|
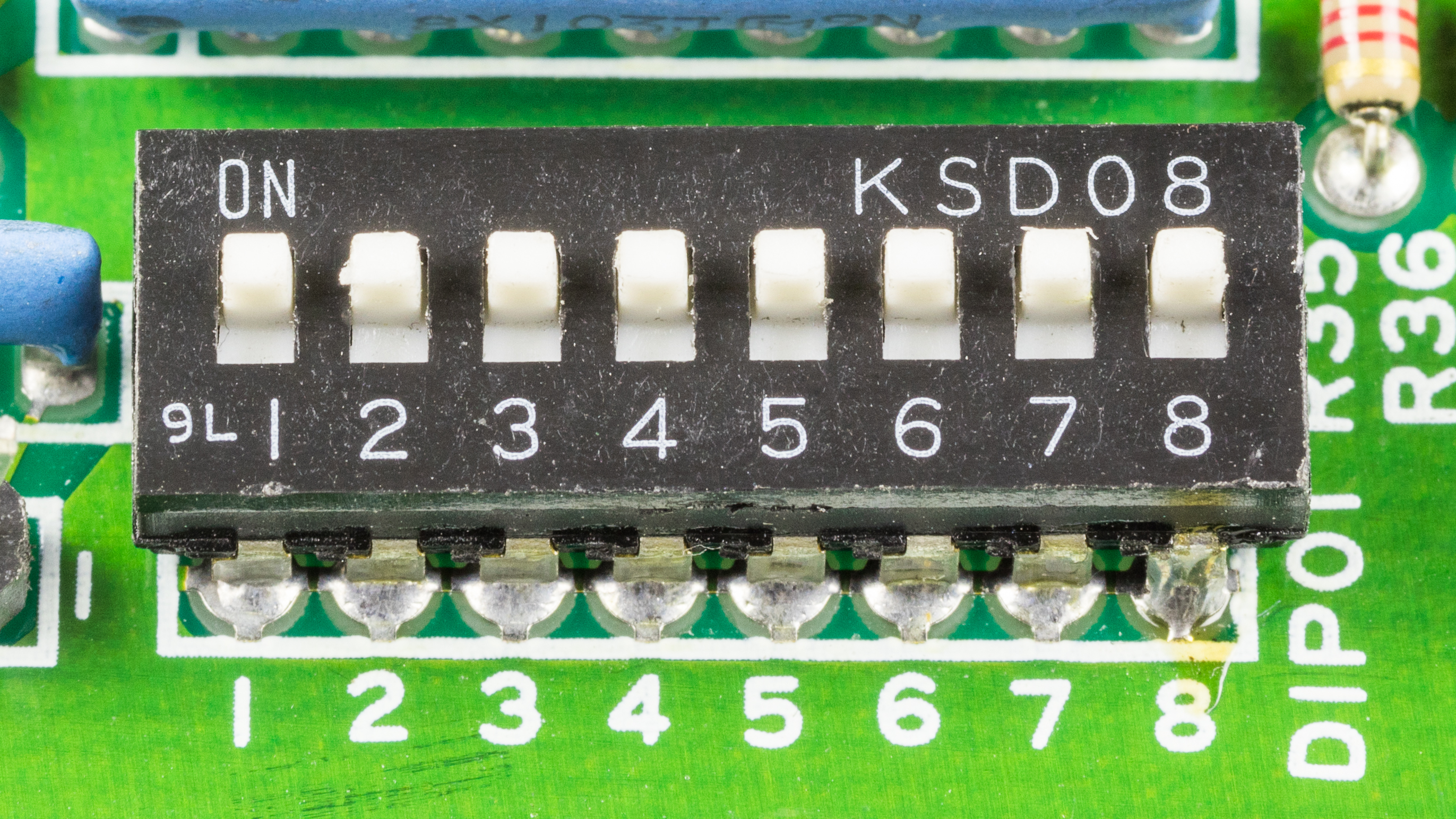
DIP Switch
A DIP switch is a manual electric switch that is packaged with others in a group in a standard dual in-line package (DIP). The term may refer to each individual switch, or to the unit as a whole. This type of switch is designed to be used on a printed circuit board along with other electronics, electronic components and is commonly used to customize the behavior of an electronic device for specific situations. DIP switches are an alternative to jumper (computing), jumper blocks. Their main advantages are that they are quicker to change and there are no parts to lose. History US patent 3621157, filed in 1970 by Pierre Schwab,U.S. Patent 3621157. "Miniature switch with multiple cam-operated switch contacts", filed June 1, 1970. is the earliest known DIP switch patent, which discloses a rotary style DIP switch. US patent 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nedap ESD1 - Printer Controller - DIP Switch - All Off-91979
Nedap (N.V. Nederlandsche Apparatenfabriek; ) is a Dutch Multinational corporation, multinational technology company. Its principal place of business is Groenlo, Netherlands. It has subsidiaries in the United States, Belgium, France, Germany, UK, the Netherlands and Spain, and is listed on the Euronext exchange. The company develops and supplies technologies in the fields of people & vehicle identification, access control systems, farm automation, Radio-frequency identification (RFID) systems for loss prevention and stock management, and software for management, healthcare and flextime working. Nedap's activities are organized in the following Market Groups: Healthcare, Light Controls, Identification Systems, Livestock Management, Retail, Security Management and Staffing Solutions. History and Shareholders Nedap was established in 1929 and has been listed on the Euronext stock exchange since 1947. As of 2022, the company has over 800 employees and is active around the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
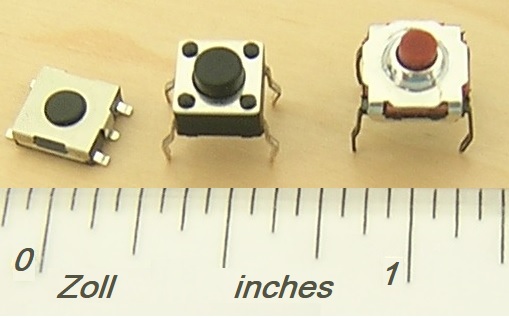
Single Pole, Single Throw
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle switch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Monochrome Display Adapter
The Monochrome Display Adapter (MDA, also MDA card, Monochrome Display and Printer Adapter, MDPA) is IBM's standard video display card and computer display standard for the IBM PC introduced in 1981. The MDA does not have any pixel-addressable graphics modes, only a single monochrome text mode which can display 80 columns by 25 lines of high-resolution text characters or symbols useful for drawing forms. Hardware design The original IBM MDA was an 8-bit ISA card with a Motorola 6845 display controller, 4 KB of RAM, a DE-9 output port intended for use with an IBM monochrome monitor. A parallel port for attachment of a printer is also included, avoiding the need to purchase a separate card. Capabilities The MDA was based on the IBM System/23 Datamaster's display system, and was intended to support business and word processing use with its sharp, high-resolution characters. Each character is rendered in a box of 9 × 14 pixels, of which 7 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter (CGA), originally also called the ''Color/Graphics Adapter'' or ''IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter'', introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card for the IBM PC and established a De facto standard, de facto computer display standard. Hardware design The original IBM CGA graphics card was built around the Motorola 6845 display controller, came with 16 kilobytes of video memory built in, and featured several graphics and text modes. The highest display resolution of any mode was 640 × 200, and the highest color depth supported was 4-bit (16 colors). The CGA card could be connected either to a direct-drive CRT monitor using a 4-bit digital (Transistor-transistor logic, TTL) RGB(I), RGBI interface, such as the IBM 5153 color display, or to an NTSC-compatible television or composite video computer monitor, monitor via an RCA connector. The RCA connector provided only baseband video, so to connect the CGA card to a television set w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics accelerator, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or colloquially GPU) is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a computer monitor, monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called ''discrete'' or ''dedicated'' graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an graphics processing unit#Integrated graphics processing unit, integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole erroneously. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the CPU. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Code
A rolling code (or sometimes called a hopping code) is used in keyless entry systems to prevent a simple form of replay attack, where an eavesdropper records the transmission and replays it at a later time to cause the receiver to 'unlock'. Such systems are typical in garage door openers and keyless car entry systems. Techniques * Common PRNG (pseudorandom number generator) — preferably cryptographically secure — in both transmitter and receiver * Transmitter sends 'next' code in sequence * Receiver compares 'next' to its calculated 'next' code. * A typical implementation compares within the next 256 codes in case receiver missed some transmitted keypresses. HMAC-based one-time password employed widely in multi-factor authentication uses similar approach, but with pre-shared secret key and HMAC instead of PRNG and pre-shared random seed. Application in RF remote control A rolling code transmitter is useful in a security system for improving the security of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
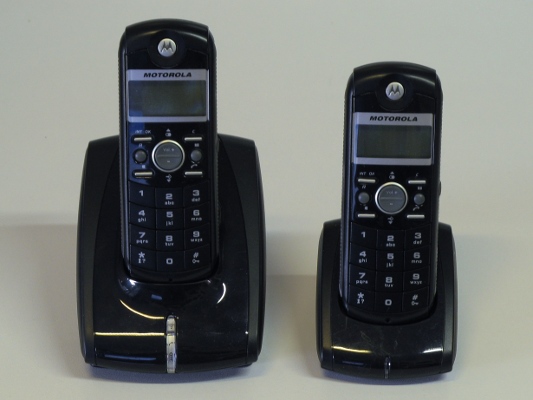
Cordless Phone
A cordless telephone or portable telephone has a portable telephone handset that connects by radio to a base station connected to the public telephone network. The operational range is limited, usually to the same building or within some short distance from the base station. A cordless telephone differs functionally from a mobile phone in its limited range and by depending on the base station on the subscriber premises. Current cordless telephone standards, such as PHS and DECT, have blurred the once clear-cut line between cordless and mobile telephones by implementing cell handoff (handover); various advanced features, such as data-transfer; and even, on a limited scale, international roaming. In specialized models, a commercial mobile network operator may maintain base stations and users subscribe to the service. Unlike a corded telephone, a cordless telephone needs mains electricity (to power the base station). The cordless handset contains a rechargeable battery, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garage Door Opener
A garage door opener is a motorized device that opens and closes a garage door controlled by switches on the garage wall. Most also include a handheld radio remote control carried by the owner, which can be used to open and close the door from a short distance. The electric opener The electric overhead garage door opener was invented by C.G. Johnson in 1926 in Hartford City, Indiana. Electric Garage Door openers did not become popular until Era Meter Company of Chicago offered one after World War II where the overhead garage door could be opened via a key pad located on a post at the end of the driveway or a switch inside the garage. As in an elevator, the electric motor does not provide most of the power to move a heavy garage door. Instead, most of door's weight is offset by the counterbalance springs attached to the door. (Even manually operated garage doors have counterbalances; otherwise, they would be too heavy for a person to open or close them.) In a typical desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade Game
An arcade game or coin-op game is a coin-operated entertainment machine typically installed in public businesses such as restaurants, bars and amusement arcades. Most arcade games are presented as primarily game of skill, games of skill and include arcade video games, pinball machines, electro-mechanical games, redemption games or merchandisers. Types Broadly, arcade games are nearly always considered Game of skill, games of skill, with only some elements of game of chance, games of chance. Games that are solely games of chance, like slot machines and pachinko, often are categorized legally as gambling devices and, due to restrictions, may not be made available to minors or without appropriate oversight in many jurisdictions. Arcade video games Arcade video games were first introduced in the early 1970s, with ''Pong'' as the first commercially successful game. Arcade video games use Electronics, electronic or computerized circuitry to take input from the player and translate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Address
In computing, a memory address is a reference to a specific memory location in memory used by both software and hardware. These addresses are fixed-length sequences of digits, typically displayed and handled as unsigned integers. This numerical representation is based on the features of CPU (such as the instruction pointer and incremental address registers). Programming language constructs often treat the memory like an array. Types Physical addresses A digital computer's main memory consists of many memory locations, each identified by a unique physical address (a specific code). The CPU or other devices can use these codes to access the corresponding memory locations. Generally, only system software (such as the BIOS, operating systems, and specialized utility programs like memory testers) directly addresses physical memory using machine code instructions or processor registers. These instructions tell the CPU to interact with a hardware component called the memory c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrupt Request
In a computer, an interrupt request (or IRQ) is a hardware signal sent to the processor that temporarily stops a running program and allows a special program, an interrupt handler, to run instead. Hardware interrupts are used to handle events such as receiving data from a modem or network card, key presses, or mouse movements. Interrupt lines are often identified by an index with the format of ''IRQ'' followed by a number. For example, on the Intel 8259 family of programmable interrupt controllers (PICs) there are eight interrupt inputs commonly referred to as ''IRQ0'' through ''IRQ7''. In x86 based computer systems that use two of these PICs, the combined set of lines are referred to as ''IRQ0'' through ''IRQ15''. Technically these lines are named ''IR0'' through ''IR7'', and the lines on the ISA bus to which they were historically attached are named ''IRQ0'' through ''IRQ15'' (although historically as the number of hardware devices increased, the total possible number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |