incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device-independent Pixel
A device-independent pixel (also: ''density-independent pixel'', ''dip'', ''dp'') is a unit of length. A typical use is to allow mobile device software to scale the display of information and user interaction to different screen sizes. The abstraction allows an application to work in pixels as a measurement, while the underlying graphics system converts the abstract pixel measurements of the application into real pixel measurements appropriate to the particular device. For example, on the Android operating system a device-independent pixel is equivalent to one physical pixel on a 160 dpi screen, while the Windows Presentation Foundation Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a free and open-source user interface framework for Windows-based desktop applications. WPF applications are based in .NET, and are primarily developed using C# and XAML. Originally developed by Microso ... specifies one device-independent pixel as equivalent to 1/96th of an inch. As dp is a physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Inversion Principle
In object-oriented design, the dependency inversion principle is a specific methodology for Coupling (computer programming), loosely coupled software Modular programming, modules. When following this principle, the conventional dependency (computer science), dependency relationships established from high-level, policy-setting modules to low-level, dependency modules are reversed, thus rendering high-level modules independent of the low-level module implementation details. The principle states: By dictating that high-level and low-level objects must depend on the same abstraction, this design principle the way some people may think about object-oriented programming. The idea behind points A and B of this principle is that when designing the interaction between a high-level module and a low-level one, the interaction should be thought of as an abstract interaction between them. This has implications for the design of both the high-level and the low-level modules: the low-level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |