|
Croeseid
The Croeseid, anciently ''Kroiseioi stateres'', was a type of coin, either in gold or silver, which was minted in Sardis by the king of Lydia Croesus (561–546 BC) from around 550 BC. Croesus is credited with issuing the first true gold coins with a standardised purity for general circulation, and the world's first bimetallic monetary system. Precedents Before Croesus, his father Alyattes had already started to mint various types of non-standardized coins. They were made in a naturally occurring material called electrum, a variable mix of gold and silver (with about 54% gold and 44% silver), and were in use in Lydia, its capital city Sardis and surrounding areas for about 80 years before Croesus' reign as King of Lydia. The unpredictability of electrum coins' composition implied that they had a variable value, which greatly hampered the development of standardised coinage. The royal symbol stamped on the coin, similar to a seal, was a declaration of the value of the contents i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croeseid Equivalence
The Croeseid, anciently ''Kroiseioi stateres'', was a type of coin, either in gold or silver, which was minted in Sardis by the king of Lydia Croesus (561–546 BC) from around 550 BC. Croesus is credited with issuing the first true gold coins with a standardised purity for general circulation, and the world's first bimetallic monetary system. Precedents Before Croesus, his father Alyattes had already started to mint various types of non-standardized coins. They were made in a naturally occurring material called electrum, a variable mix of gold and silver (with about 54% gold and 44% silver), and were in use in Lydia, its capital city Sardis and surrounding areas for about 80 years before Croesus' reign as King of Lydia. The unpredictability of electrum coins' composition implied that they had a variable value, which greatly hampered the development of standardised coinage. The royal symbol stamped on the coin, similar to a seal, was a declaration of the value of the contents i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange between them. For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the moneys of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most moneys in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimetallism, where the law guarant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange between them. For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the moneys of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most moneys in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimetallism, where the law guarant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siglos
The Achaemenid Empire issued coins from 520 BCE–450 BCE to 330 BCE. The Persian daric was the first gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos (from grc, σίγλος, he, שֶׁקֶל, '' shékel'') represented the first bimetallic monetary standard.Michael Alram"DARIC" ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'', December 15, 1994, last updated November 17, 2011 It seems that before the Persians issued their own coinage, a continuation of Lydian coinage under Persian rule is likely. Achaemenid coinage includes the official imperial issues (Darics and Sigloi), as well as coins issued by the Achaemenid provincial governors (satraps), such as those stationed in Asia Minor. Early coinage of Western Asia under the Achaemenid Empire When Cyrus the Great (550–530 BC) came to power, coinage was unfamiliar in his realm. Barter, and to some extent silver bullion, was used instead for trade. The practice of using silver bars for currency also seems to have been current in Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak, Manisa and inland Izmir. The ethnic group inhabiting this kingdom are known as the Lydians, and their language, known as Lydian, was a member of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The capital of Lydia was Sardis.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek World 478–323 BC''. 2nd edition. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2010, p. 6. The Kingdom of Lydia existed from about 1200 BC to 546 BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a province of the Achaemenid Persian Empire, known as the satrapy of Lydia or ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of silver, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apadana Hoard
The Apadana hoard is a hoard of coins that were discovered under the stone boxes containing the foundation tablets of the Apadana Palace in Persepolis. The coins were discovered in excavations in 1933 by Erich Schmidt, in two deposits, each deposit under the two deposition boxes that were found. The deposition of this hoard, which was visibly part of the foundation ritual of the Apadana, is dated to circa 515 BCE. Foundation tablets The gold and silver tablets retrieved from the stone boxes contained a trilingual inscription by Darius in Old Persian, Elamite and Akkadian, which describes his Empire in broad geographical terms, and is known as the DPh inscription: Foundation hoard The coins found in the hoard were: * Northeastern deposit: Four gold lightweight Croeseids (Sardis mint), a tetradrachm of Abdera, a stater of Aegina. * Southeastern deposit: Four gold lightweight Croeseids (Sardis mint), three double- sigloi from Cyprus (one attributed to Lapethus, one to Paph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apadana Palace
, native_name_lang = , alternate_name = , image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis. , map = , map_type = Iran#West Asia , map_alt = , map_caption = , map_size = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = yes , coordinates = , map_dot_label = , location = Marvdasht, Fars Province, Iran , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , and , material = Limestone, mud-brick, cedar wood , built = 6th century BC , abandoned = , epochs = Achaemenid Empire , cultures = Persian , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = *Battle of the Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
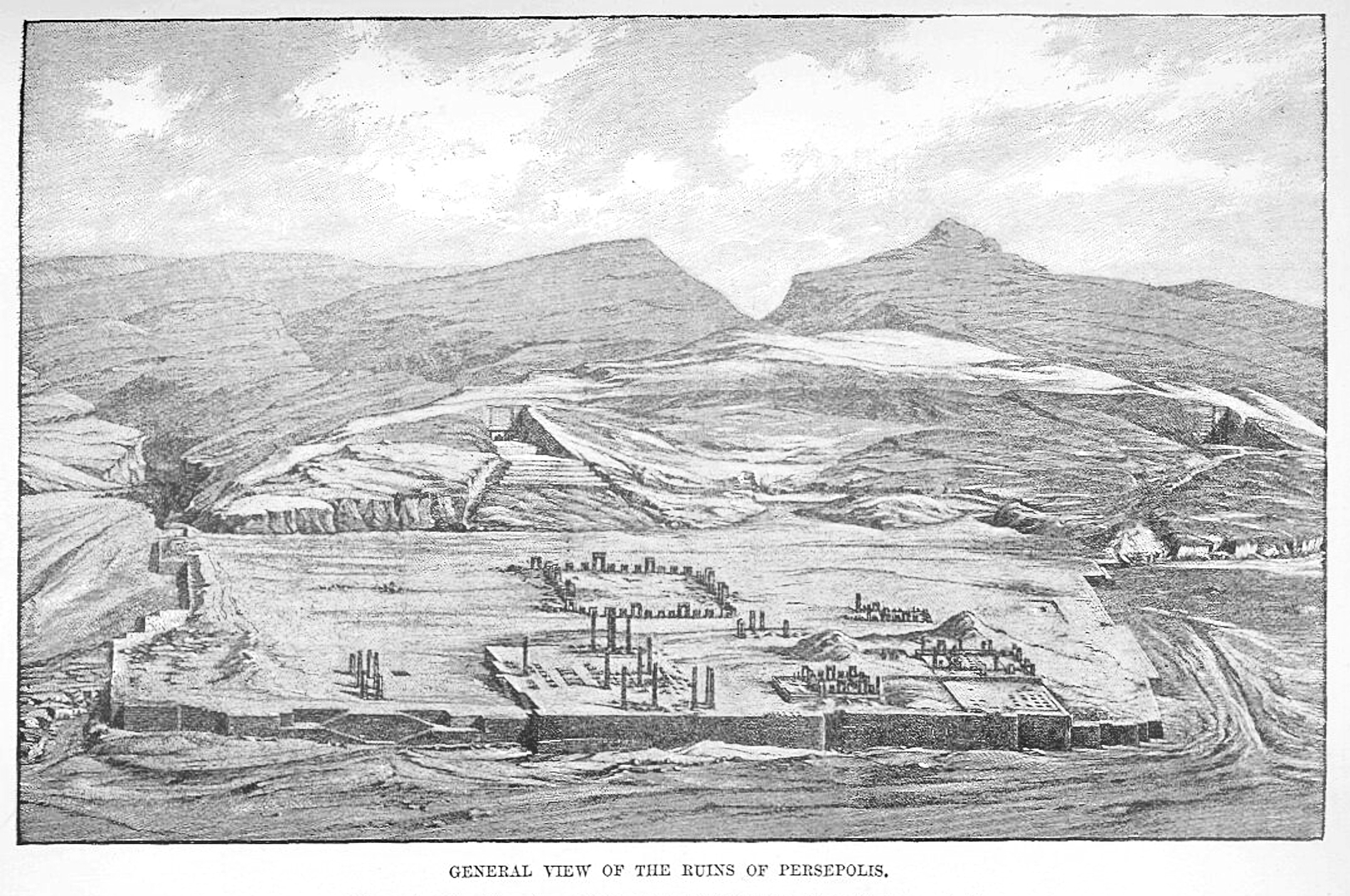
Persepolis
, native_name_lang = , alternate_name = , image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis. , map = , map_type = Iran#West Asia , map_alt = , map_caption = , map_size = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = yes , coordinates = , map_dot_label = , location = Marvdasht, Fars Province, Iran , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , and , material = Limestone, mud-brick, cedar wood , built = 6th century BC , abandoned = , epochs = Achaemenid Empire , cultures = Persian , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = *Battle of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. Croesus was renowned for his wealth; Herodotus and Pausanias noted that his gifts were preserved at Delphi. The fall of Croesus had a profound effect on the Greeks, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least," J. A. S. Evans has remarked, "Croesus had become a figure of myth, who stood outside the conventional restraints of chronology." Name The name of Croesus was not attested in contemporary inscriptions in the Lydian language. In 2019, D. Sasseville and K. Euler published a research of Lydian coins apparently minted during his rule, where the name of the ruler was rendered as ''Qλdãns''. The name comes from the Latin transliteration of the Greek , which was itself the ancient Hellenic adaptation of the Lydia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially, and is also known as " green gold".Emsley, John (2003Nature's building blocks: an A–Z guide to the elements Oxford University Press. . p. 168 Electrum was used as early as the third millennium BC in Old Kingdom of Egypt, sometimes as an exterior coating to the pyramidions atop ancient Egyptian pyramids and obelisks. It was also used in the making of ancient drinking vessels. The first known metal coins made were of electrum, dating back to the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 6th century BC. For several decades, the medals awarded with the Nobel Prize have been made of gold-plated green gold. Etymology The name "electrum" is the Latinized form of the Greek word ἤλεκτρον (''ḗlektron''), mentioned in the ''Ody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrum Trite, Alyattes, Lydia, 620-563 BC
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially, and is also known as " green gold".Emsley, John (2003Nature's building blocks: an A–Z guide to the elements Oxford University Press. . p. 168 Electrum was used as early as the third millennium BC in Old Kingdom of Egypt, sometimes as an exterior coating to the pyramidions atop ancient Egyptian pyramids and obelisks. It was also used in the making of ancient drinking vessels. The first known metal coins made were of electrum, dating back to the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 6th century BC. For several decades, the medals awarded with the Nobel Prize have been made of gold-plated green gold. Etymology The name "electrum" is the Latinized form of the Greek word ἤλεκτρον (''ḗlektron''), mentioned in the ''Odysse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Coinage
The history of ancient Greek coinage can be divided (along with most other Greek art forms) into four periods: the Archaic, the Classical, the Hellenistic and the Roman. The Archaic period extends from the introduction of coinage to the Greek world during the 7th century BC until the Persian Wars in about 480 BC. The Classical period then began, and lasted until the conquests of Alexander the Great in about 330 BC, which began the Hellenistic period, extending until the Roman absorption of the Greek world in the 1st century BC. The Greek cities continued to produce their own coins for several more centuries under Roman rule. The coins produced during this period are called Roman provincial coins or Greek Imperial Coins. Weight standards and denominations The three most important standards of the ancient Greek monetary system were the Attic standard, based on the Athenian drachma of of silver, the Corinthian standard based on the stater of of silver, that was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)
