|
D Class (other)
D class may refer to: Ships * D-class cruiser (Germany), a pair of proposed cruisers * D-class cruiser (United Kingdom), British light cruisers that served during World War II * D-class lifeboat, British lifeboats * D-class destroyer (other), several classes of ships * British D-class submarine * United States D-class submarine * D-class ferry, roll-on/roll-off ferries operated by DFDS Seaways Rail vehicles Australia * MRWA D class, 2-8-0 type steam locomotives * WAGR D class, 4-6-4T tank locomotive * WAGR D class (1884), 0-4-0ST tank locomotives * WAGR D class (diesel), diesel locomotives * D-class Melbourne tram * D-class Sydney tram India * DHR D Class, 0-4-0+0-4-0 Garratt-type articulated steam locomotives New Zealand * NZR D class (1874), 33 2-4-0T tank locomotives * NZR D class (1929), 1 experimental 0-4-0T locomotives United Kingdom * Metropolitan Railway D Class, tank engines * NBR D class 0-6-0T, tank locomotives * LNWR Class D, 0-8-0 steam locomotives * SECR D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
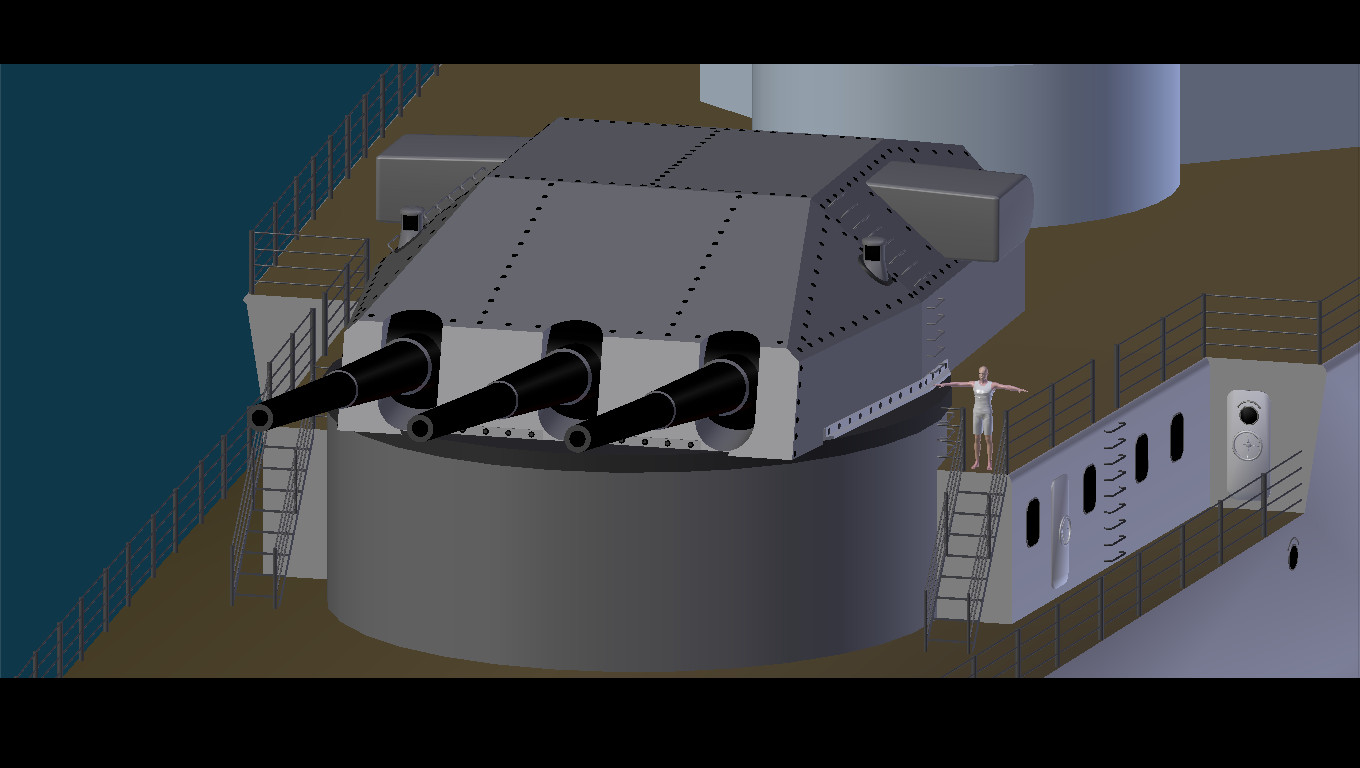
D-class Cruiser (Germany)
The D-class cruisers were a pair of German heavy cruisers, classified as ("armored ships") by the (Navy of the Realm). The ships were improved versions of the preceding s, authorized by Adolf Hitler in 1933. They were intended to counter a new French naval construction program. displacement (ship), Displacement increased to , but Hitler allowed only increases to armor, prohibiting additions to the ships' main battery armament. Both ships were keel laying, laid down in February 1934, but not much work done before work was cancelled pending a significant revision of the design. It was determined that the ships should be enlarged to counter the new French . The construction contracts for both ships were superseded by the s. Design The ships were designed as follow-ons to the s. In 1933, the rise of the Nazi Party brought Adolf Hitler to power in Germany. At the time, he opposed a large-scale naval rearmament program, but decided to allow limited construction to counter French na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DHR D Class
The DHR D Class was a gauge Garratt-type articulated steam locomotive used on the Darjeeling Himalayan Railway (DHR) in West Bengal, India. Service history The sole member of the class was built by Beyer, Peacock & Company, Manchester, England in 1910, and entered service the following year, as no. 31 in the DHR fleet. Its basic dimensions were designed to be roughly equivalent to those of two of the DHR's existing B Class engines, with the intention that it would produce approximately double the power of those engines. However, in practice it was only able to haul 65% more load than a single B Class unit. Although the DHR did not acquire any further articulated locomotives, no. 31 remained in service until November 1954. See also * Rail transport in India#History *Indian Railways *Locomotives of India *Rail transport in India Rail transport in India consists of primarily of passenger train, passenger and Rail freight transport, freight shipments along an integrated r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class D (other)
{{disambig ...
The term Class D may refer to: * Class D (baseball), a defunct class in minor league baseball in North America * Class-D amplifier or switching amplifier * Class D fire extinguisher * Class D league, a classification of minor league baseball from 1902 to 1962 * Class D star, a stellar classification * Class D, IP addresses on a classful network * Class D, an airspace class as defined by the ICAO * Class D, a type of Driver's license in the United States * Class D, a North American broadcast station class * Class-D, a type of character in the video game ''SCP – Containment Breach'' See also * D class (other) * D (other) * * Delta class (other) ''Delta'' class may refer to: * ''Delta''-class submarine () Soviet designations ''Project 667B "Murena", Project 667BD "Murena-M", Project 667BDR "Kalmar", Project 667BDRM "Delfin"''; NATO reporting names ''Delta I, Delta II, Delta III, Delta IV' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCP Foundation
The SCP Foundation is a fictional organization featured in stories created by contributors on the SCP Wiki, a wiki-based Collaborative fiction, collaborative writing project. Within the project's shared universe, shared fictional universe, the SCP Foundation is a secret organization that is responsible for capturing, containing, and studying various paranormal, supernatural, and other mysterious phenomena (known as "anomalies" or "SCPs"), while also keeping their existence hidden from the rest of society. The collaborative writing project includes elements of many genres such as Horror fiction, horror, science fiction, and urban fantasy. The majority of works on the SCP Wiki consist of thousands of SCP files that mock confidential scientific reports and document various SCPs and associated containment procedures. The website also contains "Foundation Tales", short stories featuring various characters and settings in the SCP universe. The wiki's literary works have been praised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-segment
The D-segment is the 4th category of the Euro Car Segment, European segments for passenger cars, and is described as "large cars". It is equivalent to the Euro NCAP "large family car" size class, and the present-day definition of the mid-size car category used in North America. Compact executive cars are part of the D-segment size category. D-segment sales represented about 7% of the market in the 2010s. Characteristics Most D-segment cars are Sedan (automobile), sedans/saloons or Station wagon, wagons/estates but hatchbacks, and coupes have been common. Pricing and specification of D-segment cars can vary greatly, from basic low-cost transport to more luxurious and expensive models. As of 2021 the typical D-segment category size ranges from about . Current models D-segment cars in Europe are the BMW 3 Series, Mercedes-Benz C-Class, Audi A4/S4/RS4, Mazda6, Škoda Superb, Volvo S60/V60, Jaguar XE, Citroën C5, Peugeot 508, Audi A5/S5/RS5, BMW 4 Series, Volkswagen Arteon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-class Blimp
The D class blimp was a patrol airship used by the US Navy in the early 1920s. The D-type blimps were slightly larger than the C-type and had many detail improvements. The Navy continued the practice of dividing the envelope production between Goodyear and Goodrich. The control cars were manufactured by the Naval Aircraft Factory. The major improvements over the C-type blimps were a better control car design and easier, more reliable controls and instrumentation. The engines were moved to the rear to reduce noise and allow easier communications between crew members. The fuel tanks were suspended from the sides of the envelope. The envelope was identical to the C-type, except an additional six-foot panel was inserted for a total length of and a volume of . The last of the D-Class, D-6, had a redesigned control car by Leroy Grumman who later founded the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. Operational history On the day of its maiden fight, the D-1 caught fire and burned in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SECR D Class
The SECR D class is a class of 4-4-0 tender locomotives designed by Harry Wainwright for the South Eastern and Chatham Railway. Overview The construction of the initial 20 engines was shared between Ashford railway works and the Glasgow builder, Sharp, Stewart and Company. The first of the class to enter service in 1901 was a Glasgow product, and by 1907 fifty-one were in traffic. Of these twenty-one were Ashford built while the rest were supplied by outside contractors. The D class was a Harry Wainwright design and he was responsible for the overall look of the engine. The detail work was undertaken by Robert Surtees, his chief draughtsman at Ashford works. D1 class In 1913, Richard Maunsell started the rebuilding of 21 D Class locomotives with Belpaire fireboxes to produce the more powerful D1 class. These bigger engines were needed to cope with increasing loads on the Kent Coast Line through Chatham. Operation Initially the D class was put to work on the Kent coast an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNWR Class D
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Class D was a class of steam locomotives. They were simple engine rebuilds of earlier Webb Class A three-cylinder compound engines. History Though the original rebuilds of the Class As had reused the existing small (4 ft 3 in diameter) boilers with 19.5 in diameter cylinders ( Class C, the smaller boilers could not raise adequate steam, so from 1906 the next 62 rebuilds (63 according to the LNWR Society) were rebuilt with a larger 5 ft 2 in diameter Experiment-type boilers, retaining the cylinders. These, from 1911, would be classified D. These rebuilds left smaller boilers available and so from 1906 rebuilds used these smaller boilers with smaller cylinders to Class C1. To these compound rebuilds was added the prototype eight-coupled goods engine No. 2524 which was rebuilt with a larger boiler in 1906. Previously it had been similar to the Class C with a smaller boiler; though was not classified as such since the letter classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBR D Class 0-6-0T
The NBR D Class (LNER Class J83) was a class of 0-6-0 tank locomotives designed by Matthew Holmes for short distance freight, station pilot, and heavy shunting duties on the North British Railway. Service history They were introduced in 1900 and had inside cylinders and piston valves operated by Stephenson valve gear. Forty of these new Class D engines were delivered in 1900–01, twenty each from Neilson and Company and Sharp, Stewart and Company. At grouping they became LNER class J83. The class were highly successful in service, with only three failing to complete during their lifetime. One locomotive, No. 9830, managed to complete . The engines were commonly seen across the entire North British Railway network, and were the second largest class of tank engines on the railway, after the NBR A class. Numbering On the NBR they were numbered in a sequence commencing with 795 (and are sometimes referenced as 795 class engines). A total of 40 locomotives were built, all but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Railway D Class
The Metropolitan Railway D Class was a group of six locomotives built for the Metropolitan Railway in 1894-1895 by Sharp, Stewart and Company. Overview Two locomotives were used on the Verney Junction-Aylesbury section. The other four ran between Aylesbury and Baker Street Baker Street is a street in the Marylebone district of the City of Westminster in London. It is named after builder James Baker. The area was originally high class residential, but now is mainly occupied by commercial premises. The street is ... and were fitted with condensing apparatus, but this was later removed.Day, J. and Fenton, W. ''The Last Drop - London Transport Steam 1863-1971'', London Transport Publications 1971, P.14 Withdrawal The class was withdrawn starting in 1920. Some were sold, while others were scrapped, but none were ultimately preserved. References External links * http://www.railwayarchive.org.uk/stories/getobjectstory.php?rnum=L2597&enum=LE130&pnum=13&maxp=18 D 2- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR D Class (1929)
The NZR D class of 1929 comprised one 0-4-0 tank locomotive that was built for the New Zealand Railways Department by the Clayton Wagons Ltd in Lincoln, England. History D 1 was purchased for railcar-type service, but it was not successful. It had a White-Forster type boiler designed for a working pressure of , had four vertical cylinders housed in the rear of the cab and was high geared. At a normal engine speed of 400 rpm, the unit was calculated to develop . The engine drove a central transverse jackshaft through reduction gearing, the drive from the jackshaft being transmitted to the wheels through conventional side rods. In service On arrival in New Zealand, D 1 was found to be more than 25 per cent heavier than the specified maximum of and, after trials in Wellington was allocated for use as a shunting engine at the Otahuhu Workshops Otahuhu Railway Workshops were a major rolling stock construction, maintenance and repair facility operated by the New Zealand Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR D Class (1874)
NZR D class steam tank locomotives operated on New Zealand's national railway network. The first entered service in 1874 all had been withdrawn by the end of 1927, which allowed the D classification to be used again in 1929. Introduction The boiler and cylinders were the same as the slightly earlier C class, but its driving wheels had a larger diameter and it was aesthetically different from the C. The class was ordered in a number of batches: eight from Neilson and Company in 1874, five from Dübs and Company and four from Neilson in 1878, seven from Neilson in 1880, ten from Scott Brothers in 1887, and the final D from Scott Brothers in 1890. The order with Scott Brothers, placed in 1884, was the first large-scale construction of locomotives in New Zealand. Names Four of the 1874 locomotives were named: *D 143: ''Trout'' *D 144: ''Kingfisher'' *D 169: ''Possum'' *D 240: ''Snapper'' Operation The class was not particularly powerful and was employed on light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |