|
Digital Author Identification
The Digital Author Identifier (DAI) was a Dutch initiative to create an person identifier for researchers to (1) enhance linkability of scholarly communication and other types of output to a single author and (2) to disambiguate between authors with similar or even the same names. As a form of authority control, DAI was envisioned to assign a unique national id for every author active within a Dutch university, university of applied sciences, or research institute. The DAI is prepared from the ISO standard "ISNI" ( International Standard Name Identifier). The DAI links the PICA database in institutional libraries with the METIS national research information system subsequently made available to international search engines. Specifically, SURFfoundation has, in cooperation with OCLC PICA, created a connection with PICA National Thesaurus Authornames (NTA) that is supplied and maintained by university libraries. Important to this is the connection between the research information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholarly Communication
Scholarly communication involves the creation, publication, dissemination, and discovery of academic research, primarily in peer-reviewed journals and books. It is “the system through which research and other scholarly writings are created, evaluated for quality, disseminated to the scholarly community, and preserved for future use." This primarily involves the publication of peer-reviewed academic journals, books, and conference papers. There are many issues with scholarly communication, which include authors' rights, the peer review process, the economics of scholarly resources, new models of publishing (including open access and institutional repositories), rights and access to federally funded research, and preservation of intellectual assets. Common methods of scholarly communication include publishing peer-reviewed articles in academic journals, academic monographs and books, book reviews, and conference papers. Other textual formats used include preprints and wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Author
In legal discourse, an author is the creator of an original work that has been published, whether that work exists in written, graphic, visual, or recorded form. The act of creating such a work is referred to as authorship. Therefore, a sculptor, painter, or composer is considered the author of their respective sculptures, paintings, or musical compositions. Although in common usage, the term "author" is often associated specifically with the writer of a book, Article (publishing), article, Play (theatre), play, or other written work. In cases involving a work for hire, the employer or commissioning party is legally considered the author of the work, even if it was created by someone else. Typically, the first owner of a copyright is the creator of the copyrighted work, i.e., the author. If more than one person created the work, then joint authorship has taken place. Copyright laws differ around the world. The United States Copyright Office, for example, defines copyright as "a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
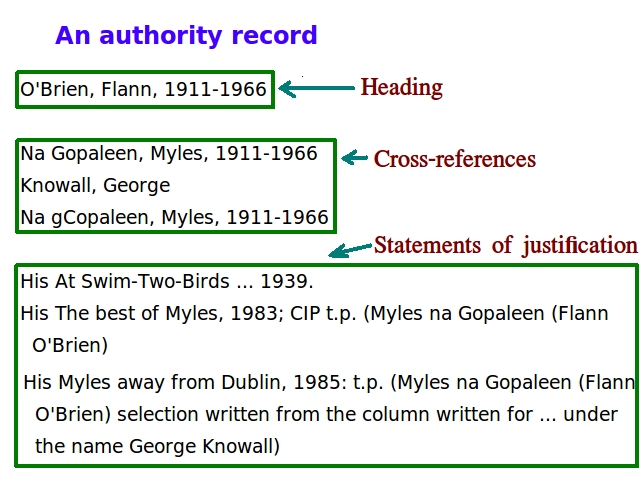
Authority Control
In information science, authority control is a process that organizes information, for example in library catalogs, by using a single, distinct spelling of a name (heading) or an identifier (generally persistent and alphanumeric) for each topic or concept. The word ''authority'' in ''authority control'' derives from the idea that the names of people, places, things, and concepts are ''authorized,'' i.e., they are established in one particular form. Note: root words for both ''author'' and ''authority'' are words such as ''auctor'' or ''autor'' and ''autorite'' from the 13th century. These one-of-a-kind headings or identifiers are applied consistently throughout catalogs which make use of the respective authority file, and are applied for other methods of organizing data such as linkages and cross references. Each controlled entry is described in an authority ''record'' in terms of its scope and usage, and this organization helps the library staff maintain the catalog and make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocational University
A vocational university or university of applied sciences (UAS), less commonly called a polytechnic university is an institution of higher education and increasingly research that provides applied professional education and grants academic degrees. It should not be confused with vocational schools or technical schools that do not meet the strict standards of higher education nor have the ability to grant officially accredited academic degrees. In some countries, a vocational university more precisely grants professional degrees like professional bachelor's degree, professional master's degree and professional doctorates. The term is not officially used in many countries, and an assignment to a certain type of university in a certain country's educational system is therefore difficult. The UK once had a very extensive vocational university sector with its polytechnic system dating back to the mid-19th century. Vocational universities are often regulated and funded differently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of ISO Standards
This is a list of publishedThis list generally excludes draft versions. standardization, standards and other deliverables of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).ISO deliverables include "specifications" (ISO/PAS, ISO/TS), "reports" (ISO/TR), etc, which are not referred to by ISO as "standards". For a complete and up-to-date list of all the ISO standards, see the ISO catalogue. The standards are protected by copyright and most of them must be purchased. However, about 300 of the standards produced by ISO and International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC's Joint Technical Committee 1 (ISO/IEC JTC 1, JTC 1) have been made freely and publicly available. ISO 1 – ISO 19999 * List of ISO standards 1–1999, ISO 1 – ISO 1999 * List of ISO standards 2000–2999, ISO 2000 – ISO 2999 * Li ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Standard Name Identifier
The International Standard Name Identifier (ISNI) is an identifier system for uniquely identifying the public identities of contributors to media content such as books, television programmes, and newspaper articles. Such an identifier consists of 16 digits. It can optionally be displayed as divided into four blocks. ISNI can be used to disambiguate named entities that might otherwise be confused, and links the data about names that are collected and used in all sectors of the media industries. It was developed under the auspices of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) aDraft International Standard 27729 the valid standard was published on 15 March 2012. The ISO technical committee 46, subcommittee 9 (TC 46/SC 9) is responsible for the development of the standard. ISNI format The FAQ of the isni.org websites states "An ISNI is made up of 16 digits, the last character being a check character." ISNI consists of 15 digits followed by a check character. The check ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OCLC PICA
OCLC PICA was a library automation systems and services company which originated from a co-operation of the Pica Foundation (''Stichting Pica'') of the Netherlands and the non-profit library company OCLC Online Computer Library Center (OCLC) of the U.S. In 2007, OCLC acquired the shares of OCLC PICA it did not already hold to become the sole owner of OCLC PICA. By the end of 2007, OCLC PICA lost its separate identity and was integrated with OCLC under the OCLC brand. . OCLC News Release, 22 October 2007 The Pica Foundation was created in 1969 as an initiative of the Koninklijke Bibliotheek [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
METIS
Metis or Métis, meaning "mixed" in French, may refer to: Ethnic groups * Métis, recognized Indigenous communities in Canada and the United States whose distinct culture and language emerged after early intermarriage between First Nations peoples and early European settlers, primarily French fur trappers * Métis (Belgian Congo), mixed-race children born in the Congo during Belgian colonial rule Places * Grand-Métis, Quebec, Canada * Métis-sur-Mer, Quebec, Canada * Saint-Paul-des-Métis, now St. Paul, Alberta, Canada * Metis Shoal, the tip of a submarine volcano in Tonga * Metiş, a village in Mihăileni, Sibiu, Romania * Metis Island in Antarctica Other uses * 9 Metis, an asteroid * 9K115 Metis, a Russian anti–tank missile system * 9K115-2 Metis-M, a Russian anti–tank missile system * Metis (American musician) (fl. 21st century), American rapper * Metis (theorem prover), an automated theorem prover * Metis (Japanese musician) (born 1984), Japanese reggae sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Research Information System
A current research information system (CRIS) is a database or other information system to store, manage and exchange contextual metadata for the research activity funded by a research funder or conducted at a research-performing organisation (or aggregation thereof). CRIS systems are also known as Research Information Management or RIM Systems (RIMS). Features The data model underpinning a CRIS relies on a set of basic entities as defined by the Common European Research Information Format model maintained by the non-profit organisation euroCRIS. The links connecting these entities provide a standardised semantic layer that provides consistency to the data model. The basic CERIF entities are people, organisations, projects and outputs (publications, research data, patents). Further second-level entities in the comprehensive snapshot of research provided by CERIF are for instance funding, research facilities and equipment or skills. System interoperability lies at the core of CRI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many "working group, sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional activities are also significant. Objectivity (philosophy), Objectivity is expected to be achieved by the scientific method. Peer review, through discussion and debate within journals and conferences, assists in this objectivity by maintaining the quality of research methodology and interpretation of results. History of scientific communities The eighteenth century had some societies made up of men who studied nature, also known as natural philosophy, natural philosophers and natural history, natural historians, which included even amateurs. As such these societies were more like local clubs and groups with diverse interests than actual scientific communities, which usually had interests on specialized disciplines. Though there were a few olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORCID
The ORCID (; Open Researcher and Contributor ID) is a nonproprietary alphanumeric code to uniquely identify authors and contributors of scholarly communication. This addresses the problem that a particular author's contributions to the scientific literature or humanities publications can be hard to recognize, as most personal names are not unique, they can change ( such as with marriage), have cultural differences in name order, contain inconsistent use of first-name abbreviations and employ different writing systems. It provides a persistent identity for humans, similar to tax ID numbers, that are created for content-related entities on digital networks by digital object identifiers (DOIs). The ORCID system includes a website and services to look up authors and their bibliographic output (and other user-supplied pieces of information). Uses ORCID aims to provide a persistent code for people, to address the problem that a particular author's contributions to scholarly commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ResearcherID
ResearcherID is an identifying system for scientific authors. The system was introduced in January 2008 by Thomson Reuters Corporation. This unique identifier aims at solving the problem of author identification and correct attribution of works. In scientific and academic literature, it is common to cite the name, surname, and initials of the authors of an article. However, there are sometimes authors with the same name, initials; or the journal may misspell names, resulting in several spellings for the same authors, and different authors with the same spelling. Researchers can use ResearcherID to claim their published works and link their unique and persistent ResearcherID number to these works for correct attribution. In this way, they can also keep their publication list up to date and online. The combined use of the Digital Object Identifier with the ResearcherID allows a unique association of authors and research articles. It can be used to link researchers with register ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |