|
Critical Plane Analysis
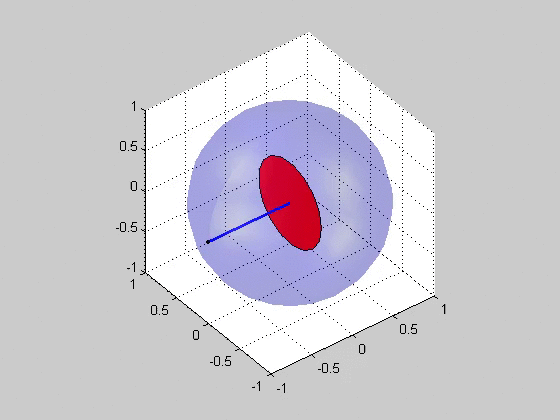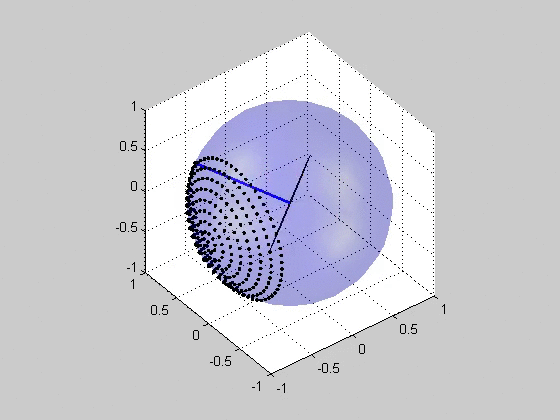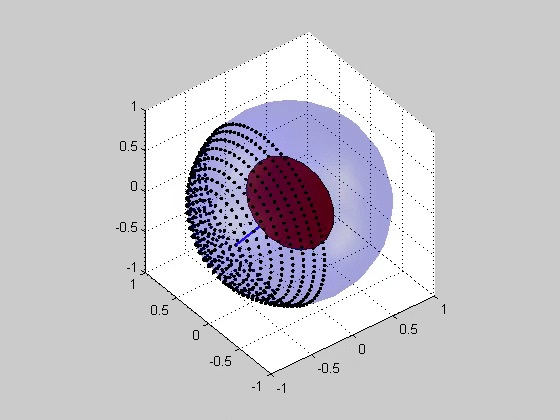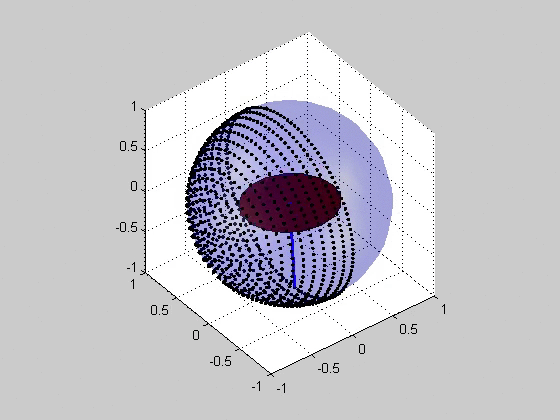
Critical plane analysis refers to the analysis of stresses or strains as they are experienced by a particular plane in a material, as well as the identification of which plane is likely to experience the most extreme damage. Critical plane analysis is widely used in engineering to account for the effects of cyclic, multiaxial load histories on the fatigue life of materials and structures. When a structure is under cyclic multiaxial loading, it is necessary to use multiaxial fatigue criteria that account for the multiaxial loading. If the cyclic multiaxial loading is nonproportional it is mandatory to use a proper multiaxial fatigue criteria. The multiaxial criteria based on the Critical Plane Method are the most effective criteria. For the plane stress case, the orientation of the plane may be specified by an angle in the plane, and the stresses and strains acting on this plane may be computed via Mohr's circle. For the general 3D case, the orientation may be specified via a uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (mechanics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity. It is a quantity that describes the magnitude of forces that cause deformation. Stress is defined as ''force per unit area''. When an object is pulled apart by a force it will cause elongation which is also known as deformation, like the stretching of an elastic band, it is called tensile stress. But, when the forces result in the compression of an object, it is called compressive stress. It results when forces like tension or compression act on a body. The greater this force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Therefore, stress is measured in newton per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |