|
De Soto County, Mississippi
DeSoto County is a county - located on the northwestern border of the U.S. state of Mississippi. As of the 2020 census, the population was 185,314, making it the third-most populous county in Mississippi. Its county seat is Hernando. DeSoto County is part of the Memphis metropolitan area. It is the second-most populous county in that statistical area. The county has lowland areas that were developed in the 19th century for cotton plantations, and hill country in the eastern part of the county. History DeSoto County, Mississippi, was formally established February 9, 1836.Robert Lowry and William H. McCardle, ''A History of Mississippi: From the Discovery of the Great River by Hernando DeSoto, Including the Earliest Settlement Made by the French Under Iberville to the Death of Jefferson Davis.'' Jackson, MS: R.H. Henry & Co., 1891; p. 473. The original county lines included territory now part of Tate County, which was carved out in 1873. The county is named for Spanish explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando De Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1497 – 21 May 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States (through Florida, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, Tennessee, Alabama, North Carolina, South Carolina, Mississippi, and most likely Arkansas). He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River. De Soto's North American expedition was a vast undertaking. It ranged throughout what is now the southeastern United States, searching both for gold, which had been reported by various Native Americans of the United States, Native American tribes and earlier coastal explorers, and for a passage to China or the Pacific coast. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the Mississippi River; sources disagree on the exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
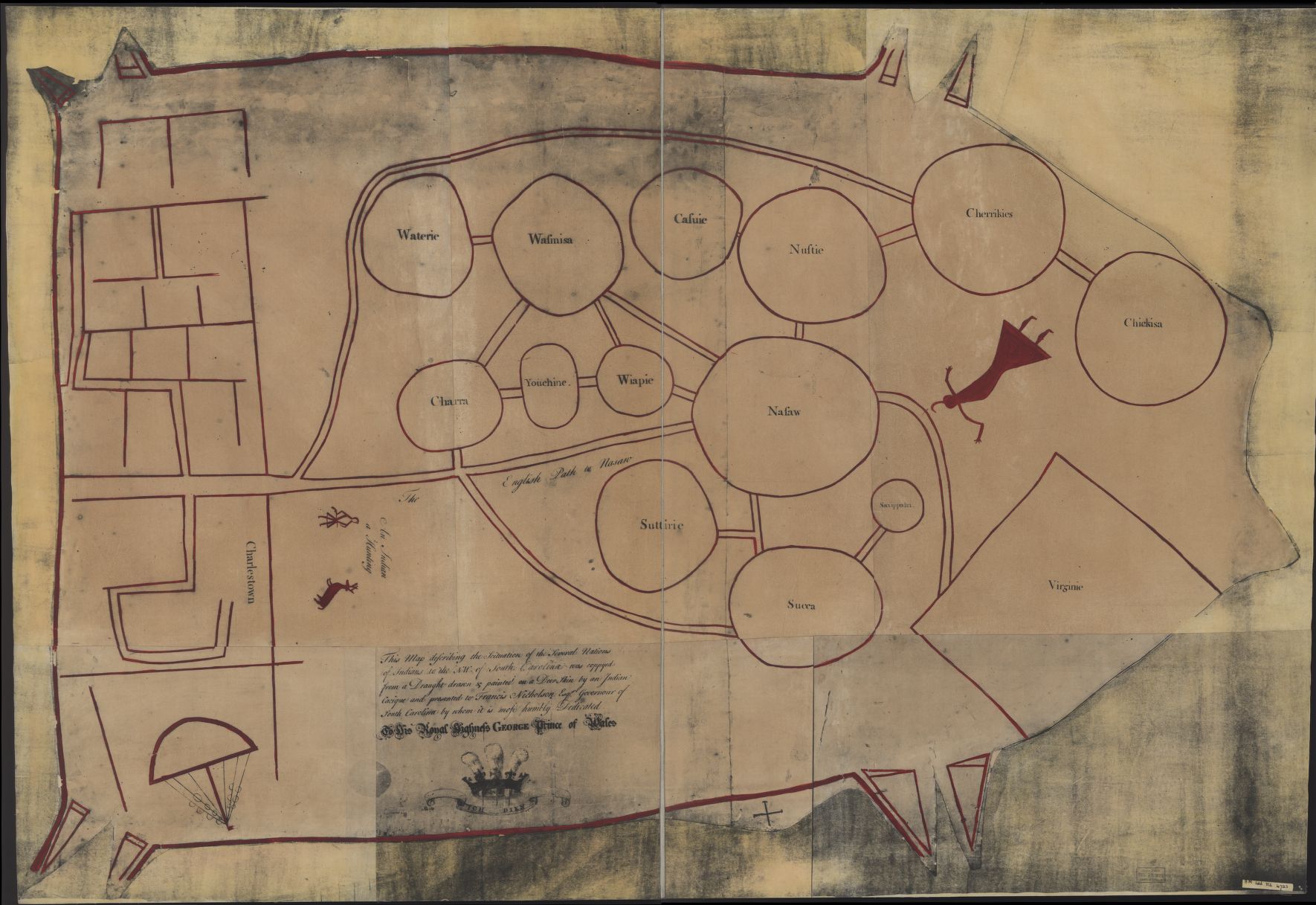
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, United States. Their traditional territory was in northern Mississippi, northwestern and northern Alabama, western Tennessee and southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Chickasaw Nation. Chickasaw people have a migration story in which they moved from a land west of the Mississippi River to reach present-day northeast Mississippi, northwest Alabama, and into Lawrence County, Tennessee. They had interaction with French, English, and Spanish colonists during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial period. The United States considered the Chickasaw one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted numerous practices of European Americans. Resisting European-American settlers encroaching on their territory, they were forced by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeSoto County Co-op, DeSoto County, Mississippi (1954)
De Soto commonly refers to * Hernando de Soto (c. 1500 – 1542), Spanish explorer * DeSoto (automobile), an American automobile brand from 1928 to 1961 De Soto, DeSoto, Desoto, or de Soto may also refer to: Places in the United States of America ;Populated places * De Soto, Georgia * De Soto, Illinois * De Soto, Iowa * De Soto, Kansas * De Soto, Mississippi * De Soto, Missouri * De Soto, Nebraska * De Soto, Wisconsin * DeSoto, Indiana * DeSoto, Texas ;Administrative divisions * De Soto Parish, Louisiana * DeSoto County, Florida * DeSoto County, Mississippi ;Parks and geographic features * De Soto National Forest in Mississippi * DeSoto Falls (Alabama) * DeSoto Falls (Georgia) * DeSoto Lake, a lake in Georgia * DeSoto National Wildlife Refuge, in Nebraska and Iowa * Fort De Soto Park in St. Petersburg, Florida * De Soto National Memorial in Bradenton, Florida * DeSoto Site Historic State Park in Tallahassee, Florida People * de Soto (surname) Other uses *The De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy Tests
A literacy test assesses a person's literacy skills: their ability to read and write. Literacy tests have been administered by various governments, particularly to immigrants. Between the 1850s and 1960s, literacy tests were used as an effective tool for disenfranchising African Americans in the Southern United States. Literacy tests were typically administered by white clerks who could pass or fail a person at their discretion based on race. Illiterate whites were often permitted to vote without taking these literacy tests because of grandfather clauses written into legislation. Other countries, notably Australia, as part of its White Australia policy, and South Africa adopted literacy tests either to exclude certain racialized groups from voting or to prevent them from immigrating to the country. Voting From the 1890s to the 1960s, many state governments administered literacy tests to prospective voters, to test their literacy in order to vote. The first state to establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poll Taxes
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sense of "counting heads" is found in phrases like polling place and opinion poll. Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments from ancient times until the 19th century. In the United Kingdom, poll taxes were levied by the governments of John of Gaunt in the 14th century, Charles II in the 17th and Margaret Thatcher in the 20th century. In the United States, voting poll taxes (whose payment was a precondition to voting in an election) have been used to disenfranchise impoverished and minority voters (especially after Reconstruction). Poll taxes are regressive, meaning the higher someone's income is, the lower the tax is as a proportion of income: for example, a $100 tax on an income of $10,000 is a 1% tax rate, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disfranchisement After Reconstruction Era
Disfranchisement after the Reconstruction era in the United States, especially in the Southern United States, was based on a series of laws, new constitutions, and practices in the South that were deliberately used to prevent black citizens from registering to vote and voting. These measures were enacted by the former Confederate states at the turn of the 20th century. Efforts were also made in Maryland, Kentucky, and Oklahoma. Their actions were designed to thwart the objective of the Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1870, which prohibited states from depriving voters of their voting rights based on race. The laws were frequently written in ways to be ostensibly non-racial on paper (and thus not violate the Fifteenth Amendment), but were implemented in ways that selectively suppressed black voters apart from other voters. In the 1870s, white racists had used violence by domestic terrorism groups (such as the Ku Klux Klan), as well as fraud, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharecroppers
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement in which a landowner allows a tenant (sharecropper) to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land. Sharecropping is not to be conflated with tenant farming, providing the tenant a higher economic and social status. Sharecropping has a long history and there are a wide range of different situations and types of agreements that have used a form of the system. Some are governed by tradition, and others by law. The French '' métayage'', the Catalan '' masoveria'', the Castilian ''mediero'', the Slavic ''połownictwo'' and ''izdolshchina, the Italian mezzadria'', and the Islamic system of ''muzara‘a'' (المزارعة), are examples of legal systems that have supported sharecropping. Overview Under a sharecropping system, landowners provided a share of land to be worked by the sharecropper, and usually provided other necessities such as housing, tools, seed, or working animals. Local merchants usually provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, slaves were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self-purchase. A fugitive slave is a person who escaped enslavement by fleeing. Ancient Rome Rome differed from Greek city-states in allowing freed slaves to become plebeian citizens. The act of freeing a slave was called ''manumissio'', from ''manus'', "hand" (in the sense of holding or possessing something), and ''missio'', the act of releasing. After manumission, a slave who had belonged to a Roman citizen enjoyed not only passive freedom from ownership, but active political freedom ''(libertas)'', including the right to vote. A slave who had acquired ''libertas'' was known as a ''libertus'' ("freed person", feminine ''liberta'') in relation to his former master, who was called his or her patron ''( patronus)''. As a social class, fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act of 1830 was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States president Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for their removal west of the Mississippi River, river Mississippi". During the presidency of Jackson (1829–1837) and his successor Martin Van Buren (1837–1841), more than 60,000 Native Americans from at least 18 tribes were forced to move west of the Mississippi River where they were allocated new lands. The southern tribes were resettled mostly in Indian Territory (Oklahoma). The northern tribes were resettled initially in Kansas. With a few exceptions, the United States east of the Mississippi and south of the Great Lakes was emptied of its Native American population. The movement westward of Tribe, indigenous tribes was characterized by a large number of deaths due to the hardships of the journey. Also available in reprint from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
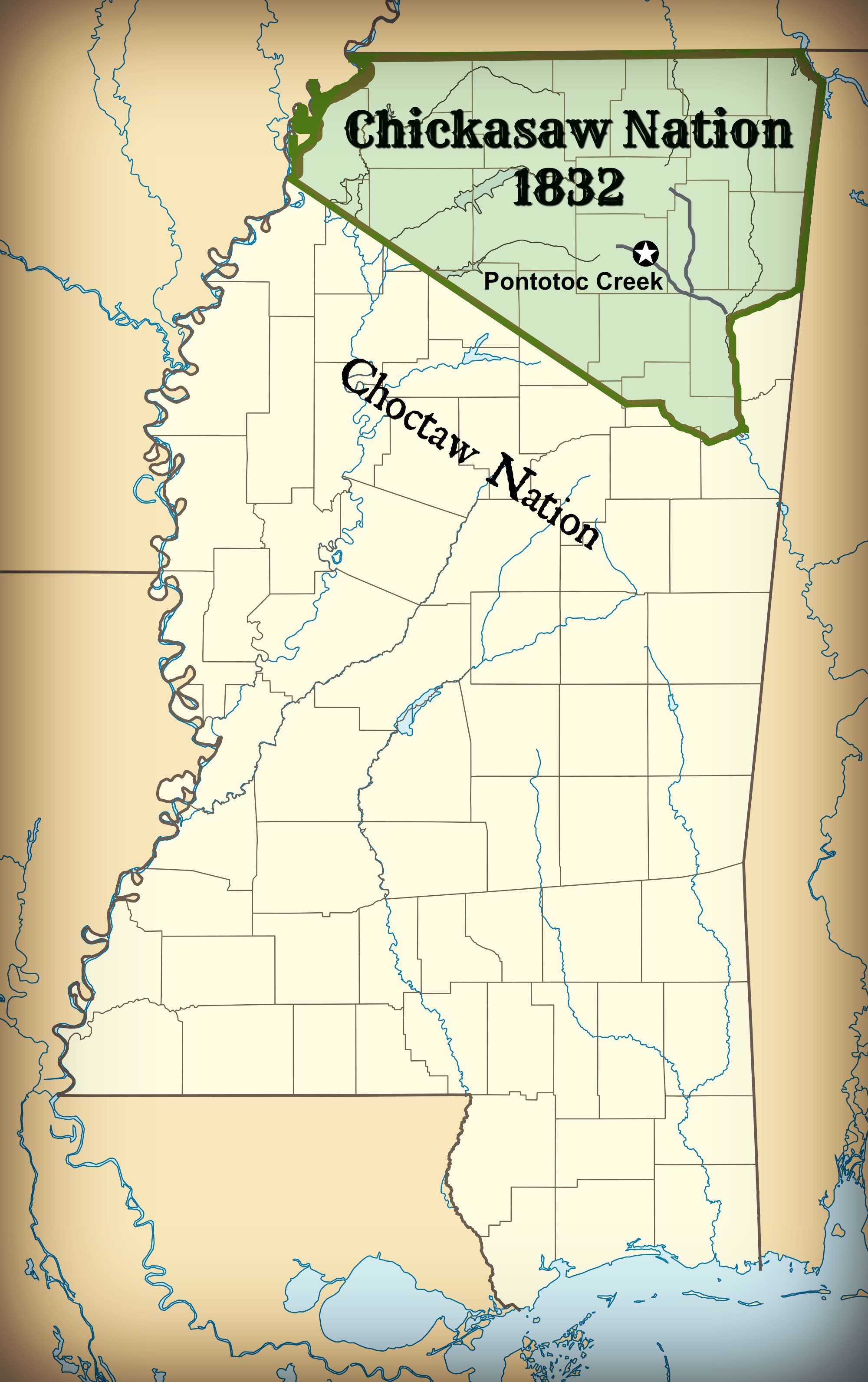
Treaty Of Pontotoc
The Treaty of Pontotoc Creek was a treaty signed on October 20, 1832 by representatives of the United States and the Chiefs of the Chickasaw Nation assembled at the National Council House on Pontotoc Creek in Pontotoc, Mississippi. The treaty ceded the 6,283,804 million acres of the remaining Chickasaw homeland in Mississippi in return for Chickasaw relocation on an equal amount of land west of the Mississippi River. The treaty followed an earlier agreement to move west of the Mississippi in 1830 which the Chickasaw refused to honor after discovering the poor nature of the land they received. Pressured by the aggression of the State of Mississippi to establish its jurisdiction over the Indians, Chickasaw Chiefs relented in 1832 to President Andrew Jackson's and his representatives offer of relocation in the west. The land was ceded to the U.S. with the understanding that the proceeds made in the sale of the land to white settlers would go to the Chickasaw. The treaty led to the Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Territory
Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who held aboriginal title, original Indian title to their land as an independent nation. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Indian Territory in the American Civil War, American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of Cultural assimilation of Native Americans#Americanization and assimilation (1857–1920), assimilation. Indian Territory later came to refer to an Territories of the United States#Formerly unorganized territories, unorganized territory whose general borders were initially set by the Nonintercourse Act of 1834, and was the successor to the remainder of the Missouri Territory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |