|
Cosmographia (Sebastian Münster)
The ''Cosmographia'' (" Cosmography") from 1544 by Sebastian Münster (1488–1552) is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian and Czech. Only extracts have been translated into English. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munster's death. The ''Cosmographia'' was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within ''Cosmographia'' is the map "Tabula novarum insularum", which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete. His earlier geographic works were ''Germania descriptio'' (1530) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmographia Titelblatt Der Erstausgabe
''Cosmographia'' (Latin, from Greek κόσμος, "world, universe", and γραφή, "representation") may refer to: Written works *''Cosmographia'', an alternative name for Ptolemy's ''Geographia'' *''Cosmographia'', a late antique or early medieval geographical work by Julius Honorius *''Cosmographia'', an early medieval geographical work feigned to record the travels of one Aethicus Ister *''Ravenna Cosmography'', a seventh- or eighth-century work by an anonymous of Ravenna * ''Cosmographia'' (Bernardus Silvestris), a twelfth-century allegory by Bernardus Silvestris *''Cosmographia'', a fifteenth-century work by the German geographer Nicolaus Germanus *''Cosmographia'', an alternative title of Petrus Apianus' sixteenth-century ''Cosmographicus liber'' * ''Cosmographia'' (Sebastian Münster), a sixteenth-century work by the German geographer Sebastian Münster *''Cosmographia'', a sixteenth-century work by the Portuguese geographer Bartolomeu Velho *''Cosmographia'', a sixteenth-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Moselle wine region. Founded by the Celts in the late 4th century BC as ''Treuorum'' and conquered 300 years later by the Romans, who renamed it ''Augusta Treverorum'' ("The City of Augustus among the Treveri"), Trier is considered Germany's oldest city. It is also the oldest seat of a bishop north of the Alps. Trier was one of the four capitals of the Roman Empire during the Tetrarchy period in the late 3rd and early 4th centuries. In the Middle Ages, the archbishop-elector of Trier was an important prince of the Church who controlled land from the French border to the Rhine. The archbishop-elector of Trier also had great si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, and southeast of the Arabian Sea; it is separated from the Indian subcontinent by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. Sri Lanka shares a maritime border with India and Maldives. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is its legislative capital, and Colombo is its largest city and financial centre. Sri Lanka has a population of around 22 million (2020) and is a multinational state, home to diverse cultures, languages, and ethnicities. The Sinhalese are the majority of the nation's population. The Tamils, who are a large minority group, have also played an influential role in the island's history. Other long established groups include the Moors, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
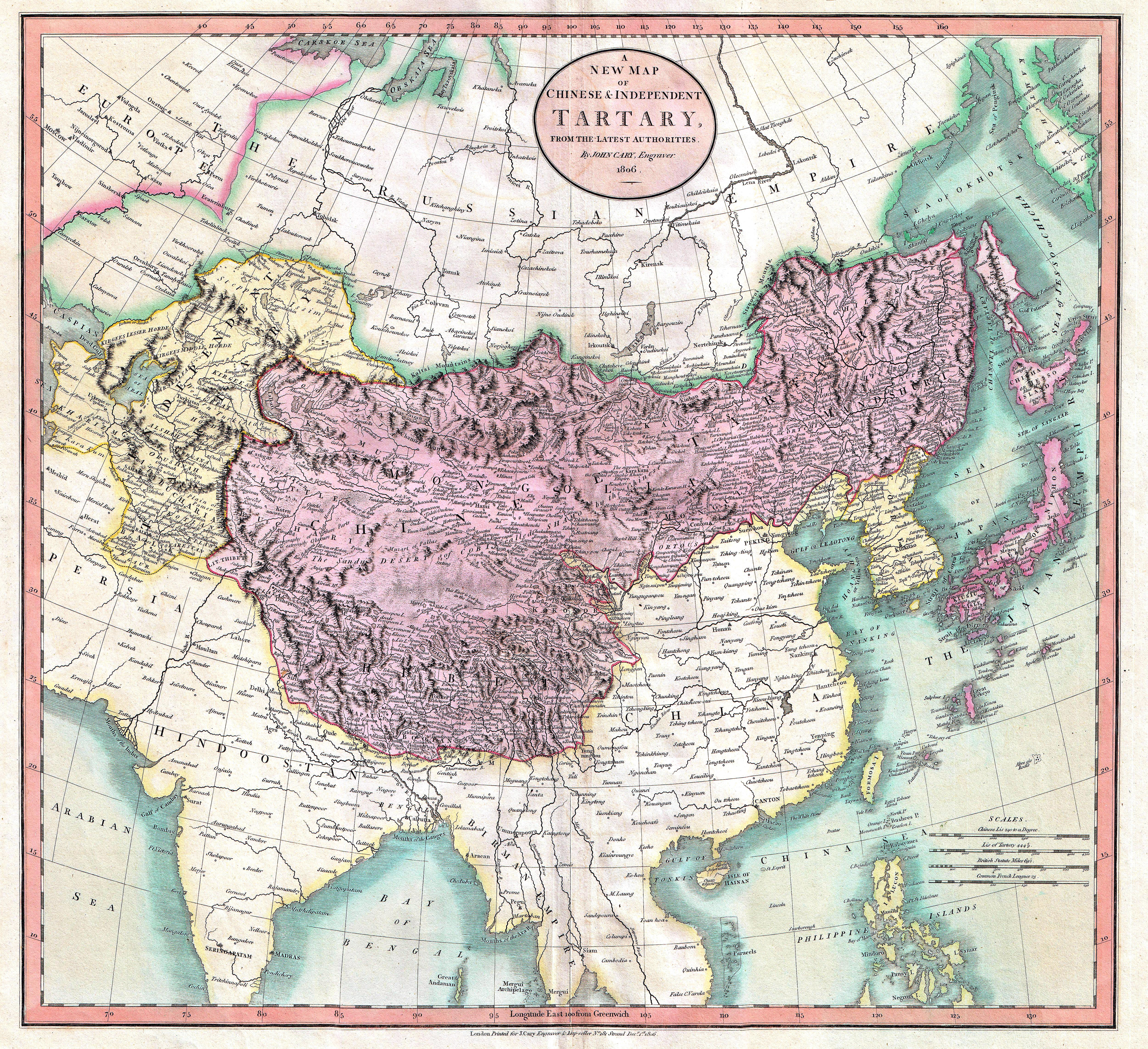
Tartary
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounded by the Caspian Sea, the Ural Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the northern borders of China, India and Persia, at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers. The active use of the toponym (place name) can be traced from the 13th to the 19th centuries. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main nomadic population of which in the past was en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe. History Background Origins of the Scythians The Scythians originated in Central Asia possibly around the 9th century BC, and they arrived in the Caucasian Steppe in the 8th and 7th centuries BC as part of a significant movement of the nomadic peoples of the Eurasian Steppe. This movement started when another nomadic Iranian tribe closely related to the Scythians, either the Massagetae or the Issedones, migrated westwards, forcing the Early Scythians to the west across the Araxes river, following which the Scythians moved into the Caspian Steppe, where they conquered the territory of the Cimmerians, who were also a nomadic Iranian people closely related to the Scythians, and assimilated most of them while displacing the rest, before settling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia is traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was forced to accept the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire; this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livland
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Лифляндия, Liflyandiya) is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia. By the end of the 13th century, the name was extended to most of present-day Estonia and Latvia, which had been conquered during the Livonian Crusade (1193–1290) by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword. Medieval Livonia, or Terra Mariana, reached its greatest extent after Saint George's Night Uprising that in 1346 forced Denmark to sell the Duchy of Estonia (northern Estonia conquered by Denmark in the 13th century) to the State of the Teutonic Order. Livonia, as understood after the retreat of Denmark in 1346, bordered on the Gulf of Finland in the north, Lake Peipu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a " Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to the German states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg, while the eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian, Pomeranian and Kuyavian-Pomeranian voivodeships of Poland. Its historical border in the west is the Mecklenburg-Western Pomeranian border '' Urstromtal'' which now constitutes the border between the Mecklenburgian and Pomeranian part of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, while it is bounded by the Vistula River in the east. The easternmost part of Pomerania is alternatively known as Pomerelia, consisting of four sub-regions: Kashubia inhabited by ethnic Kashubians, Kociewie, Tuchola Forest and Chełmno Land. Pomerania has a relatively low population density, with its largest cities being Gdańsk and Szczecin. Ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language (minority in Upper Silesia). Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrava a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia. The medieval and early modern Margraviate of Moravia was a crown land of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown from 1348 to 1918, an imperial state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1004 to 1806, a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1804 to 1867, and a part of Austria-Hungary from 1867 to 1918. Moravia was one of the five lands of Czechoslovakia founded in 1918. In 1928 it was merged with Czech Silesia, and then dissolved in 1949 during the abolition of the land system following the communist coup d'état. Its area of 22,623.41 km2 is home to more than 3 million people. The people are historically named Moravians, a subgroup of Czechs, the other group being called Bohemians. Moravia also had been home of a large German-speaking popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia proper as a means of distinction. Bohemia was a duchy of Great Moravia, later an independent principality, a kingdom in the Holy Roman Empire, and subsequently a part of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empire. After World War I and the establishment of an independent Czechoslovak state, the whole of Bohemia became a part of Czechoslovakia, defying claims of the German-speaking inhabitants that regions with German-speaking majority should be included in the Republic of German-Austria. Between 1938 and 1945, these border regions were joined to Nazi Germany as the Sudetenland. The remainder of Czech territory became the Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)