|
Dionizas Poška
Dionizas Poška (; October 1764 – 12 May 1830) was a Lithuanian poet, historian and lexicographer sometimes described also as Polish-Lithuanian He contributed to the early 19th-century Samogitian Revival, the early stage of the Lithuanian National Revival. Born to a family of petty Samogitian nobility, Poška attended Kražiai College. From 1786–1821, with some breaks, Poška worked as a lawyer, regent, clerk in the courts of Raseiniai. From 1790, he lived in the purchased Barzdžiai manor. Poška excavated ancient graves and hillforts, collected archeological fossils, weapons, money, books. In 1812, he established the first museum of antiquities in Lithuania, within the trunk of a thousand-year-old oak called Baublys. He corresponded and communicated with Samogitians such as , Jurgis Plateris, Simonas Daukantas, , Kajetonas Nezabitauskis and others as well as Vilnius University professorship, e.g. Joachim Lelewel and Ivan Loboiko. Poška wrote his works in Lithuani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United States, Lithuanians in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Lithuanian Brazilians, Brazil and Lithuanian Canadians, Canada. Their native language is Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, one of only two surviving members of the Baltic language family along with Latvian language, Latvian. According to the Lithuanian census of 2021, census conducted in 2021, 84.6% of the population of Lithuania identified themselves as Lithuanians. Most Lithuanians belong to the Catholic Church in Lithuania, Catholic Church, while the Lietuvininkai who lived in the northern part of East Prussia prior to World War II, were mostly Lutherans. History The territory of the Balts, including modern Lithuania, was once inhabited by several Baltic tribal entities (Sudovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verse Letter
Verse may refer to: Poetry * Verse (poetry), a line or lines in a poetic composition * Blank verse, a type of poetry having regular meter but no rhyme * Free verse, a type of poetry written without the use of strict meter or rhyme, but still recognized as poetry * ''Versed'' (poetry collection), 2009 collection of poetry by Rae Armantrout * ''Verse'', an international poetry journal with Henry Hart (author) as founding editor Religion * Chapters and verses of the Bible * Ayah, one of the 6,236 verses found in the Qur'an Music * Verse (band), a hardcore punk band * Verse (rapper) (b. 1986), British hip hop artist * Verse (popular music), roughly corresponds to a poetic stanza * ''Verses'' (album), a 1987 album by jazz trumpeter Wallace Roney * ''Verses (Apallut)'', a 2001 album by the Alaskan group Pamyua * ''Verse'', a 2002 album by Patricia Barber * Ben Mount (born 1977), also known as The Verse or MC Verse, British rapper, producer and record label owner * "Verses", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Nobility
The Lithuanian nobility () or ''szlachta'' of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (, ) was historically a legally privileged hereditary elite class in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Polish Lithuanian Commonwealth (including during period of foreign rule 1795–1918) consisting of Lithuanians from Lithuania Proper; Samogitians from Duchy of Samogitia; following Lithuania's eastward expansion into what is now Belarus, Ukraine and Russia, many ethnically Ruthenian noble families (''boyars''); and, later on, predominantly Baltic German families from the Duchy of Livonia and Inflanty Voivodeship.Krzysztof Buchowski, ''Litwomani i polonizatorzy'', p. 20–50, 2006 Białystok, Uniwersytet w Białymstoku, Initially, the privileged social group of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was called ''boyars''. Boyars became part of the szlachta (nobility) during the Union of Horodło on October 2, 1413, initiating nobility in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania following the Western European model (wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Language
Lithuanian (, ) is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic languages, Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 1 million speakers elsewhere. Around half a million inhabitants of Lithuania of non-Lithuanian background speak Lithuanian daily as a second language. Lithuanian is closely related to neighbouring Latvian language, Latvian, though the two languages are not mutually intelligible. It is written in a Latin script. In some respects, some linguists consider it to be the most conservative (language), conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šilalė District Municipality
Šilalė (; Samogitian dialect, Samogitian: ''Šėlalė'', ) is a city in western Lithuania, Samogitia, Tauragė County. It is located north of Tauragė. The River Lokysta flows through the town and there is a pond in the centre of the town. History The town is part of the Samogitian Ethnography, ethnographic Regions of Lithuania, region of Lithuania and was first mentioned in the sixteenth century. Its name derives from the generic word sila ("Pinewood") and Samogitian suffix ''-alė.'' It was located in the Duchy of Samogitia in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania within the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During World War II, the town was under Soviet occupation from 1940, and then under German occupation of Lithuania during World War II, German occupation from 1941 to 1944. In July 1941, 135 Jewish men from Šilalė were shot on a site in the Jewish cemetery. In September 1941, the Jewish women and children of Šilalė were shot in the Tūbinės forest. Around 1,300 Jews were ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaltinėnai
Kaltinėnai (Samogitian dialect, Samogitian: ''Kaltinienā'', ) is a small town in the west of Lithuania, located near Žemaičių highway in Šilalė district municipality, Tauragė County. Kaltinėnai has around 728 inhabitants (2011). The town is in a hollow, and it is rumoured that a large lake existed at the end of the Ice age where it now sits. Kaltinėnai is surrounded by famous mounds such as Skuburkalnis, Švedkalnis, Kepaluškalnis and Medvėgalis. There are also two rivers nearby, the Akmena and the Ižnė. Notable buildings include the church, an old wooden synagogue, a home for Old age, the elderly and the Rehabilitation Centre. History A stone axe discovered in the town suggests that the area was already inhabited by the Neolithic period. Historians believe that the town was originally part of a larger settlement, but later it split and Kaltinėnai became a separate region. Kaltinėnai was first mentioned in a German chronicle as ''terram Kalctene'' in 1371. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed during late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages in Europe and lasted in some countries until the mid-19th century. Unlike slaves, serfs could not be bought, sold, or traded individually, though they could, depending on the area, be sold together with land. Actual slaves, such as the kholops in Russia, could, by contrast, be traded like regular slaves, abused with no rights over their own bodies, could not leave the land they were bound to, and marry only with their lord's permission. Serfs who occupied a plot of land were required to work for the lord of the manor who owned that land. In return, they were entitled to protection, justice, and the right to cultivate certain fields within the manor to maintain their own subsistence. Serfs wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šilalė District
Šilalė (; Samogitian: ''Šėlalė'', ) is a city in western Lithuania, Samogitia, Tauragė County. It is located north of Tauragė. The River Lokysta flows through the town and there is a pond in the centre of the town. History The town is part of the Samogitian ethnographic region of Lithuania and was first mentioned in the sixteenth century. Its name derives from the generic word sila ("Pinewood") and Samogitian suffix ''-alė.'' It was located in the Duchy of Samogitia in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania within the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During World War II, the town was under Soviet occupation from 1940, and then under German occupation from 1941 to 1944. In July 1941, 135 Jewish men from Šilalė were shot on a site in the Jewish cemetery. In September 1941, the Jewish women and children of Šilalė were shot in the Tūbinės forest. Around 1,300 Jews were massacred by an Einsatzgruppen of Germans and local Lithuanian collaborators. Population Ethnic compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
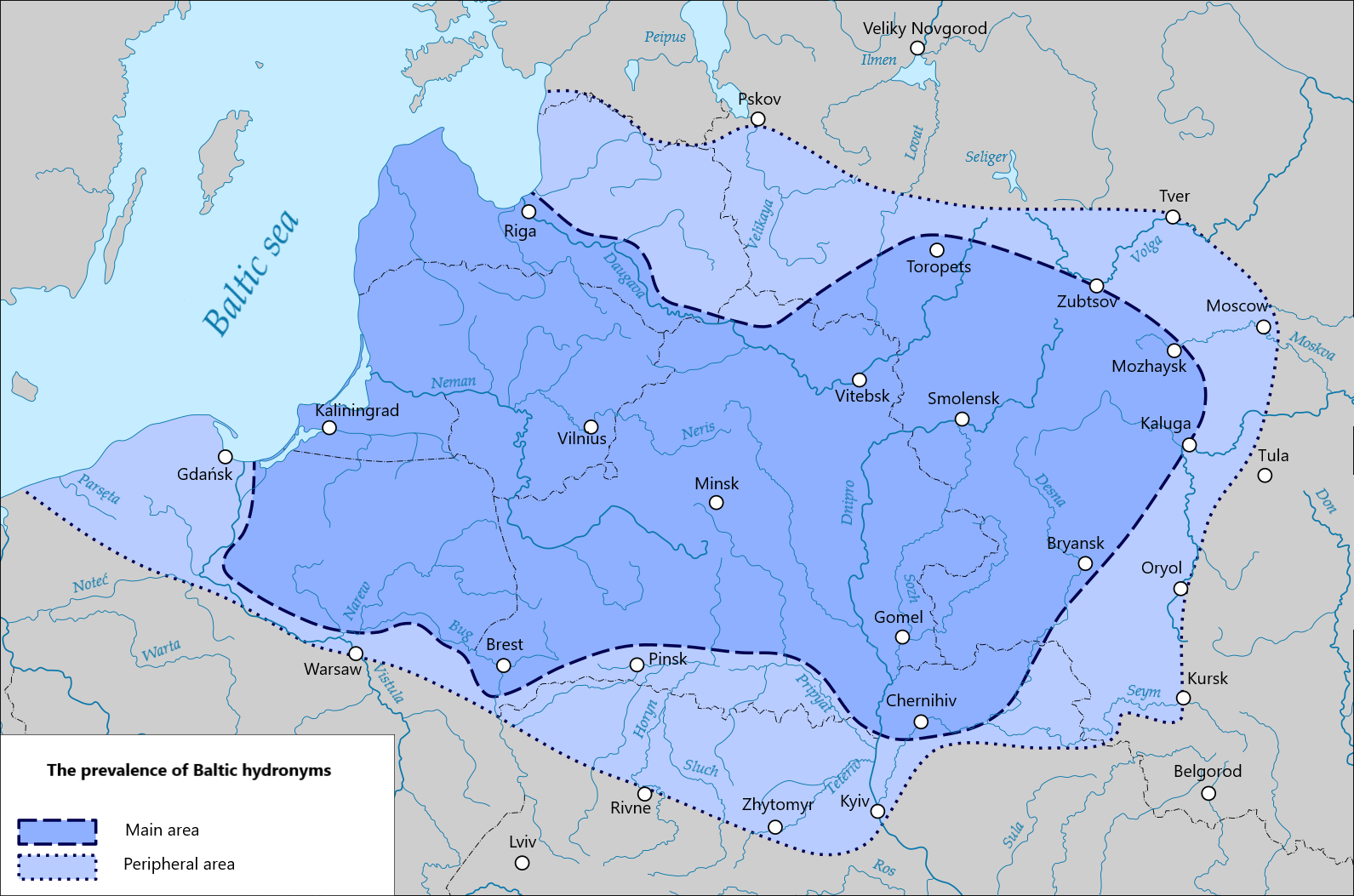
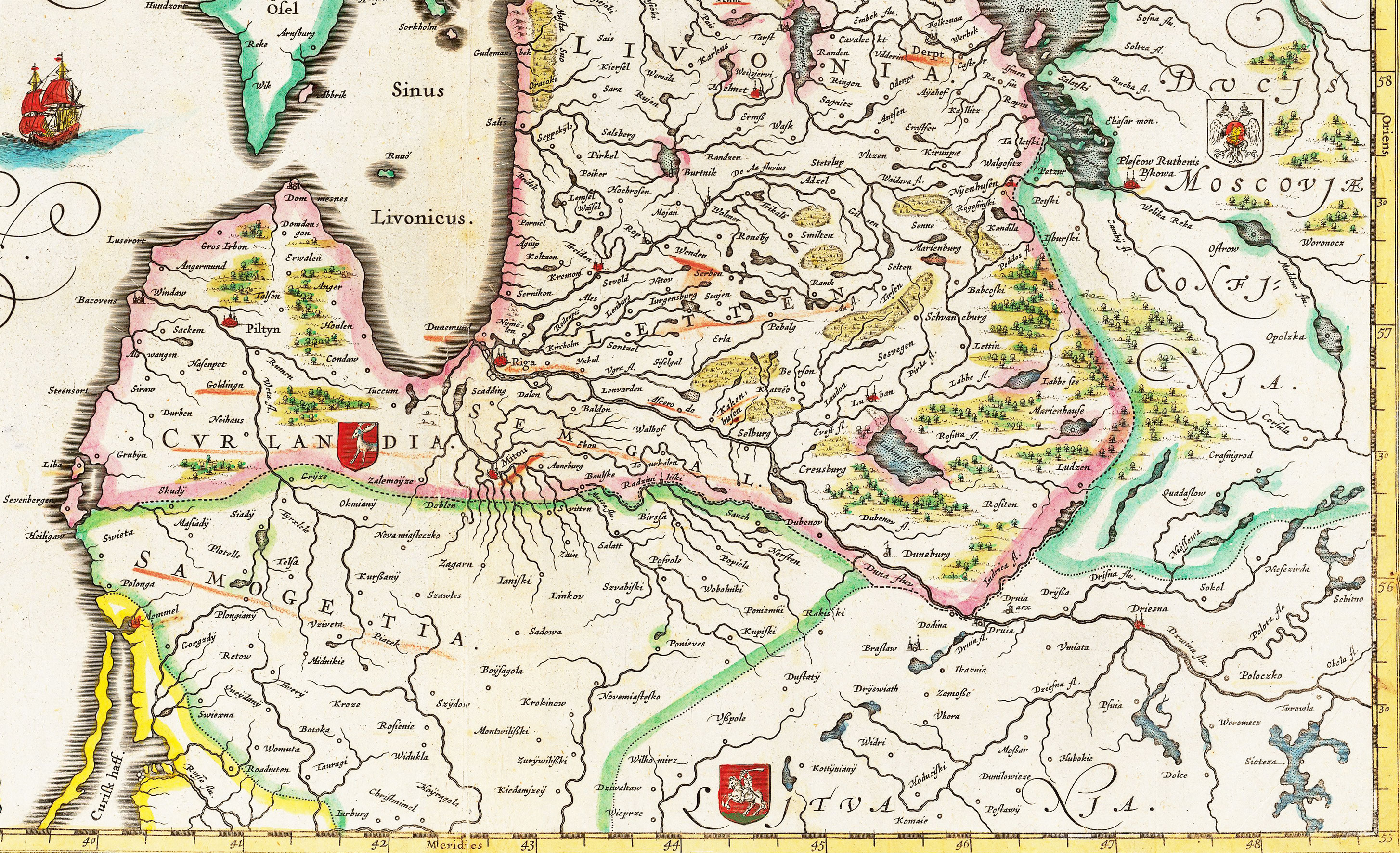
Samogitians
Samogitians ( Samogitian: ''žemaitē'', , ) are the inhabitants of Samogitia, an ethnographic region of Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian language, which in Lithuania is mostly considered a dialect of the Lithuanian language together with the Aukštaitian dialect. The Samogitian language differs the most from the standard Lithuanian language. Whether Samogitians are considered to be a distinct ethnic group or merely a subset of Lithuanians varies. However, 2,169 people declared their ethnicity as Samogitian during the Lithuanian census of 2011, of whom 53.9% live in Telšiai County. The political recognition and cultural understanding of the Samogitian ethnicity has, however, changed drastically throughout the last few centuries as 448,022 people declared themselves Samogitians, not Lithuanians, in the 1897 Russian Empire census. History On 13 July 1260, the Samogitians decisively defeated the joint forces of the Teutonic Knights from Prussia and Livonian Order from Liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |