|
Delayed Sleep–wake Phase Disorder
Delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD), more often known as delayed sleep phase syndrome and also as delayed sleep–wake phase disorder, is the delaying of a person's circadian rhythm (biological clock) compared to those of societal norms. The disorder affects the timing of biological rhythms including sleep, peak period of alertness, core body temperature, and hormonal cycles. People with this disorder are often called night owls. The diagnosis of this disorder is currently a point of contention among specialists of sleep disorders. Many insomnia-related disorders can present significantly differently between patients, and circadian rhythm disorders and melatonin related disorders are not well understood by modern medical science. The orexin system was only identified in 1998, yet it appears intimately implicated in human sleep-wake systems. Evidence for the plasticity of human circadian rhythm cycles has been provided by multiple studies. In one example, several dozen volun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Medicine
Sleep medicine is a medical specialty or subspecialty devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of sleep disturbances and disorders. From the middle of the 20th century, research has provided increasing knowledge of, and answered many questions about, sleep–wake functioning. The rapidly evolving field has become a recognized medical subspecialty in some countries. Dental sleep medicine also qualifies for board certification in some countries. Properly organized, minimum 12-month, postgraduate training programs are still being defined in the United States. In some countries, the sleep researchers and the physicians who treat patients may be the same people. The first sleep clinics in the United States were established in the 1970s by interested physicians and technicians; the study, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea were their first tasks. As late as 1999, virtually any American physician, with no specific training in sleep medicine, could open a sleep laborator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene is a behavioral and environmental practice developed in the late 1970s as a method to help people with mild to moderate insomnia. Clinicians assess the sleep hygiene of people with insomnia and other conditions, such as depression, and offer recommendations based on the assessment. Sleep hygiene recommendations include establishing a regular sleep schedule, using naps with care, not exercising physically (or mentally) too close to bedtime, limiting worry, limiting exposure to light in the hours before sleep, getting out of bed if sleep does not come, not using bed for anything but sleep and sex, avoiding alcohol (as well as nicotine, caffeine, and other stimulants) in the hours before bedtime, and having a peaceful, comfortable and dark sleep environment. Assessment Assessment of sleep hygiene includes a clinical interview and self-report questionnaires and sleep diaries, which are typically kept from one to two weeks, to record a representative sample data. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Lag
Jet lag is a temporary physiological condition that occurs when a person's circadian rhythm is out of sync with the time zone they are in, and is a typical result from travelling rapidly across multiple time zones (east–west or west–east). For example, someone travelling from New York to London, i.e. from west to east, feels as if the time were five hours ''earlier'' than local time, and someone travelling from London to New York, i.e. from east to west, feels as if the time were five hours ''later'' than local time. The phase shift when travelling from east to west is referred to as ''phase-delay'' of the circadian cycle, whereas going west to east is ''phase-advance'' of the cycle. Most travellers find that it is harder to adjust time zones when travelling east. Jet lag is caused by a misalignment between the internal circadian clock and the external environment, and it has been classified within the category of a circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorder, reflecting its bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea (sleep apnoea or sleep apnœa in British English) is a sleep-related breathing disorder in which repetitive Apnea, pauses in breathing, periods of shallow breathing, or collapse of the upper airway during sleep results in poor ventilation and sleep disruption. Each pause in breathing can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and often occurs many times a night. A choking or snorting sound may occur as breathing resumes. Common symptoms include daytime sleepiness, snoring, and non restorative sleep despite adequate sleep time. Because the disorder disrupts normal sleep, those affected may experience sleepiness or feel tired during the day. It is often a chronic condition. Sleep apnea may be categorized as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), in which breathing is interrupted by a blockage of air flow, central sleep apnea (CSA), in which regular unconscious breath simply stops, or a combination of the two. OSA is the most common form. OSA has four key contributors; these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders. Sleep disorders are broadly classified into dyssomnias, parasomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders involving the timing of sleep, and other disorders, including those caused by medical or psychological conditions. When a person struggles to fall asleep or stay asleep without any obvious cause, it is referred to as insomnia, which is the most common sleep disorder. Other sleep disorders include sleep apnea, narcolepsy, hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of the sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking, and night terrors. Sleep disruptions can be caused by various issues, including teeth grinding (bruxism) and night terrors. Managing sleep disturbances that are seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invisible Disability
Invisible disabilities, also known as hidden disabilities or non-visible disabilities (NVDs), are disabilities that are not immediately apparent. They are typically chronic illnesses and conditions that significantly impair normal activities of daily living. For example, some people with visual or auditory disabilities who do not wear glasses or hearing aids, or who use discreet hearing aids, may not be obviously disabled. Some people who have vision loss may wear contact lenses. Invisible disabilities can also include issues with mobility, such as a sitting disability like chronic back pain, joint problems, or chronic pain. People affected may not use mobility aids on some days, or at all, because severity of pain or level of mobility may change from day to day. Most people with repetitive strain injury move in a typical and inconspicuous way, and are even encouraged by the medical community to be as active as possible, including playing sports; yet those people can have dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Clock
Body may refer to: In science * Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space * Body (biology), the physical material of an organism * Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of animals * Human body, the entire structure of a human organism ** Dead body, cadaver, or corpse, a dead human body * (living) matter, see: Mind–body problem, the relationship between mind and matter in philosophy * Aggregates within living matter, such as inclusion bodies In arts and entertainment In film and television * ''Jism'' (2003 film) or ''Body'', a 2003 Indian film * ''Body'' (2015 Polish film), a 2015 Polish film * ''Body'' (2015 American film), a 2015 American film * "Body" (''Wonder Showzen'' episode), a 2006 episode of American sketch comedy television series ''Wonder Showzen'' * "Body", an episode of the Adult Swim television series, '' Off the Air'' In literature and publishing * body text, the text forming the main conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurohormone
A neurohormone is any hormone produced and released by neuroendocrine cells (also called neurosecretory cells) into the blood. By definition of being hormones, they are secreted into the circulation for systemic effect, but they can also have a role of neurotransmitter or other roles such as autocrine (self) or paracrine (local) messenger. The hypothalamus releasing hormones are neurohypophysial hormones in specialized hypothalamic neurons which extend to the median eminence and posterior pituitary. The adrenal medulla produces adrenomedullary hormones in chromaffin cells, cells which are very similar in structure to post-synaptic sympathetic neurons, even though they are not neurons they are derivatives of the neural crest. Enterochromaffin and enterochromaffin-like cells, both being enteroendocrine cells, are also considered neuroendocrine cells due to their structural and functional similarity to chromaffin cells, although they are not derivatives of the neural crest. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
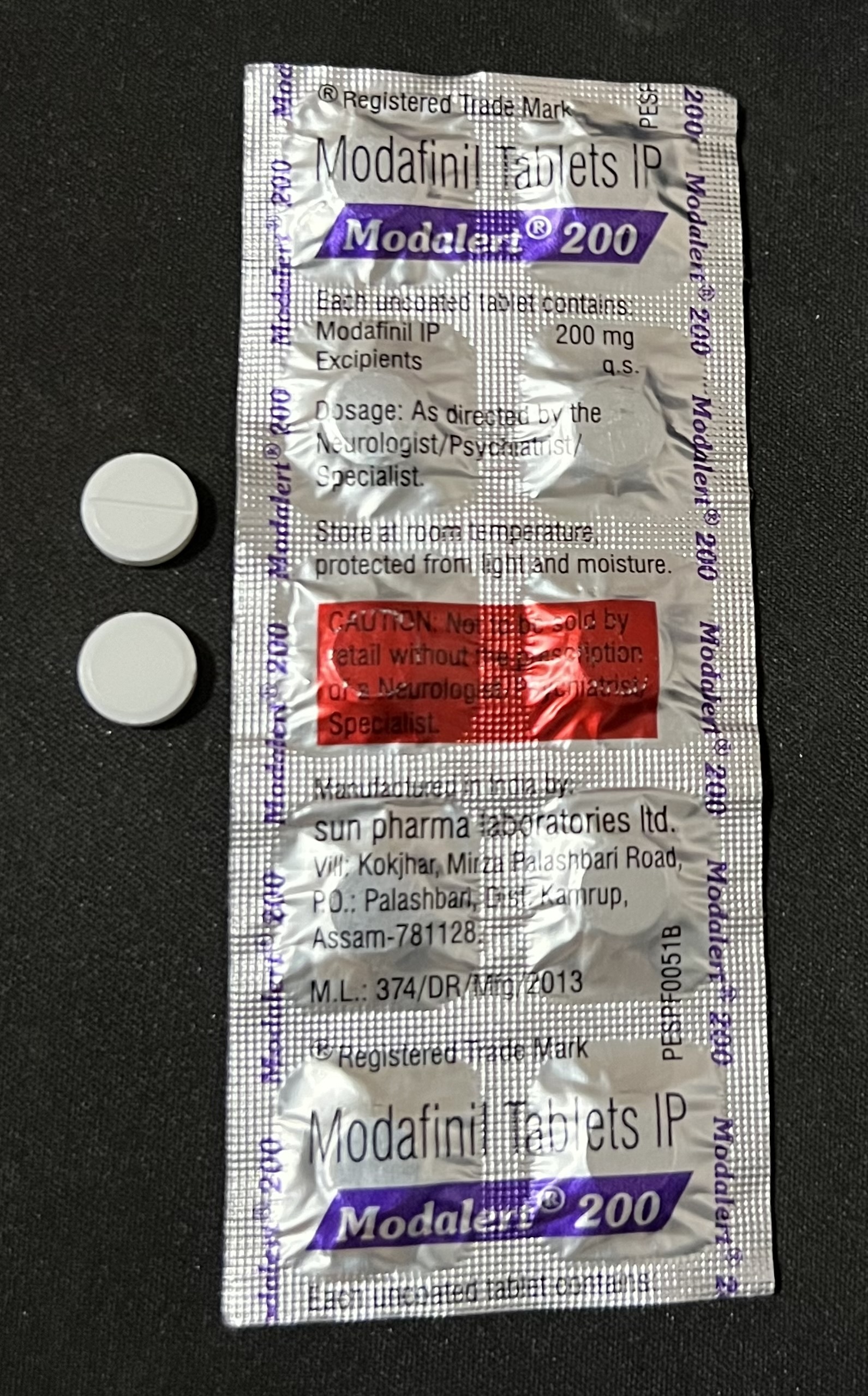
Modafinil
Modafinil, sold under the brand name Provigil among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and wakefulness-promoting agent, eugeroic (wakefulness promoter) medication used primarily to treat narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden Microsleep, sleep attacks. Modafinil is also approved for stimulating wakefulness in people with sleep apnea and shift work sleep disorder. It is taken by mouth. Modafinil is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in people under 17 years old. Common side effects of Modafinil include anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, and headache. Modafinil has potential for causing severe allergic reactions, Psychiatry, psychiatric effects, hypersensitivity, adverse effect, adverse drug interaction, interactions with prescription drugs, and misuse or drug abuse, abuse. Modafinil may harm the fetus if taken during or two months prior to pregnancy. While modafinil is used as a Nootropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melatonin (medication)
Melatonin is a naturally occurring hormone produced in the brain that is also used as a dietary supplement and medication. As a hormone, melatonin is released by the pineal gland and is involved in sleep–wake cycles. As a supplement, it is often used for the short-term treatment of disrupted sleep patterns such as from jet lag or shift work, and is typically taken orally. There is evidence of its benefit for insomnia, but the evidence is not strong. A 2017 review found that sleep onset occurred six minutes faster with use on average, but found no change in total time asleep. Side effects from melatonin supplements are minimal at low doses for short durations (the studies reported that side effects occurred about equally for both melatonin and placebo). Side effects of melatonin are rare but may occur in 1 to 10 patients out of 1,000. They may include somnolence, headaches, nausea, diarrhea, abnormal dreams, irritability, restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, migraine, leth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agomelatine
Agomelatine, sold under the brand names Valdoxan and Thymanax, among others, is an atypical antidepressant most commonly used to treat major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. One review found that it is as effective as other antidepressants with similar discontinuation rates overall but fewer discontinuations due to side effects. Another review also found it was similarly effective to many other antidepressants. Common side effects include headaches, nausea, and dizziness, which usually subside in the first few weeks, as well as liver problems – due to the potential effect on the liver, blood tests before treatment initiation, at specific time-points after initiation, and after dose increase is recommended. Its use is not recommended in people with dementia, or who are under the age of 18 or over 75. There is tentative evidence that it may have fewer side effects than some other antidepressants. It acts by serotonin receptor antagonist, blocking certain ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |