|
Deep Learning In Photoacoustic Imaging
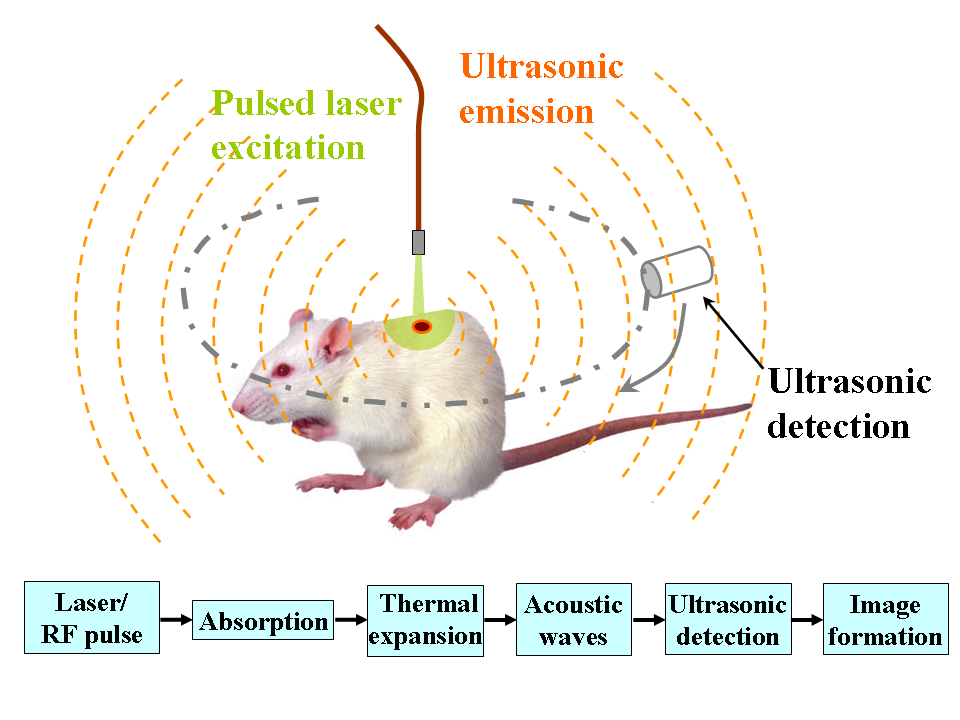
Deep learning in photoacoustic imaging combines the hybrid imaging modality of photoacoustic imaging (PA) with the rapidly evolving field of deep learning. Photoacoustic imaging is based on the photoacoustic effect, in which optical absorption causes a rise in temperature, which causes a subsequent rise in pressure via thermo-elastic expansion. This pressure rise propagates through the tissue and is sensed via ultrasonic transducers. Due to the proportionality between the optical absorption, the rise in temperature, and the rise in pressure, the ultrasound pressure wave signal can be used to quantify the original optical energy deposition within the tissue. Photoacoustic imaging has applications of deep learning in both photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) and photoacoustic microscopy (PAM). PACT utilizes wide-field optical excitation and an array of unfocused ultrasound transducers. Similar to other computed tomography methods, the sample is imaged at multiple view angles, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Adversarial Network
A generative adversarial network (GAN) is a class of machine learning frameworks designed by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in June 2014. Two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. Given a training set, this technique learns to generate new data with the same statistics as the training set. For example, a GAN trained on photographs can generate new photographs that look at least superficially authentic to human observers, having many realistic characteristics. Though originally proposed as a form of generative model for unsupervised learning, GANs have also proved useful for semi-supervised learning, fully supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The core idea of a GAN is based on the "indirect" training through the discriminator, another neural network that can tell how "realistic" the input seems, which itself is also being updated dynamically. This means that the generator is not tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Footnotes
A note is a string of text placed at the bottom of a page in a book or document or at the end of a chapter, volume, or the whole text. The note can provide an author's comments on the main text or citations of a reference work in support of the text. Footnotes are notes at the foot of the page while endnotes are collected under a separate heading at the end of a chapter, volume, or entire work. Unlike footnotes, endnotes have the advantage of not affecting the layout of the main text, but may cause inconvenience to readers who have to move back and forth between the main text and the endnotes. In some editions of the Bible, notes are placed in a narrow column in the middle of each page between two columns of biblical text. Numbering and symbols In English, a footnote or endnote is normally flagged by a superscripted number immediately following that portion of the text the note references, each such footnote being numbered sequentially. Occasionally, a number between bracke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoacoustic Effect
The photoacoustic effect or optoacoustic effect is the formation of sound waves following light absorption in a material sample. In order to obtain this effect the light intensity must vary, either periodically (''modulated light'') or as a single flash (''pulsed light'').Rosencwaig, A. (1980''Photoacoustics and photoacoustic spectroscopy'' Chemical Analysis: a Series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry and Its Applications, Vol. 57. New York:John Wiley & Sons, . The photoacoustic effect is quantified by measuring the formed sound (pressure changes) with appropriate detectors, such as microphones or piezoelectric sensors. The time variation of the electric output (current or voltage) from these detectors is the photoacoustic signal. These measurements are useful to determine certain properties of the studied sample. For example, in photoacoustic spectroscopy, the photoacoustic signal is used to obtain the actual absorption of light in either opaque or transparent objects. It is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoacoustic Microscopy
Photoacoustic microscopy is an imaging method based on the photoacoustic effect and is a subset of photoacoustic tomography. Photoacoustic microscopy takes advantage of the local temperature rise that occurs as a result of light absorption in tissue. Using a nanosecond pulsed laser beam, tissues undergo thermoelastic expansion, resulting in the release of a wide-band acoustic wave that can be detected using a high-frequency ultrasound transducer. Since ultrasonic scattering in tissue is weaker than optical scattering, photoacoustic microscopy is capable of achieving high-resolution images at greater depths than conventional microscopy methods. Furthermore, photoacoustic microscopy is especially useful in the field of biomedical imaging due to its scalability. By adjusting the optical and acoustic foci, lateral resolution may be optimized for the desired imaging depth. Photoacoustic signal The goal of photoacoustic microscopy is to find the local pressure rise p_0, which can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert Transform
In mathematics and in signal processing, the Hilbert transform is a specific linear operator that takes a function, of a real variable and produces another function of a real variable . This linear operator is given by convolution with the function 1/(\pi t) (see ). The Hilbert transform has a particularly simple representation in the frequency domain: It imparts a phase shift of ±90° ( radians) to every frequency component of a function, the sign of the shift depending on the sign of the frequency (see ). The Hilbert transform is important in signal processing, where it is a component of the analytic representation of a real-valued signal . The Hilbert transform was first introduced by David Hilbert in this setting, to solve a special case of the Riemann–Hilbert problem for analytic functions. Definition The Hilbert transform of can be thought of as the convolution of with the function , known as the Cauchy kernel. Because is not integrable across , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raster-scan
A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image systems. The word '' raster'' comes from the Latin word '' rastrum'' (a rake), which is derived from '' radere'' (to scrape); see also rastrum, an instrument for drawing musical staff lines. The pattern left by the lines of a rake, when drawn straight, resembles the parallel lines of a raster: this line-by-line scanning is what creates a raster. It is a systematic process of covering the area progressively, one line at a time. Although often a great deal faster, it is similar in the most general sense to how one's gaze travels when one reads lines of text. The data to be drawn is stored in an area of memory called the Framebuffer. This memory area holds the values for each pixel on the screen. These values are retrieved from the refresh bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Ultrasound
Cranial ultrasound is a technique for scanning the brain using high-frequency sound waves. It is used almost exclusively in babies because their fontanelle (the soft spot on the skull) provides an "acoustic window". A different form of ultrasound-based brain scanning, transcranial Doppler, can be used in any age group. This uses Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow through the major arteries in the brain, and can scan through bone. It is not usual for this technique to be referred to simply as "cranial ultrasound". Additionally, cranial ultrasound can be used for intra-operative imaging in adults undergoing neurosurgery once the skull has been opened, for example to help identify the margins of a tumour. Uses Premature babies are especially vulnerable to certain conditions involving the brain. These include intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH), which often occurs during the first few days, and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL), which tends to occur later on. One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio (imaging)
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is used in imaging to characterize image quality. The sensitivity of a (digital or film) imaging system is typically described in the terms of the signal level that yields a threshold level of SNR. Industry standards define sensitivity in terms of the ISO film speed equivalent, using SNR thresholds (at average scene luminance) of 40:1 for "excellent" image quality and 10:1 for "acceptable" image quality. SNR is sometimes quantified in decibels (dB) of signal power relative to noise power, though in the imaging field the concept of "power" is sometimes taken to be the power of a voltage signal proportional to optical power; so a 20 dB SNR may mean either 10:1 or 100:1 optical power, depending on which definition is in use. Definition of SNR Traditionally, SNR is defined to be the ratio of the average signal value \mu_\mathrm to the standard deviation of the signal \sigma_\mathrm: : \mathrm = \frac when the signal is an optical intensity, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |