|
Diadectes
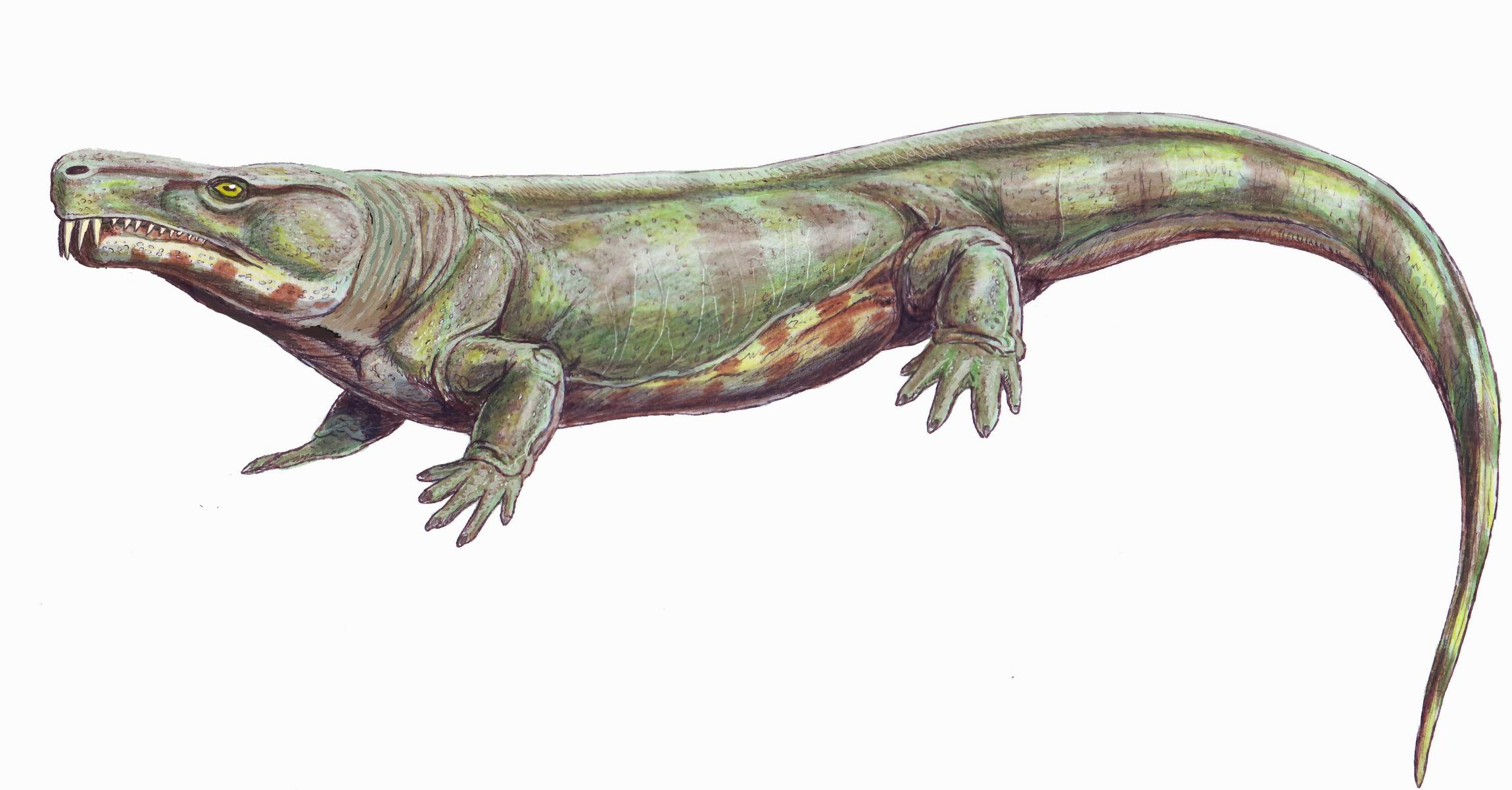
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period ( Artinskian- Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. High-resolution X-ray microcomputed tomography has revealed an endosseous labyrinth in the opisthotic, prootic, and supraoccipital of ''D. absitus'', along with a well-preserved vestibule, three semicircular canals, and a developed cochlear recess. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectes Scale
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period (Artinskian-Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivore, herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. High-resolution X-ray microcomputed tomography has revealed an endosseous labyrinth in the opisthotic, prootic, and supraoccipital of ''D. absitus'', along with a well-preserved vestibule, three semicircular canals, and a developed cochlear rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tetrapoda, stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous geologic period, period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the anamniote, non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/toads, salamanders/newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three fetal membranes, extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; rib, costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenal cortex, adrenocortical and chromaffin cell, chromaffin tissues as adrenal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisuralian
The Cisuralian, also known as the Early Permian, is the first series/epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the Pennsylvanian and followed by the Guadalupian. The Cisuralian Epoch is named after the western slopes of the Ural Mountains in Russia and Kazakhstan and dates between 298.9 ± 0.15 – 272.3 ± 0.5 Ma. In the regional stratigraphy of southwestern North America, the Cisuralian encompasses two series: the Wolfcampian (Asselian to mid-Artinskian) and Leonardian (mid-Artinskian to Kungurian). The series saw the appearance of beetles and flies and was a relatively stable warming period of about 21 million years. Name and background The Cisuralian is the first series or epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the last Pennsylvanian epoch ( Gzhelian) and is followed by the Permian Guadalupian Epoch. The name "Cisuralian" was proposed in 1982, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. The Cisuralian Epoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorph
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and '' Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, " Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confusin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodontia
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymouriamorpha
Seymouriamorpha were a small but widespread group of limbed vertebrates (tetrapods). They have long been considered stem group, stem-amniotes (reptiliomorphs), and most paleontologists still accept this point of view, but some analyses suggest that seymouriamorphs are stem-tetrapods (not more closely related to Amniota than to Lissamphibia). Many seymouriamorphs were terrestrial or semi-aquatic. However, aquatic larvae bearing external gills and grooves from the lateral line system have been found, making them unquestionably non-amniotes. As they matured, they became more terrestrial and reptile-like. They ranged from 30 cm (1 ft) long lizard-sized creatures to the 1.5 m (5 ft) long ''Enosuchus''. If seymouriamorphs are reptiliomorphs, they were the distant relatives of amniotes. Seymouriamorphs are divided into three main groups: Kotlassiidae, Discosauriscidae, and Seymouriidae, which includes the best-known genus, ''Seymouria''. The last seymouriamorphs became Permian-Triassic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artinskian
In the geologic timescale, the Artinskian is an age (geology), age or stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Permian. It is a subdivision of the Cisuralian Epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Series. The Artinskian likely lasted between and megaannum, million years ago (Ma) according to the most recent revision of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) in 2022. It was preceded by the Sakmarian and followed by the Kungurian. Stratigraphy The Artinskian is named after the goniatite grits of Artinsk which was introduced by Roderick Murchison, Édouard de Verneuil and count Alexander von Keyserling in their ''The Geology of Russia in Europe and the Ural Mountains'' (1845). The grits of Artinsk, in turn, get its name from the Artinsky District with center in the Russian smalltown of Arti, Russia, Arti (formerly ''Artinsk zavod''), situated in the middle Ural Mountains, Urals, about 170 km southwest of Yekaterinburg. The stage was introduced into scientific li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otic Notch
Otic notches are invaginations in the posterior margin of the skull roof, one behind each orbit. Otic notches are one of the features lost in the evolution of amniotes from their tetrapod ancestors. The notches have been interpreted as part of an auditory structure and are often reconstructed as holding a tympanum similar to those seen in modern anurans. Analysis of the ''columella'' (the stapes in amphibians and reptiles) of labyrinthodonts however indicates that it did not function in transmitting low-energy vibrations, thus rendering these animals effectively deaf to airborne sound. The otic notch instead functioned as a spiracle, at least in the early forms.Laurin, M. (1996)Hearing in Stegocephalians from the Tree of Life Web Project The Tree of Life Web Project (ToL) is an Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Anatomical Record
''The Anatomical Record'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering anatomy. It was established by the American Association of Anatomists in 1906 and is published by John Wiley & Sons. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.064. See also * List of biology journals This is a list of articles about scientific journals in biology and its various subfields. General Agriculture * Advances in Agronomy * '' Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment'' * '' Agroecology and Sustainable Food Systems'' * ''Animal'' ... References External links * Anatomy journals Wiley (publisher) academic journals Publications established in 1906 Monthly journals English-language journals 1906 establishments in the United States {{biology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |