|
Congenital Cataract
Congenital cataracts refers to a lens opacity which is present at birth. Congenital cataracts cover a broad spectrum of severity: whereas some lens opacities do not progress and are visually insignificant, others can produce profound visual impairment. Congenital cataracts may be unilateral or bilateral. They can be classified by morphology, presumed or defined genetic cause, presence of specific metabolic disorders, or associated ocular anomalies or systemic findings. Signs and symptoms Congenital cataracts occur in a variety of morphologic configurations, including lamellar, polar, sutural, coronary, cerulean, nuclear, capsular, complete, membranous. Cause In general, approximately one-third of congenital cataracts are a component of a more extensive syndrome or disease (e.g., cataract resulting from congenital rubella syndrome), one-third occur as an isolated inherited trait, and one-third result from undetermined causes. Metabolic diseases tend to be more commonly associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Rubella Syndrome
Congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) can occur in a developing fetus of a pregnant woman who has contracted rubella, usually in the first trimester. If infection occurs 0–28 days before conception, the infant has a 43% risk of being affected. If the infection occurs 0–12 weeks after conception, the risk increases to 81%. If the infection occurs 13–26 weeks after conception, the risk is 54% of the infant being affected by the disease. Infants are not generally affected if rubella is contracted during the third trimester, or 26–40 weeks after conception. Problems rarely occur when rubella is contracted by the mother after 20 weeks of gestation and continues to disseminate the virus after birth. It was discovered in 1941 by Australian Norman McAlister Gregg. __TOC__ Signs and symptoms The classic triad for congenital rubella syndrome is: * Sensorineural deafness (58% of patients) * Eye abnormalities—especially retinopathy, cataract, glaucoma, and microphthalmia (43% of pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany (involuntary muscle contraction), and several other symptoms. It is a very rare disease. The condition can be inherited, but it is also encountered after thyroid or parathyroid gland surgery, and it can be caused by immune system-related damage as well as a number of rarer causes. The diagnosis is made with blood tests, and other investigations such as genetic testing depending on the results. The primary treatment of hypoparathyroidism is calcium and vitamin D supplementation. Calcium replacement or vitamin D can ameliorate the symptoms but can increase the risk of kidney stones and chronic kidney disease. Additionally, injectable medications such as recombinant human parathyroid hormone or teriparatide may be given by injection to replace the missi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenticonus
Lenticonus (/len·ti·co·nus/ (len″tĭ-ko´nus)) ens + L. conus, coneis a rare congenital anomaly of the eye characterized by a conical protrusion on the crystalline lens capsule and the underlying cortex. It can reach a diameter of 2 to 7 mm. The conus may occur anteriorly or posteriorly. If the bulging is spherical, instead of conical, the condition is referred to as ''lentiglobus''. It produces a decrease in visual acuity and irregular refraction that cannot be corrected by either spectacle or contact lenses. Biomicroscopically ''lenticonus'' is characterized by a transparent, localized, sharply demarcated conical projection of the lens capsule and cortex, usually axial in localization. In an early stage, retro-illumination shows an oil dropletconfiguration. Using a narrow slit, the image of a conus is observed. In a more advanced stage associated subcapsular and cortical opacities appear. Retinoscopically the oil droplet produces a pathognomonic scissors movement of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (PHPV), also known as persistent fetal vasculature (PFV), is a rare congenital developmental anomaly of the eye that results following failure of the embryological, primary vitreous and hyaloid vasculature to regress. It can be present in three forms: purely anterior ( persistent tunica vasculosa lentis and persistent posterior fetal fibrovascular sheath of the lens), purely posterior (falciform retinal septum and ablatio falcicormis congenita) and a combination of both. Most examples of PHPV are unilateral and non-hereditary. When bilateral, PHPV may follow an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Symptoms The primary vitreous used in formation of the eye during fetal development remains in the eye upon birth and is hazy and scarred. The symptoms are leukocoria, strabismus, nystagmus and blurred vision, blindness. Causes #Trisomy 13 A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Segment Dysgenesis
Anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis, or simply anterior segment dysgenesis (ASD), is a failure of the normal development of the tissues of the anterior segment of the eye. It leads to anomalies in the structure of the mature anterior segment, associated with an increased risk of glaucoma and corneal opacity. Peters' (frequently misspelled as Peter's) anomaly is a specific type of mesenchymal anterior segment dysgenesis, in which there is central corneal leukoma, adhesions of the iris and cornea and abnormalities of the posterior corneal stroma, Descemet's membrane, corneal endothelium, lens and anterior chamber. Pathophysiology Several gene mutations have been identified underlying these anomalies, with the majority of ASD genes encoding transcriptional regulators. In this review, the role of the ASD genes, ''PITX2'' and '' FOXC1'', is considered in relation to the embryology of the anterior segment, the biochemical function of these proteins, and their role in development an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniridia
Aniridia is the absence of the iris, a muscular structure that opens and closes the pupil to allow light into the eye. It is also responsible for eye color. Without it, the central eye appears all black. It can be congenital, in which both eyes are usually involved, or caused by a penetrant injury. Isolated aniridia is a congenital disorder which is not limited to a defect in iris development, but is a panocular condition with macular and optic nerve hypoplasia, cataract, and corneal changes. Vision may be severely compromised and the disorder is frequently associated with a number of ocular complications: nystagmus, amblyopia, buphthalmos, and cataract. Aniridia in some individuals occurs as part of a syndrome, such as WAGR syndrome ( kidney nephroblastoma (Wilms tumour), genitourinary anomalies and intellectual disability), or Gillespie syndrome (cerebellar ataxia). PAX6 The AN2 region of the short arm of chromosome 11 (11p13) includes the PAX6 gene (named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
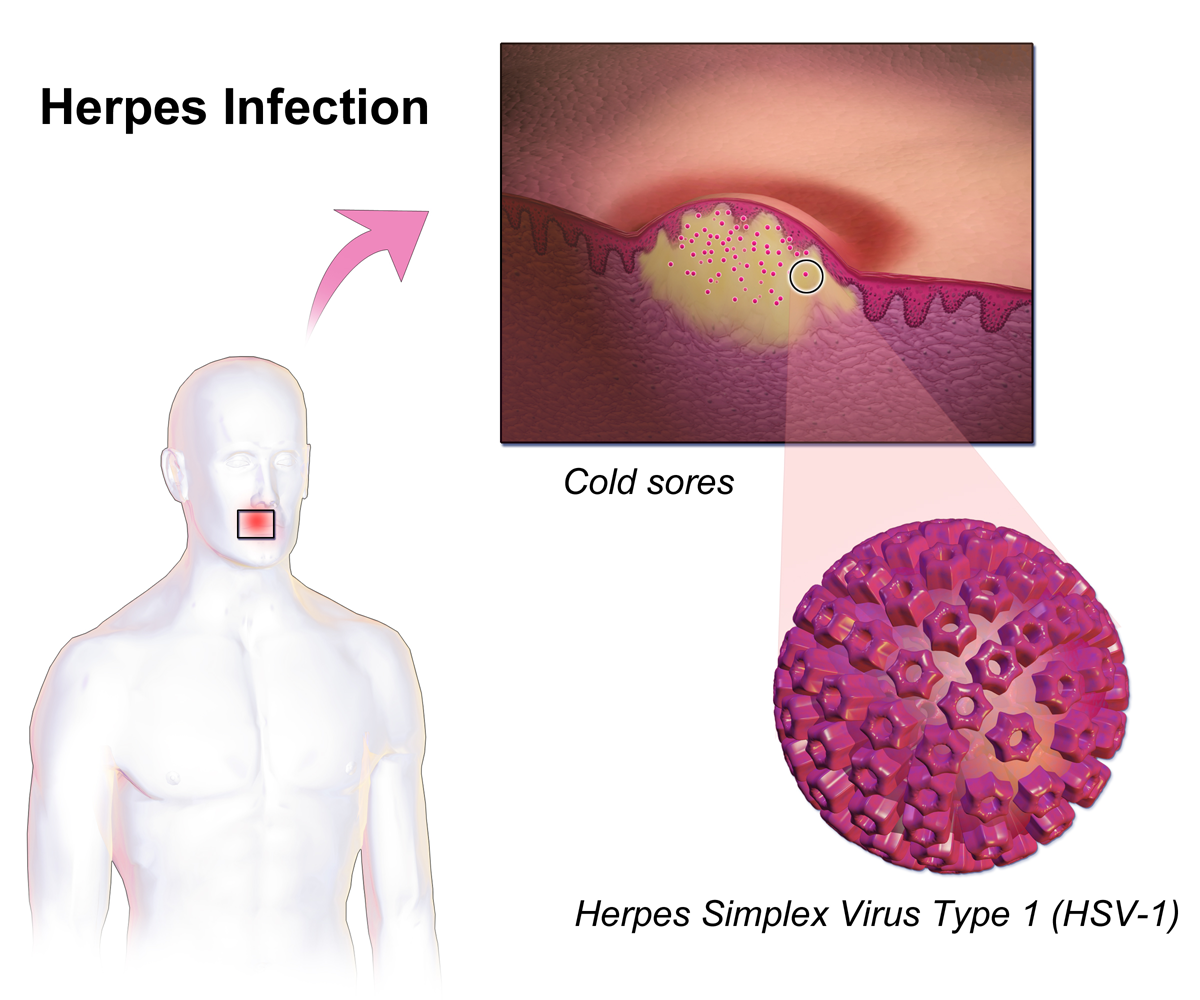
Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Herpetic whitlow typically involves the fingers or thumb. Herpes simplex keratitis involves the eye. Herpesviral encephalitis inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvovirus B19
Primate erythroparvovirus 1, generally referred to as B19 virus (B19V), parvovirus B19 or sometimes erythrovirus B19, is the first (and until 2005 the only) known human virus in the family '' Parvoviridae'', genus ''Erythroparvovirus''; it measures only 23–26 nm in diameter. The name is derived from Latin, parvum meaning small, reflecting the fact that B19 ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. B19 virus is most known for causing disease in the pediatric population; however, it can also affect adults. It is the classic cause of the childhood rash called fifth disease or erythema infectiosum, or "slapped cheek syndrome". The virus was discovered by chance in 1975 by Australian virologist Yvonne Cossart. It gained the B19 name because it was discovered in well B19 of a large series of microtiter plates. Virology Erythroviruses belong to the '' Parvoviridae'' family of small DNA viruses. Human parvovirus B19 is a non-enveloped, icosahedral virus that contains a single-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as " the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the ''Picornaviridae'' family of nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus ''Enterovirus'', which also includes poliovirus and echovirus. Enteroviruses are among the most common and important human pathogens, and ordinarily its members are transmitted by the fecal–oral route. Coxsackieviruses share many characteristics with poliovirus. With control of poliovirus infections in much of the world, more attention has been focused on understanding the nonpolio enteroviruses such as coxsackievirus. Coxsackieviruses are among the leading causes of aseptic meningitis (the other usual suspects being echovirus and mumps virus). The entry of coxsackievirus into cells, especially endothelial cells, is mediated by coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor. Groups Coxsackieviruses are divided into group A and group B viruses based on early observations of their pathogenicity in n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |