|
Dakshayani
Sati (, , , ), also known as Dakshayani (Sanskrit: , IAST: ''Dākṣāyaṇī'', lit. 'daughter of Daksha'), is the Hindu goddess of marital felicity and longevity, and is worshipped as an aspect of the mother goddess Shakti. Sati was the first wife of Shiva, the other being Parvati, who was Sati's reincarnation after her death. The earliest mentions of Sati are found in the time of the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, but details of her story appear in the Puranas. Legends describe Sati as the favourite child of Daksha, who marries Shiva against her father's wishes. Later, when Daksha organises a yajna (fire-sacrifice) in which he doesn't invite her and her husband, Sati goes to attend it, only to be humiliated by her father. She then immolates herself to protest against him, and uphold the honour of her husband. In Hinduism, both Sati and Parvati, successively play the role of bringing Shiva away from ascetic isolation into creative participation with the world. Sati's story pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakta Pithas
The Shakta pithas, also called Shakti pithas or Sati pithas (, , ''seats of Shakti''), are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the mother goddess denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various forms of Adi Shakti. Various Puranas such as Srimad Devi Bhagavatam state the existence of a varying number of 51, 52, 64 and 108 Shakta pithas of which 18 are named as Astadasha ''Maha'' (major) in medieval Hindu texts. Legends abound about how the Shakta pithas came into existence. The most popular is based on the story of the death of Sati, a deity according to Hinduism. Shiva carried Sati's body, reminiscing about their moments as a couple, and roamed around the universe with it. Vishnu cut her body into 51 body parts, using his Sudarshana Chakra, which fell on earth to become sacred sites where all the people can pay homage to the goddess. To complete this task, Shiva took the form of Bhairava. Most of these historic places of goddess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daksha Yajna
Dakṣayajña is an important event in Hindu mythology that is narrated in various Hindu scriptures. It refers to a yajna (ritual-sacrifice) organised by Daksha, where his daughter, Sati, immolates herself. The wrath of the god Shiva, Sati's husband, thereafter destroys the sacrificial ceremony. The tale is also called Daksha-Yajna-Nasha ("destruction of Daksha's sacrifice). The legend forms the liturgical basis of the establishment of the Shakti Pithas, the temples of Mahadevi, the supreme deity of Shaktism. It also becomes a prelude to the legend of Parvati, Sati's reincarnation, who later marries Shiva. The tale is mainly told in the '' Vayu Purana''. It is also mentioned in the ''Kasi Kanda'' of the ''Skanda Purana'', the '' Kurma Purana'', '' Harivamsa Purana,'' and the ''Padma Purana''. The ''Linga Purana'', ''Shiva Purana'', and '' Matsya Purana'' also detail the incident. Variations of the legend may be observed in later Puranas, each text lending a superior account to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
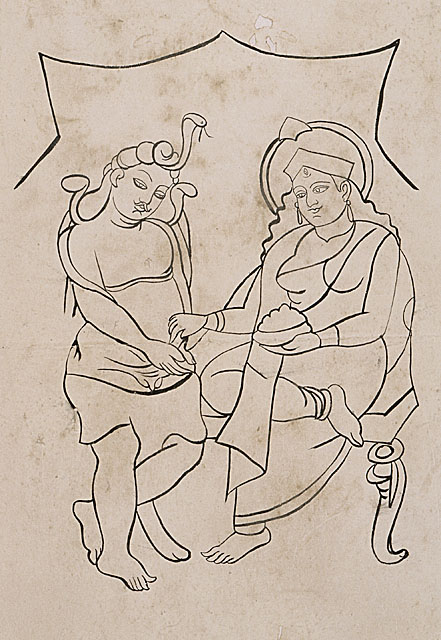
Kalighat Painting
Kalighat painting, Kalighat Patachitra, or Kalighat Pat (Bengali: '':bn:কালীঘাট পটচিত্র, কালীঘাট পটচিত্র'') is a style of Indian paintings which originated in the 19th century. It was first practiced by a group of specialized scroll painters known as the patuas in the vicinity of the Kalighat Kali Temple in Kolkata (formerly Calcutta), in the present Indian state of West Bengal. Composed of bold outlines, vibrant colour tones, and minimal background details, these paintings and drawings were done on both hand-made and machine manufactured paper. The paintings depicted mythological stories, figures of Hindu gods and goddesses, as well as scenes from everyday life and society, thereby recording a socio-cultural landscape which was undergoing a series of transitions during the 19th and early 20th century, when the Kalighat pat reached its pinnacle. Today the Victoria and Albert Museum in London hosts the single largest collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in South India, Southern India), Sri Lanka, and Nepal.Keay, p.xxvii. The followers of Shaivism are called Shaivas or Shaivites. According to Chakravarti, Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Aryan religions and traditions, Vedic Rudra, and post-Vedic traditions, accommodating local traditions and Yoga, puja and bhakti. According to Bisschop, early shaivism is rooted in the worship of vedic deity Rudra. The earliest evidence for sectarian Rudra-Shiva worship appears with the Pasupata (early CE), possibly owing to the Origins of Hinduism, Hindu synthesis, when many local traditions were aligned with the Brahmanism, Vedic-Brahmanical fold. The Pāśupata movement rapidly expanded through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kartikeya
Kartikeya (/Sanskrit phonology, kɑɾt̪ɪkejə/; ), also known as Skanda (Sanskrit phonology, /skən̪d̪ə/), Subrahmanya (/Sanskrit phonology, sʊbɾəɦməɲjə/, /ɕʊ-/), Shanmukha (Sanskrit phonology, /ɕɑnmʊkʰə/) and Murugan (/Sanskrit phonology, mʊɾʊgən/), is the Hinduism, Hindu List of war deities, god of war. He is generally described as the son of the deities Shiva and Parvati and the brother of Ganesha. Kartikeya has been an important deity in the Indian subcontinent since Vedic period, ancient times. Mentions of Skanda in the Sanskrit literature data back to fifth century BCE and the mythology relating to Kartikeya became widespread in North India around the second century BCE. Archaeological evidence from the first century CE and earlier shows an association of his iconography with Agni, the Hindu god of fire, indicating that Kartikeya was a significant deity in early Hinduism. He is hailed as the "favoured god of the Tamils", and the tutelary dei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Brahman
''Para Brahman'' or ''Param Brahman'' () in Hindu philosophy is the "Supreme Brahman" that which is beyond all descriptions and conceptualisations. It is described as beyond the form or the formlessness (in the sense that it is devoid of Maya) that eternally pervades everything, everywhere in the universe and whatever is beyond. Para Brahman is conceptualised in diverse ways. In the Advaita Vedanta tradition, the Para Brahman is a synonym of ''nirguna brahman'', i.e., the attribute-less Absolute. Conversely, in Dvaita Vedanta and Vishistadvaita Vedanta traditions, the Para Brahman is defined as ''saguna brahman'', i.e., the Absolute with attributes. In Vaishnavism, Shaivism, and Shaktism, Vishnu, Shiva, and Adi Shakti respectively are Para Brahman. Mahaganapati is held to be Para Brahman by the Ganapatya sect, Kartikeya by the Kaumaram. Etymology ''Para'' is a Sanskrit word that means "higher" in some contexts, and "highest or supreme" in others. ''Brahman'' in Hinduism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kena Upanishad
The Kena Upanishad (, ) (also alternatively known as Talavakara Upanishad) is a Vedic Sanskrit text classified as one of the primary or Mukhya Upanishads that is embedded inside the last section of the ''Talavakara Brahmanam'' of the Samaveda.Paul Deussen, Sixty Upanishads of the Veda, Volume 1, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 207-213 It is listed as number 2 in the Muktikā, the canon of the 108 Upanishads of Hinduism. The Kena Upanishad was probably composed sometime around the middle of the 1st millennium BCE. It has an unusual structure where the first 13 are verses composed as a metric poem, followed by 15 prose paragraphs of main text plus 6 prose paragraphs of epilogue. Paul Deussen suggests that the latter prose section of the main text is far more ancient than the poetic first section, and Kena Upanishad bridged the more ancient prose Upanishad era with the metric poetic era of Upanishads that followed. Kena Upanishad is notable in its discussion of Brahman with attribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudrani
Rudrani () is the consort of Rudra, a Vedic deity regarded to be a form of Shiva in contemporary Hinduism. Rudrani is an epithet of Parvati, the consort of Shiva Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w .... References Hindu goddesses Forms of Parvati Rigvedic deities {{hindu-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudra
Rudra (/ ɾud̪ɾə/; ) is a Rigvedic deity associated with Shiva, the wind or storms, Vayu, medicine, and the hunt. One translation of the name is 'the roarer'. In the ''Rigveda'', Rudra is praised as the "mightiest of the mighty". Rudra means "who eradicates problems from their roots". Depending upon the period, the name Rudra can be interpreted as 'the most severe roarer/howler' or 'the most frightening one'. This name appears in the Shiva Sahasranama, and R. K. Sharma notes that it is often used as a name of Shiva in later languages. The " Shri Rudram" hymn from the ''Yajurveda'' is dedicated to Rudra and is important in the Shaivite sect.For an overview of the Śatarudriya see: . In the Prathama Anuvaka of Namakam ( Taittiriya Samhita 4.5), Rudra is revered as Sadasiva (meaning 'mighty Shiva') and Mahadeva. Sadashiva is the Supreme Being, Paramashiva, in the Siddhanta sect of Shaivism. Etymology The etymology of the theonym ''Rudra'' is uncertain.. It is usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudarshana Chakra
The Sudarshana Chakra (, ) is a divine discus, attributed to Vishnu in the Hindu scriptures. The Sudarshana Chakra is generally portrayed on the right rear hand of the four hands of Vishnu, who also holds the Panchajanya (conch), the Kaumodaki (mace), and the Padma (lotus). In the ''Rigveda'', the Sudarshana Chakra is stated to be Vishnu's symbol as the wheel of time. The discus later emerged as an ayudhapurusha (an anthropomorphic form), as a fierce form of Vishnu, used for the destruction of demons. As an ''ayudhapurusha'', the deity is known as ''Chakraperumal'' or ''Chakratalvar''. Etymology The word ''Sudarshana'' is derived from two Sanskrit words – ''Su'' () meaning "good/auspicious" and '' Darshana'' () meaning "vision". In the Monier-Williams dictionary the word Chakra is derived from the root (''kram'') or (''rt'') or (''kri'') and refers among many meanings, to the wheel of a carriage, wheel of the sun's chariot or metaphorically to the wheel of time. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |