|
Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, or diffuse reflection spectroscopy, is a subset of absorption spectroscopy. It is sometimes called remission spectroscopy. Remission is the Reflection (physics), reflection or back-scattering of light by a material, while transmission is the passage of light through a material. The word ''remission'' implies a direction of scatter, independent of the scattering process. Remission includes both specular and diffusely back-scattered light. The word ''reflection'' often implies a particular physical process, such as specular reflection. The use of the term ''remission spectroscopy'' is relatively recent, and found first use in applications related to medicine and biochemistry. While the term is becoming more common in certain areas of absorption spectroscopy, the term ''diffuse reflectance'' is firmly entrenched, as in diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) and diffuse-reflectance ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
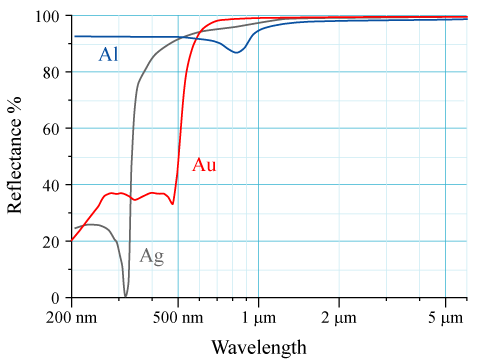
Reflectance
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
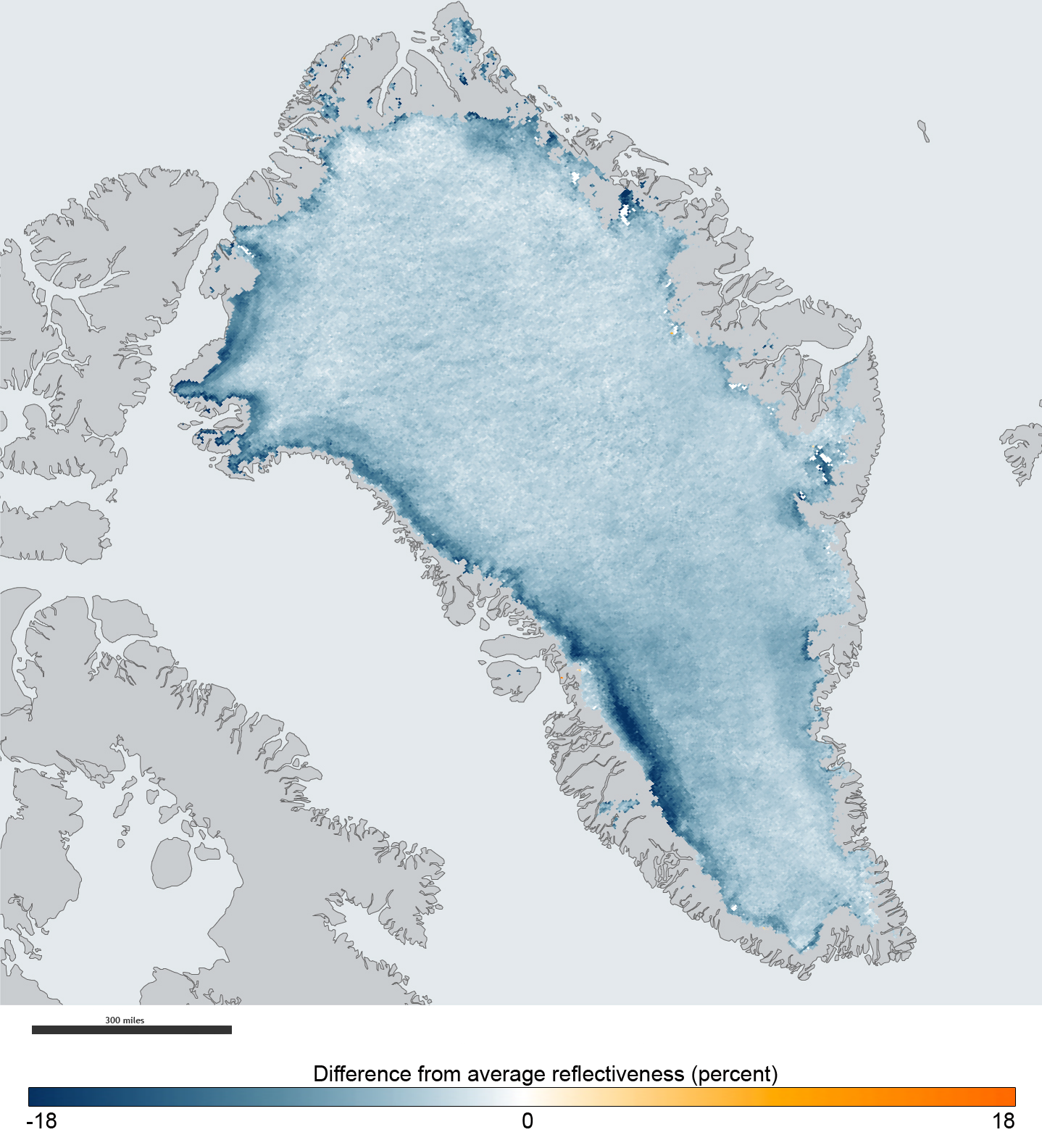
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (; 19 October 1910 – 21 August 1995) was an Indian Americans, Indian-American theoretical physicist who made significant contributions to the scientific knowledge about the structure of stars, stellar evolution and black holes. He was awarded the 1983 Nobel Prize in Physics along with William Alfred Fowler, William A. Fowler for theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars. His mathematical treatment of stellar evolution yielded many of the current theoretical models of the later evolutionary stages of massive stars and black holes. Many concepts, institutions and inventions, including the Chandrasekhar limit and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Chandra X-Ray Observatory, are named after him. Chandrasekhar worked on a wide variety of problems in physics during his lifetime, contributing to the contemporary understanding of stellar structure, white dwarfs, stellar dynamics, stochastic process, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ron Giovanelli
Ronald Gordon Giovanelli, Doctor of Science, DSc, Australian Academy of Science, FAA (International Phonetic Alphabet, /dʒoʊvɑ’nɛli/; 30 April 1915 — 27 January 1984) was an Australian solar researcher, astronomer and physicist, who contributed to the fields of astrophysics, solar physics, radiative transfer, and astronomical optics. His career spanned more than 40 years, commencing prior to World War II. Giovanelli was the recipient of the 1949 Edgeworth David Medal by the Royal Society of New South Wales for the discipline of astrophysics, which recognises distinguished contributions by scientists under the age of 35 in their respective fields. He was also elected into the Fellowship of the Australian Academy of Science in 1962 for his contributions in the field of physics. Giovanelli served as Chief of the Physics Division of the CSIRO, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) from 1958 to 1976, during which he also became Chairman of the Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiparallel Lines
In geometry, two line (geometry), lines l_1 and l_2 are antiparallel with respect to a given line m if they each make congruence (geometry), congruent angles with m in opposite Sense of rotation, senses. More generally, lines l_1 and l_2 are ''antiparallel'' with respect to another pair of lines m_1 and m_2 if they are antiparallel with respect to the angle bisector of m_1 and m_2. In any cyclic quadrilateral, any two opposite sides are antiparallel with respect to the other two sides. Relations # The line joining the feet to two altitude (triangle), altitudes of a triangle is antiparallel to the third side. (any cevians which 'see' the third side with the same angle create antiparallel lines) # The tangent to a triangle's circumcircle at a vertex is antiparallel to the opposite side. # The radius of the circumcircle at a vertex is perpendicular to all lines antiparallel to the opposite sides. Conic sections In an Cone#Elliptic cone, oblique cone, there are exactly two famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Benford
Frank Albert Benford Jr. (July 10, 1883 – December 4, 1948) was an American electrical engineer and physicist best known for rediscovering and generalizing Benford's Law, an earlier statistical statement by Simon Newcomb, about the occurrence of digits in lists of data.(subscription required) Benford is also known for having devised, in 1937, an instrument for measuring the refractive index of glass. An expert in optical measurements, he published 109 papers in the fields of optics and mathematics and was granted 20 patents on optical devices. Early life He was born in Johnstown, Pennsylvania. His date of birth is given variously as May 29 or July 10, 1883. At the age of 6 his family home was destroyed by the Johnstown Flood. Education He graduated from the University of Michigan in 1910. Career Benford worked for General Electric General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur C
Arthur is a masculine given name of uncertain etymology. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text '' Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th century Romano-British general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem '' Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a matter of debate and the poem only survives in a late 13th century manuscript entitled the Book of Aneirin. A 9th-century Breton landowner named Arthur witnessed several charters collected in the '' Cartulary of Redon''. The Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert H
Albert may refer to: Companies * Albert Computers, Inc., a computer manufacturer in the 1980s * Albert Czech Republic, a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic * Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands * Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia * Albert Music, an Australian music company now known as Alberts ** Albert Productions, a record label * Albert (organisation), an environmental organisation concerning film and television productions Entertainment * ''Albert'' (1985 film), a Czechoslovak film directed by František Vláčil * ''Albert'' (2015 film), a film by Karsten Kiilerich * ''Albert'' (2016 film), an American TV movie * ''Albert'' (album), by Ed Hall, 1988 * "Albert" (short story), by Leo Tolstoy * Albert (comics), a character in Marvel Comics * Albert (''Discworld''), a character in Terry Pratchett's ''Discworld'' series * Albert, a character in Dario Argento's 1977 film '' Suspiria'' People * Albert (given name) * Albert (surname) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorimetry
Colorimetry is "the science and technology used to quantify and describe physically the human color perception". It is similar to spectrophotometry, but is distinguished by its interest in reducing spectra to the physical correlates of color perception, most often the CIE 1931 XYZ color space tristimulus values and related quantities. History The Duboscq colorimeter was invented by Jules Duboscq in 1870. Instruments Colorimetric equipment is similar to that used in spectrophotometry. Some related equipment is also mentioned for completeness. * A tristimulus colorimeter measures the tristimulus values of a color. * A spectroradiometer measures the absolute spectral radiance (intensity) or irradiance of a light source. * A spectrophotometer measures the spectral reflectance, transmittance, or relative irradiance of a color sample. * A ''spectrocolorimeter'' is a spectrophotometer that can ''calculate'' tristimulus values. * A densitometer measures the degree of lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deane B
Deane may refer to: Places * Deane, Greater Manchester, an area of Bolton and a former historic parish * Deane, Hampshire, a village * Deane, Kentucky Ships * USS ''Deane'' (1778), US Navy frigate named after Silas Deane * HMS ''Deane'' (K551), a 1943 British Royal Navy frigate which served in the Second World War See also * Deane (name), for people with the name ''Deane'' * Dean (surname) Dean is an English surname; it can also be of Scottish and Irish origin. A variant of this surname is Deane (name), Deane. Notable people with the surname *Angela Dean, British statistician *Anna-Maria Ravnopolska-Dean, harpist *Ardie Dean (born ... * Dean (other) * Tribes of Galway, which includes Deane as one of the Tribes {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |