|
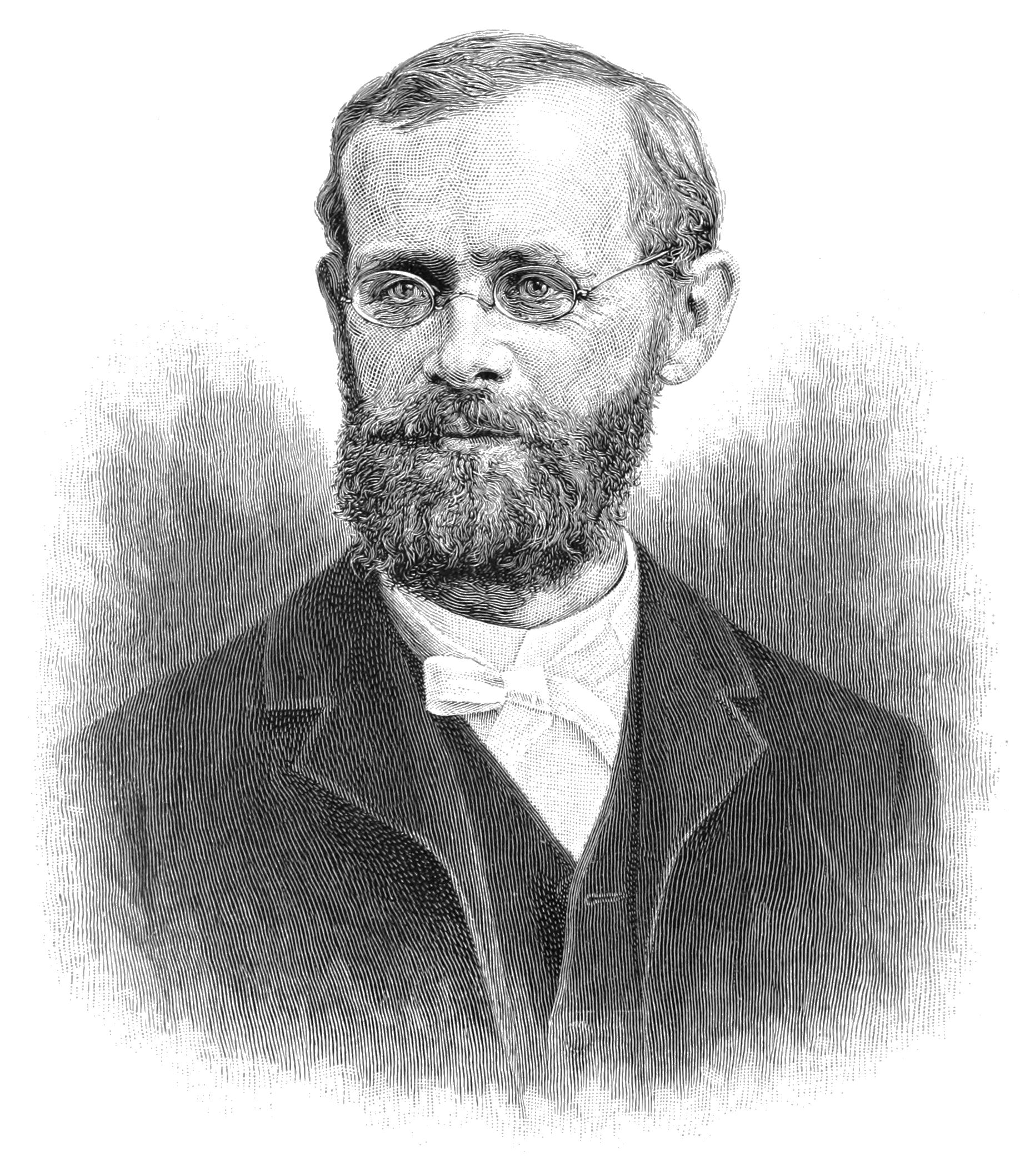
Daniel Draper (meteorologist)
Daniel Draper (2 April 1841 – 21 December 1931) was an American meteorologist and inventor who served for more than forty-two years as the official meteorologist for the city of New York and who attained worldwide distinction in the fields of science relating to astronomy and the weather.DR. DANIEL DRAPER, WEATHER MAN, DEAD; On Retirement in 1911 He Had Served City for 42 Years as Official Meteorologist. INVENTOR OF INSTRUMENTS Many of His Recording Devices Used at Central Park Observatory-- Father Was a Founder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper
Henry Draper (March 7, 1837 – November 20, 1882) was an American medical doctor and amateur astronomer. He is best known today as a pioneer of astrophotography. Life and work Henry Draper's father, John William Draper, was an accomplished doctor, chemist, botanist, and professor at New York University; he was also the first to photograph the moon through a telescope (1840). Draper's mother was Antonia Caetana de Paiva Pereira Gardner, daughter of the personal physician to the Emperor of Brazil. His niece, Antonia Maury was also an astronomer. He graduated from New York University School of Medicine, at the age of 20, in 1857. He worked first as a physician at Bellevue Hospital, and later as both a professor and dean of medicine at New York University (NYU). On May 31, 1862, he joined S Company, 12th New York Infantry Regiment as a surgeon along with his brother John Christopher, who joined as an assistant surgeon. They served until October 8, 1862. In 1867 he married Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daguerreotype
Daguerreotype was the first publicly available photography, photographic process, widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process. Invented by Louis Daguerre and introduced worldwide in 1839, the daguerreotype was almost completely superseded by 1856 with new, less expensive processes, such as ambrotype (collodion process), that yield more readily viewable images. There has been a revival of the daguerreotype since the late 20th century by a small number of photographers interested in making artistic use of early photographic processes. To make the image, a daguerreotypist polished a sheet of Plating#Silver plating, silver-plated copper to a mirror finish; treated it with fumes that made its surface light-sensitive; exposure (photography), exposed it in a camera obscura, camera for as long as was judged to be necessary, which could be as little as a few seconds for brightly sunlit subjects or much longer with less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Christopher Draper
John Christopher Draper (March 31, 1835 – December 20, 1885) was an American chemist and surgeon. He was a son of multidisciplinary scientist John William Draper and a brother of astronomer Henry Draper. Life and work Draper was born at Christiansville (now Chase City, Virginia). His father, John William Draper, was an accomplished doctor, chemist, astronomer, botanist, and professor at New York University. Draper's mother, Antonia Coetana de Paiva Pereira Gardner, was a daughter of the personal physician to the John VI of Portugal and Charlotte of Spain. In 1850–52 Draper took the arts course, and in 1855–57 the medical course, in New York University, and then studied in Europe. He was professor of natural sciences (1858–60) and of analytical and practical chemistry (1858–71) in New York University, and in 1859 was one of the first instructors of chemistry at the Cooper Union The Cooper Union for the Advancement of Science and Art, commonly known as Cooper Union, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonia Maury
Antonia Caetana de Paiva Pereira Maury (March 21, 1866 – January 8, 1952) was an American astronomer who was the first to detect and calculate the orbit of a spectroscopic binary. She published an important early catalog of stellar spectra using her own system of stellar classification, which was later adopted by the International Astronomical Union. She also spent many years studying the binary star Beta Lyrae. Maury was part of the Harvard Computers, a group of female astronomers and human computers at the Harvard College Observatory. Dorrit Hoffleit described Maury as an "independent Renegade", suffering at the Observation for her Independence not agreeing with the way Edward Charles Pickering had them working for minimal credit. Antonia Maury was awarded the Annie Jump Cannon Award in Astronomy in 1943. William Wilson Morgan, one of the developers of the MK system of stellar classification, which builds upon her work, has said that he considers Antonia Maury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tyndall
John Tyndall (; 2 August 1820 – 4 December 1893) was an Irish physicist. His scientific fame arose in the 1850s from his study of diamagnetism. Later he made discoveries in the realms of infrared radiation and the physical properties of air, proving the connection between atmospheric Carbon dioxide, CO and what is now known as the greenhouse effect in 1859. Tyndall also published more than a dozen science books which brought state-of-the-art 19th century experimental physics to a wide audience. From 1853 to 1887 he was professor of physics at the Royal Institution of Great Britain in London. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society in 1868. Early years and education Tyndall was born in Leighlinbridge, County Carlow, Ireland. His father was a local police constable, descended from Gloucestershire emigrants who settled in southeast Ireland around 1670. Tyndall attended the local schools (Ballinabranna Primary School) in County Carlow until his late t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Piazzi Smyth
Charles Piazzi Smyth (3 January 1819 – 21 February 1900) was a British astronomer who was Astronomer Royal for Scotland from 1846 to 1888; he is known for many innovations in astronomy and, along with his wife Jessica Duncan Piazzi Smyth, his Pyramidology, pyramidological and Pseudoscientific metrology, metrological studies of the Great Pyramid of Giza. Astronomical career Charles Piazzi Smyth (pronounced ) was born in Naples, Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, to Captain (later Admiral) William Henry Smyth and his wife the former Eliza Anne "Annarella" Warington. He was named Piazzi after his Godparent, godfather, the Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi, whose acquaintance his father had made at Palermo when serving in the Mediterranean. His father subsequently settled at Bedford and equipped there an observatory, at which Piazzi Smyth received his first lessons in astronomy. He was educated at Bedford School until the age of sixteen when he became an assistant to Sir Thomas Maclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentine Mott
Valentine Mott (August 20, 1785April 26, 1865) was an American surgeon. Life Valentine Mott was born at Glen Cove, New York. He graduated at Columbia College, studied under Sir Astley Cooper in London, and also spent a winter in Edinburgh. After acting as demonstrator of anatomy he was appointed professor of surgery in Columbia College in 1809. From 1811 to 1834 he was in very extensive practice as a surgeon, and most successful as a teacher and operator. He tied the innominate artery in 1818; the patient lived twenty-six days. He performed a similar operation on the carotid for the first time in the USA on 20 Sept 1829 before going on to carry out this operation forty-six times with good results; and in 1827 he was also successful in the case of the common iliac. He is said to have performed one thousand amputations and one hundred and sixty-five lithotomies. After spending seven years in Europe (1834-1841) Mott returned to New York where he was on the founding faculty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustave Eiffel
Alexandre Gustave Eiffel ( , ; Bonickhausen dit Eiffel; 15 December 1832 – 27 December 1923) was a French civil engineer. A graduate of École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, he made his name with various bridges for the French railway network, most famously the Garabit Viaduct. He is best known for the world-famous Eiffel Tower, designed by his company and built for the Exposition Universelle (1889), 1889 Universal Exposition in Paris, and his contribution to building the Statue of Liberty in New York. After his retirement from engineering, Eiffel focused on research into meteorology and aerodynamics, making significant contributions in both fields. Early life Alexandre Gustave Eiffel was born in France, in the Côte-d'Or, the first child of Catherine-Mélanie (née Moneuse) and Alexandre Bonickhausen dit Eiffel. He was a descendant of Marguerite Frédérique (née Lideriz) and Jean-René Bönickhausen, who had emigrated from the Germany, German town of Marmagen and set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James McKeen Cattell
James McKeen Cattell (May 25, 1860 – January 20, 1944) was the first professor of psychology in the United States, teaching at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. He was a long-time editor and publisher of scientific journals and publications, including ''Science'', and served on the board of trustees for Science Service, now known as Society for Science from 1921 to 1944. At the beginning of Cattell's career, many scientists regarded psychology simply as a minor field of study, or as a pseudoscience like phrenology. Cattell helped establish psychology as a legitimate science, worthy of study at the highest levels of the academy. At the time of his death, ''The New York Times'' credited him as "the dean of American science." Cattell was uncompromisingly opposed to American involvement in World War I. Baron cites C. S. Gruber (1972), "Academic freedom at Columbia University: The case of James McKeen Cattell", ''AAUP Bulletin'', Autumn, pp. 297-305, with respect to C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell (; born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was a Scottish-born Canadian Americans, Canadian-American inventor, scientist, and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the AT&T Corporation, American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885. Alexander Melville Bell, Bell's father, grandfather, and brother had all been associated with work on elocution and speech, and both his mother and wife were deaf, profoundly influencing Bell's life's work. His research on hearing and speech further led him to experiment with hearing devices, which eventually culminated in his being awarded the first United States patent law, U.S. patent for the telephone, on March 7, 1876. Bell considered his invention an intrusion on his real work as a scientist and refused to have a telephone in his study. Many other inventions marked Bell's later life, including ground-breaking work in Free-space optical commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland Abbe
Cleveland Abbe (December 3, 1838 – October 28, 1916) was an American meteorologist and advocate of time zones. While director of the Cincinnati Observatory in Cincinnati, Ohio, from 1871-1916, he developed a system of telegraphic weather reports, daily weather maps, and weather forecasts. In 1870, Congress established the U.S. National Weather Service, Weather Bureau and inaugurated the use of daily weather forecasts. In recognition of his work, Abbe, who was often referred to as "Old Probability" for the reliability of his forecasts, was appointed the first head of the new service. Early life and education Cleveland Abbe was born in New York City in 1838 and grew up in the prosperous merchant family of George Waldo and Charlotte Colgate Abbe. One of his younger brothers, Robert Abbe, Robert, became a prominent surgeon and radiologist. In school, Cleveland excelled in mathematics and chemistry, attending David B. Scott Grammar School, and graduating in 1857 from the City Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |