|
Costa Rican Spanish
Costa Rican Spanish is the form of the Spanish language spoken in Costa Rica. It is one of the dialects of Central American Spanish. Phonetics The distinguishing characteristics of Costa Rican phonetics include the following: * Assibilation of the "double-R" phoneme in some speakers (spelled word-initially and intervocalically), especially in rural areas, resulting in a voiced alveolar sibilant ()—thus ("clothing"), ''carro'' ("car"). Assibilation also affects the sequence , giving it a sound that is similar to . * The double-R phoneme and the single-R phoneme after a t, can also be realized as voiced alveolar approximant � by the majority of speakers, with a sound similar to the of American English. Thus ''ropa'' ("clothing"), ''carro'' ("car") and ''cuatro'' ("four"). Except before a consonant (this does not apply to all speakers) in which case is pronounced as a voiced alveolar trill . Thus ''puerta'' ("door"), ''guardar'' ("to save"). ''Note: This does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of . An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a unitary presidential constitutional republic. It has a long-standing and stable democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agriculture, has diversified to include sectors such as finance, corporate services for foreign companies, phar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Spanish
Old Spanish, also known as Old Castilian ( es, castellano antiguo; osp, romance castellano ), or Medieval Spanish ( es, español medieval), was originally a dialect of Vulgar Latin spoken in the former provinces of the Roman Empire that provided the root for the early form of the Spanish language that was spoken on the Iberian Peninsula from the 10th century until roughly the beginning of the 15th century, before a ''consonantal readjustment'' gave rise to the evolution of modern Spanish. The poem ('The Poem of the Cid'), published around 1200, is the best known and most extensive work of literature in Old Spanish. Phonology The phonological system of Old Spanish was quite similar to that of other medieval Romance languages. Sibilants Among the consonants, there were seven sibilants, including three sets of voiceless/ voiced pairs: * Voiceless alveolar affricate : represented by before , , , and by before or *Voiced alveolar affricate : represented by * Voiceless ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
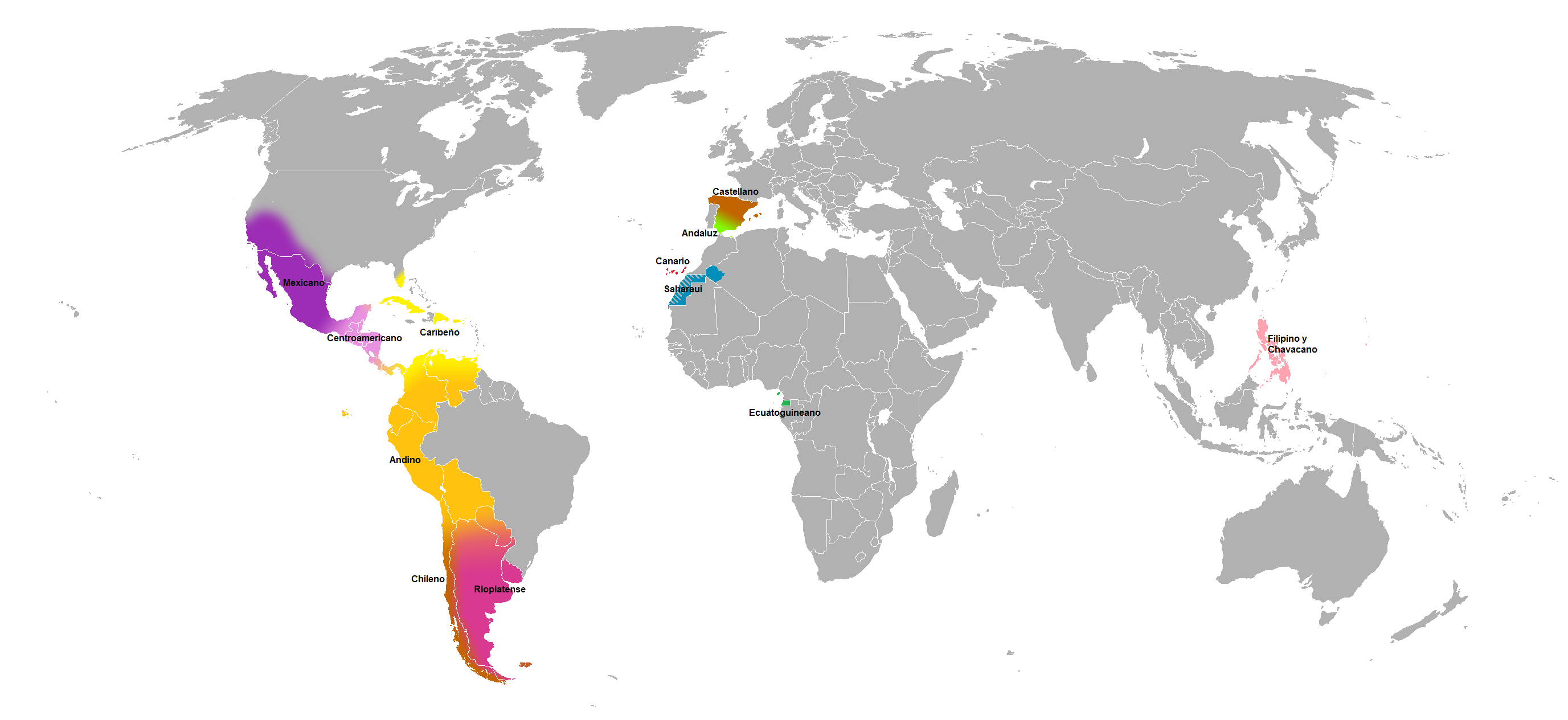
Tuteo
Some of the regional varieties of the Spanish language are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar. While all Spanish language, Spanish dialects adhere to approximately the same written standard, all spoken varieties differ from the written variety, to different degrees. There are differences between European Spanish (also called Peninsular Spanish) and the Spanish language in the Americas, Spanish of the Americas, as well as many different dialect areas both within Spain and within the Americas. Chilean Spanish, Chilean and Honduran Spanish, Honduran Spanish have been identified by various linguists as the most divergent varieties. Prominent differences of pronunciation among dialects of Spanish include: # the maintenance or lack of distinction between the phonemes and (''distinción'' vs. ''seseo'' and ''ceceo''); # the maintenance or loss of distinction between phonemes represented orthographically by ''ll'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish ( es, español mexicano) is the variety of dialects and sociolects of the Spanish language spoken in Mexican territory. Mexico has the largest number of Spanish speakers, with more than twice as many as in any other country in the world. Spanish is spoken by just over 99.2% of the population, being the mother tongue of 93.8% and the second language of 5.4%. Variation The territory of contemporary Mexico is not coextensive with what might be termed Mexican Spanish. The Spanish spoken in the southernmost state of Chiapas, bordering Guatemala, resembles the variety of Central American Spanish spoken in that country, where is used. Meanwhile, to the north, many Mexicans stayed in Texas after its independence from Mexico. After the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo many Mexicans remained in the territory ceded to the U.S., and their descendants have continued to speak Spanish within their communities in Arizona, California, Colorado, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah, and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voseo
In Spanish grammar, () is the use of as a second-person singular pronoun, along with its associated verbal forms, in certain regions where the language is spoken. In those regions it replaces , i.e. the use of the pronoun and its verbal forms. can also be found in the context of using verb conjugations for with as the subject pronoun ( verbal voseo), as in the case of Chilean Spanish, where this form coexists with the ordinary form of . In all regions with , the corresponding unstressed object pronoun is and the corresponding possessive is . is used extensively as the second-person singular in Rioplatense Spanish (Argentina and Uruguay), Eastern Bolivia, Paraguayan Spanish, and Central American Spanish (El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, southern parts of Chiapas and some parts of Oaxaca in Mexico). had been traditionally used even in formal writing in Argentina, El Salvador, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Paraguay, the Philippines and Uruguay. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quetzal
Quetzals () are strikingly colored birds in the trogon family. They are found in forests, especially in humid highlands, with the five species from the genus ''Pharomachrus'' being exclusively Neotropical, while a single species, the eared quetzal, ''Euptilotis neoxenus'', is found in Guatemala, sometimes in Mexico and very locally in the southernmost United States. In the highlands of the states of Sonora, Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Durango, Nayarit, Zacatecas, Jalisco, and Michoacán, the Eared Quetzal (Euptilotis Neoxenus) can be found from northwest to west-central Mexico. It is a Mexican indigenous species, but some reports show that it occasionally travels and nests in southeastern Arizona and New Mexico in the United States. June to October is the mating season for Eared Quetzals. Quetzals are fairly large (all over 32 cm or 13 inches long), slightly bigger than other trogon species.Restall, R. L., C. Rodner, & M. Lentino (2006). ''Birds of Northern South America.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Alveolar Affricate
A voiceless alveolar affricate is a type of affricate consonant pronounced with the tip or blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge (gum line) just behind the teeth. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are several types with significant perceptual differences: *The voiceless alveolar sibilant affricate is the most common type, similar to the ''ts'' in English ''cats''. *The voiceless alveolar non-sibilant affricate or , using the alveolar diacritic from the Extended IPA, is somewhat similar to the ''th'' in some pronunciations of English ''eighth''. It is found as a regional realization of the sequence in some Sicilian dialects of Standard Italian. *The voiceless alveolar lateral affricate is found in certain languages, such as Cherokee, Mexican Spanish, and Nahuatl. *The ''voiceless alveolar retracted sibilant affricate'' , also called apico-alveolar or grave, has a weak hushing sound reminiscent of affricates. One language in which it is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velar Nasal
The voiced velar nasal, also known as agma, from the Greek word for 'fragment', is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is the sound of ''ng'' in English ''sing'' as well as ''n'' before velar consonants as in ''English'' and ''ink''. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is N. The IPA symbol is similar to , the symbol for the retroflex nasal, which has a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of the right stem, and to , the symbol for the palatal nasal, which has a leftward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of the left stem. Both the IPA symbol and the sound are commonly called ' eng' or 'engma'. As a phoneme, the velar nasal does not occur in many of the indigenous languages of the Americas or in many European, Middle Eastern or Caucasian languages, but it is extremely common in Australian Aboriginal languages and is also common in many languages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Tap
The voiced alveolar tap or flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents a dental, alveolar, or postalveolar tap or flap is . The terms ''tap'' and ''flap'' are often used interchangeably. Peter Ladefoged proposed the distinction that a tap strikes its point of contact directly, as a very brief stop, and a flap strikes the point of contact tangentially: "Flaps are most typically made by retracting the tongue tip behind the alveolar ridge and moving it forward so that it strikes the ridge in passing." That distinction between the alveolar tap and flap can be written in the IPA with tap and flap , the 'retroflex' symbol being used for the one that starts with the tongue tip curled back behind the alveolar ridge. The distinction is noticeable in the speech of some American English speakers in distinguishing the words "potty" (tap ) and "party" (retroflex ). For linguists who make the distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Alveolar Trill
The voiced alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R. Quite often, is used in phonemic transcriptions (especially those found in dictionaries) of languages like English and German that have rhotic consonants that are not an alveolar trill. That is partly for ease of typesetting and partly because is the letter used in the orthographies of such languages. In many Indo-European languages, a trill may often be reduced to a single vibration in unstressed positions. In Italian, a simple trill typically displays only one or two vibrations, while a geminate trill will have three or more. Languages where trills always have multiple vibrations include Albanian, Spanish, Cypriot Greek, and a number of Armenian and Portuguese dialects. Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Alveolar Approximant
The voiced alveolar approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the alveolar and postalveolar approximants is , a lowercase letter ''r'' rotated 180 degrees. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r\. The most common sound represented by the letter ''r'' in English is the voiced postalveolar approximant, pronounced a little more back and transcribed more precisely in IPA as , but is often used for convenience in its place. For further ease of typesetting, English phonemic transcriptions might use the symbol even though this symbol represents the alveolar trill in phonetic transcription. The bunched or molar r sounds remarkably similar to the postalveolar approximant and can be described as a ''voiced labial pre-velar approximant with tongue-tip retraction''. It can be transcribed in IPA as or . Features Features of the voiced alveolar approximant: Occurrence Alveolar Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Alveolar Fricative
The voiced alveolar fricatives are consonantal sounds. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents these sounds depends on whether a sibilant or non-sibilant fricative is being described. * The symbol for the alveolar sibilant is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is z. The IPA letter is not normally used for dental or postalveolar sibilants in narrow transcription unless modified by a diacritic ( and respectively). * The IPA symbol for the alveolar non-sibilant fricative is derived by means of diacritics; it can be or . Voiced alveolar sibilant The voiced alveolar sibilant is common across European languages, but is relatively uncommon cross-linguistically compared to the voiceless variant. Only about 28% of the world's languages contain a voiced dental or alveolar sibilant. Moreover, 85% of the languages with some form of are languages of Europe, Africa, or Western Asia. Features *There are at least three specific variants of : ** Dentali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |