|
County Of Drenthe
The County of Drenthe ( nl, Landschap Drenthe, german: Grafschaft Drente), was a province of the Holy Roman Empire from 1046, and of the Dutch Republic from 1581 until 1795. It corresponds to the area west of the lower Ems, today the eponymous province of Drenthe in the Netherlands. Drenthe is first recorded in 820 as a '' Gau'', the basic division of the Carolingian Empire east of the Rhine. In 1046, the Emperor Henry III granted it to the Bishopric of Utrecht. At the time Drenthe included the city of Groningen, which was governed by a burgrave (prefect) enfeoffed by the bishop. By the 14th century, the prefecture was hereditary and the Lordship of Groningen was ''de facto'' separate from the County of Drenthe. Between 1225 and 1240, the free peasants of Drenthe were in conflict with the bishops over his lordship and his tithes. This even resulted in a crusade launched against them. The first and most intense phase of the conflict is retold in an eyewitness account, '' Quaeda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drenthe Door Cornelis Pijnacker-gehele-kaart
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of November 2019, Drenthe had a population of 493,449 and a total area of . Drenthe has been populated for 15,000 years. The region has subsequently been part of the Episcopal principality of Utrecht, Habsburg Netherlands, Dutch Republic, Batavian Republic, Kingdom of Holland and Kingdom of the Netherlands. Drenthe has been an official province since 1796. The capital and seat of the provincial government is Assen. The King's Commissioner of Drenthe is Jetta Klijnsma. The Labour Party (PvdA) is the largest party in the States-Provincial, followed by the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) and the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA). Drenthe is a sparsely populated rural area, unlike many other parts of the Netherlands; except for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landrecht (medieval)
The ''Landrecht'' (, "customary law of the region",Arnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 31. . plural: ''Landrechte'') was the law applying within an individual state in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and Early Modern times. The state laws that emerged in the territories of the empire from the 12th century onwards had been developed from the older tribal laws of the Saxons, Swabians, Bavarians and Bohemians. Through privileges and laws passed by the territorial princes as well as the jurisprudence of the ''Landgerichte'' or state courts, these ancient rights were supplemented and developed. Later Roman law was also accepted and incorporated into the ''Landrechte''. The ''Landrecht'' was only applied to the burghers of a town in a secondary way, because they came primarily under municipal law and the autonomous jurisdiction of their communities. Ambit The ''Landrechte'' co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States General Of The Netherlands
The States General of the Netherlands ( nl, Staten-Generaal ) is the supreme bicameral legislature of the Netherlands consisting of the Senate () and the House of Representatives (). Both chambers meet at the Binnenhof in The Hague. The States General originated in the 15th century as an assembly of all the provincial states of the Burgundian Netherlands. In 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, the States General split as the northern provinces openly rebelled against Philip II, and the northern States General replaced Philip II as the supreme authority of the Dutch Republic in 1581. The States General were replaced by the National Assembly after the Batavian Revolution of 1795, only to be restored in 1814, when the country had regained its sovereignty. The States General was divided into a Senate and a House of Representatives in 1815, with the establishment of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. After the constitutional amendment of 1848, members of the House of Representatives w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Utrecht
The Union of Utrecht ( nl, Unie van Utrecht) was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain. History The Union of Utrecht is regarded as the foundation of the Republic of the Seven United Provinces, which was not recognized by the Spanish Empire until the Twelve Years' Truce in 1609. The treaty was signed on 23 January by Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht (but not all of Utrecht), and the province (but not the city) of Groningen. The treaty was a reaction of the Protestant provinces to the 1579 Union of Arras (Dutch: ''Unie van Atrecht''), in which two southern provinces and a city declared their support for Roman Catholic Spain. During the following months of 1579, other states signed the treaty as well, such as Ghent, cities from Friesland, as well as three of the quarters of Guelders (Nijmegen Quarter, Veluwe Quarter, Zutphen County). In the summer of 1579, Amersfoor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) (Historiography of the Eighty Years' War#Name and periodisation, c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, taxation, and the rights and privileges of the nobility and cities. After Eighty Years' War, 1566–1572, the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed Army of Flanders, his armies and Eighty Years' War, 1572–1576, regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, Spanish Fury, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic- and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
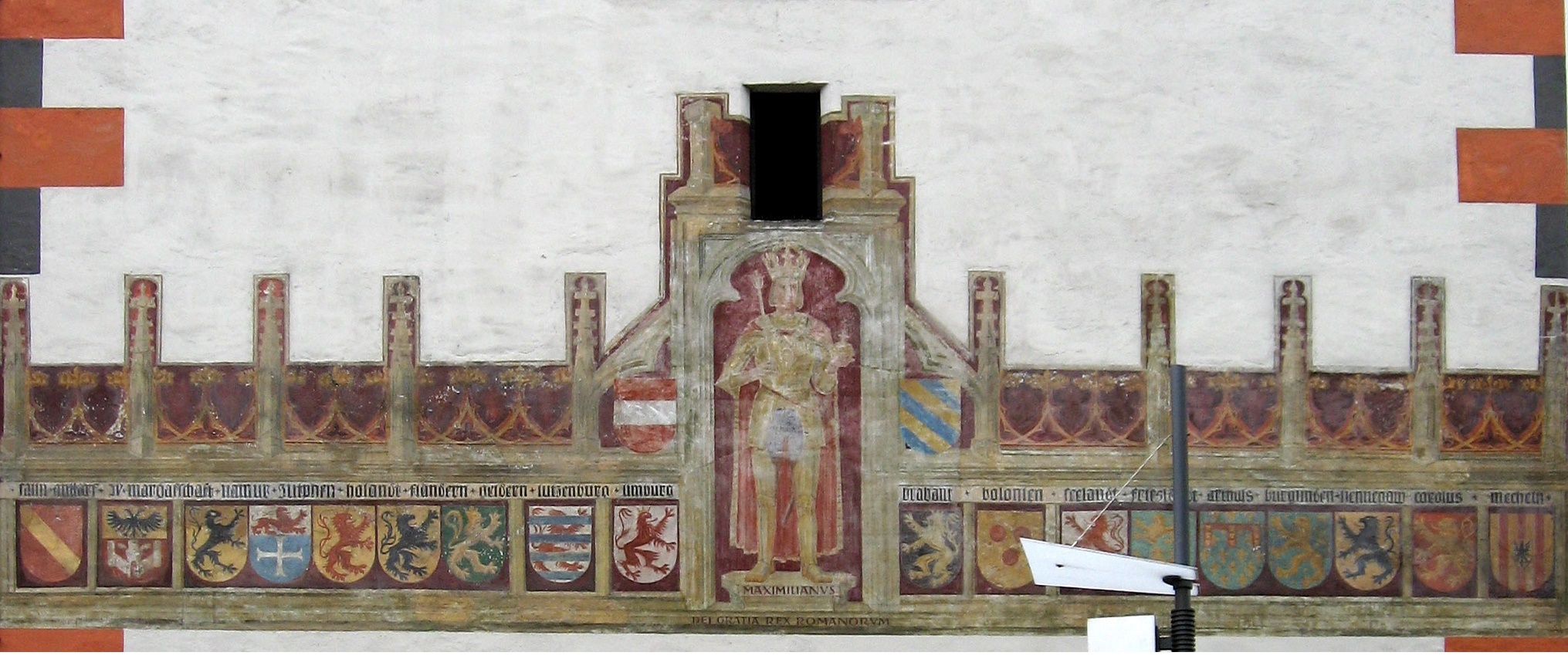
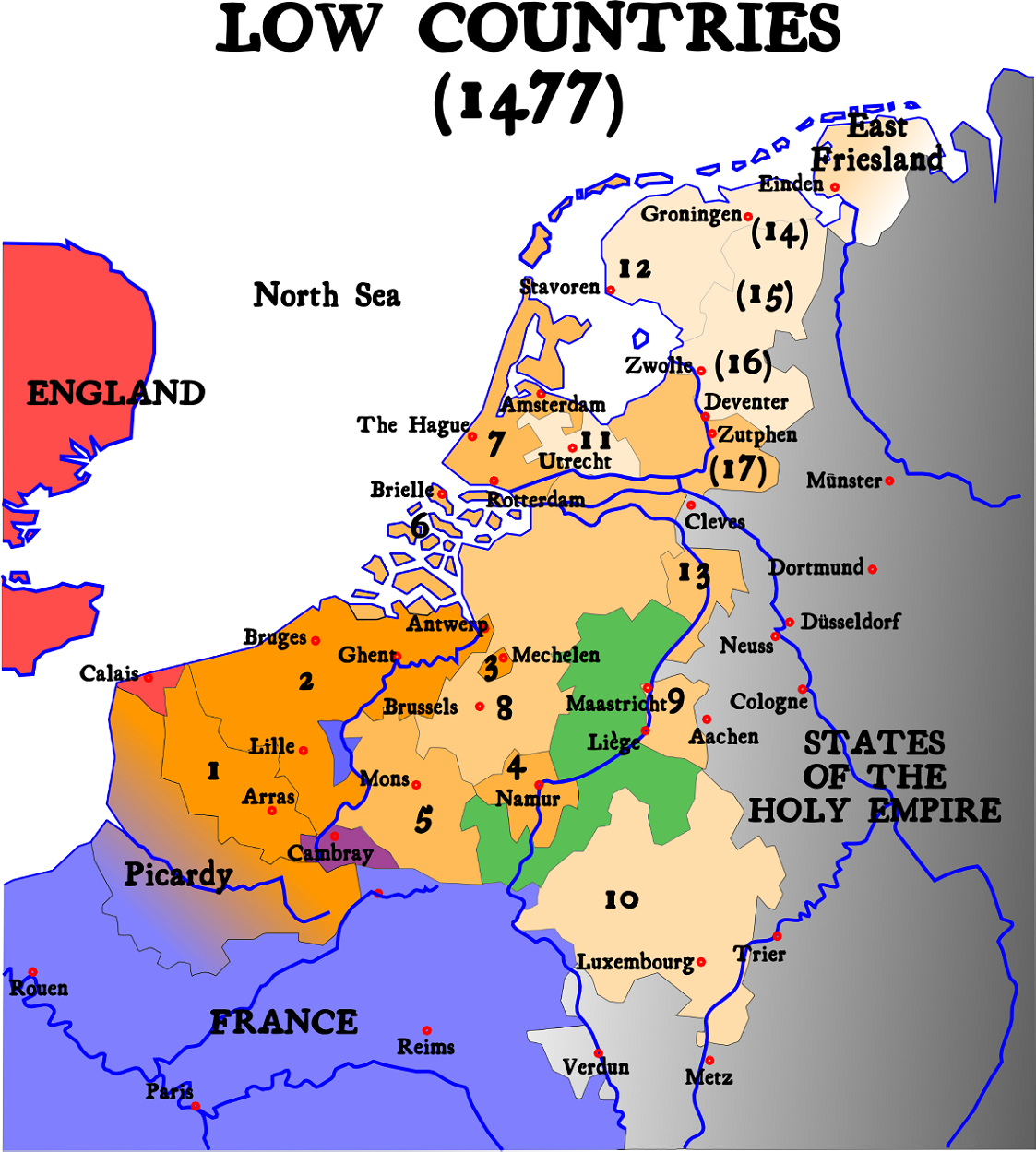
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: #th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundian Circle
The Burgundian Circle (german: Burgundischer Kreis, nl, Bourgondische Kreits, french: Cercle de Bourgogne) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire created in 1512 and significantly enlarged in 1548. In addition to the Free County of Burgundy (present-day administrative region of Franche-Comté), the Burgundian Circle roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., the areas now known as the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg and adjacent parts in the French administrative region of Nord-Pas-de-Calais. For most of its history, its lands were coterminous with the holdings of the Spanish Habsburgs in the Empire (Franche-Comté and the Habsburg Netherlands). The circle's territorial scope was reduced considerably in the 17th century with the secession of the Seven United Provinces in 1581 (recognized 1648 under the Treaty of Westphalia) and the annexation of the Free County of Burgundy by France in 1678. Consequently, in the 18th century the circle was known as Austrian Netherland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalian Circle
Westphalian may refer to: * The culture or people of the Westphalia region of Germany * Westphalian language, one of the major dialect groups of West Low German * Westphalian sovereignty, a concept in international relations * Westphalian (stage), in geology * Westphalian ham (Westfälischer Schinken) produced from acorn-fed pigs raised in Westphalia. The resulting meat is dry cured and then smoked over a mixture of beechwood and juniper branches. Animals * Westphalian horse, a warmblood horse bred in the Westphalia region of western Germany * Westphalian chicken, old hardy landrace of chicken * Westphalian Dachsbracke The Westphalian Dachsbracke is a small, short-legged scenthound, a breed of dog originating in Westphalia, a region of Germany. The Westphalian Dachsbracke was used in Sweden to develop the Drever. Appearance The Westphalian Dachsbracke (''We ..., a small, short legged scenthound {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundian Treaty Of 1548
The Burgundian treaty of 1548 (ratified on 26 June), also known as the Transaction of Augsburg, settled the status of the Habsburg Netherlands within the Holy Roman Empire. History Essentially the work of Viglius van Aytta, it represents a first step towards the emergence of the Netherlands as an independent territory. It was made possible politically by the French loss of Artois and Flanders. Administratively, a chancellery and tribunal was established at Mechelen which for the first time had as its jurisdiction "the Netherlands" exclusively. The treaty resulted in a significant shift of territories from the Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle to the Burgundian Circle. The newly formed administrative division of the empire now united all Burgundian territories, which were no longer subject to the ''Reichskammergericht''. To compensate for its territorial gain, the Burgundian Circle was now obliged to pay taxes equivalent to those of two prince-electorates, and in war taxes toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and Habsburg period (1384 – 1581/1795). The title was used for the official tasked with maintaining peace and provincial order in the early Dutch Republic and, at times, became ''de facto'' head of state of the Dutch Republic during the 16th to 18th centuries, which was an effectively hereditary role. For the last half century of its existence, it became an officially hereditary role under Prince William IV of Orange. His son, Prince William V, was the last ''stadtholder'' of the republic, whose own son, William I of the Netherlands, became the first sovereign king of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. The title ''stadtholder'' is roughly comparable to the historical titles of Lord Protector in England, Statthalter in the Holy Roman Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Grave
The Peace of Grave was signed on December 10, 1536, during the Guelders Wars between Charles II, Duke of Guelders and Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. In the treaty, Charles of Guelders handed over the City of Groningen, the Ommelanden and Drenthe to Emperor Charles. This was a confirmation of the actual situation in which Schenk van Toutenburg, Habsburg Stadtholder of Frisia, had conquered these land after defeating Charles of Guelders and his allies in the Battle of Heiligerlee (1536) The Battle of Heiligerlee (5 August 1536) was a battle during the Guelders Wars, in which the Danish allies of Charles of Guelders, under command of Meindert van Ham, were defeated by Habsburg forces under Georg Schenck van Toutenburg. In 1534, .... Sources * Israel, J.I.,''The Dutch Republic; Its rise, greatness, and fall 1477-1806'' (Oxford 1998), 63–64. 1536 History of Drenthe History of Groningen (city) History of Groningen (province) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon) from 1516 to 1556, and Lord of the Netherlands as titular Duke of Burgundy from 1506 to 1555. He was heir to and then head of the rising House of Habsburg during the first half of the 16th century, his dominions in Europe included the Holy Roman Empire, extending from Kingdom of Germany, Germany to Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), northern Italy with direct rule over the Austrian hereditary lands and the Burgundian Low Countries, and Habsburg Spain, Spain with its southern Italy, southern Italian possessions of Kingdom of Naples, Naples, Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily, and Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia. He oversaw both the continuation of the long-lasting Spanish colonization of the Americas and the short-live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)