|
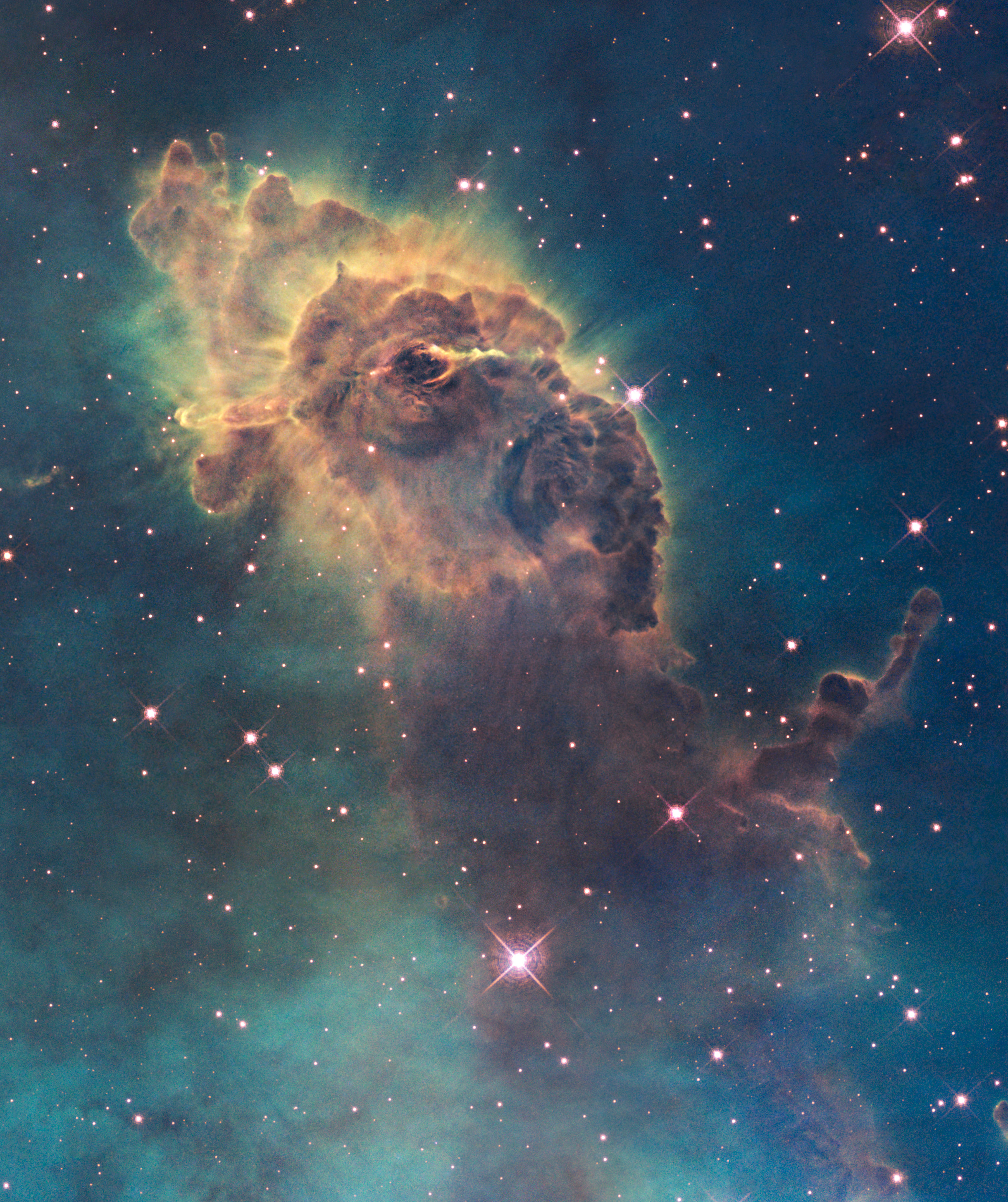
Cone Nebula (NGC 2264) Star-Forming Pillar Of Gas And Dust
The Cone Nebula is an H II region in the constellation of Monoceros. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 26, 1785, at which time he designated it H V.27. The nebula is located about 830 parsecs or 2,700 light-years away from Earth. The Cone Nebula forms part of the nebulosity surrounding the Christmas Tree Cluster. The designation of NGC 2264 in the New General Catalogue refers to both objects and not the nebula alone. The diffuse Cone Nebula, so named because of its apparent shape, lies in the southern part of NGC 2264, the northern part being the magnitude-3.9 Christmas Tree Cluster. It is in the northern part of Monoceros, just north of the midpoint of a line from Procyon to Betelgeuse. The cone's shape comes from a dark absorption nebula consisting of cold molecular hydrogen and dust in front of a faint emission nebula containing hydrogen ionized by S Monocerotis, the brightest star of NGC 2264. The faint nebula is approximately seven light-years long (wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 2264
NGC 2264 is the designation number of the New General Catalogue that identifies two astronomical objects as a single object: the Cone Nebula, and the Christmas Tree Cluster. Two other objects are within this designation but not officially included, the Snowflake Cluster, and the Fox Fur Nebula. All of the objects are located in the Monoceros constellation and are located about 720 parsecs or 2,300 light-years from Earth. Due to its relative proximity and large size, it is extremely well studied. NGC 2264 is sometimes referred to as the Christmas Tree Cluster and the Cone Nebula. However, the designation of NGC 2264 in the New General Catalogue refers to both objects and not the cluster alone. Structure NGC 2264 is the location where the Cone Nebula, the Stellar Snowflake Cluster and the Christmas Tree Cluster have formed in this emission nebula. For reference, the Stellar Snowflake Cluster is located 2,700 light years away in the constellation Monoceros. The Snowfla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffuse Nebulae
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the " Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter, and eventually will become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Nebulae
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection nebulae. The extinction of the light is caused by interstellar dust grains located in the coldest, densest parts of molecular clouds. Clusters and large complexes of dark nebulae are associated with Giant Molecular Clouds. Isolated small dark nebulae are called Bok globules. Like other interstellar dust or material, things it obscures are only visible using radio waves in radio astronomy or infrared in infrared astronomy. Dark clouds appear so because of sub-micrometre-sized dust particles, coated with frozen carbon monoxide and nitrogen, which effectively block the passage of light at visible wavelengths. Also present are molecular hydrogen, atomic helium, C18O (CO with oxygen as the 18O isotope), CS, NH3 (ammonia), H2CO (formaldehyde), c-C3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceptions Of Religious Imagery In Natural Phenomena
People have been found to perceive images with spiritual or religious themes or import, sometimes called iconoplasms or simulacra, in the shapes of natural phenomena. The images perceived, whether iconic or aniconic, may be the faces of religious notables or the manifestation of spiritual symbols in the natural, organic media or phenomena of the natural world. The occurrence or event of perception may be transient or fleeting or may be more enduring and monumental. The phenomenon appears to approach a cultural universal and may often accompany nature worship, animism, and fetishism, along with more formal or organized belief systems. Within Christian traditions, many instances reported involve images of Jesus or other Christian figures seen in food; in the Muslim world, structures in food and other natural objects may be perceived as religious text in Arabic script, particularly the word Allah or verses from the Qur'an. Many religious believers view them as real manifestations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Monocerotis
S Monocerotis, also known as 15 Monocerotis, is a massive multiple and variable star system located in the constellation Monoceros. It is the brightest star in the Christmas Tree open cluster in the area catalogued as NGC 2264. S Monocerotis is found within an open cluster and the Washington Double Star Catalog lists many companion stars. The closest and brightest is S Mon B, magnitude 7.8 and 3 arcseconds away. It is classified as B2 main sequence star with a mass of . Designated component C is an 11th-magnitude B8V star. The cluster contains another dozen or so 9th and 10th magnitude stars and many fainter stars. S Monocerotis A is a spectroscopic binary system with an eccentric orbit of about 112 years. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as the MK standard for O7 by which other stars are classified. It is also an irregular variable star with a range of less than a tenth of a magnitude. The orbital parameters can be used to derive the masses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Nebula
An emission nebula is a nebula formed of ionized gases that emit light of various wavelengths. The most common source of ionization is high-energy ultraviolet photons emitted from a nearby hot star. Among the several different types of emission nebulae are H II regions, in which star formation is taking place and young, massive stars are the source of the ionizing photons; and planetary nebulae, in which a dying star has thrown off its outer layers, with the exposed hot core then ionizing them. General information Usually, a young star will ionize part of the same cloud from which it was born, although only massive, hot stars can release sufficient energy to ionize a significant part of a cloud. In many emission nebulae, an entire cluster of young stars is contributing energy. Stars that are cooler than around 25,000K don't give off enough ultraviolet radiation with wavelengths shorter than 91.2nm (the wavelength needed in order to ionize Hydrogen atoms). This results in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection nebulae. The extinction of the light is caused by interstellar dust grains located in the coldest, densest parts of molecular clouds. Clusters and large complexes of dark nebulae are associated with Giant Molecular Clouds. Isolated small dark nebulae are called Bok globules. Like other interstellar dust or material, things it obscures are only visible using radio waves in radio astronomy or infrared in infrared astronomy. Dark clouds appear so because of sub-micrometre-sized dust particles, coated with frozen carbon monoxide and nitrogen, which effectively block the passage of light at visible wavelengths. Also present are molecular hydrogen, atomic helium, C18O (CO with oxygen as the 18O isotope), CS, NH3 (ammonia), H2CO (formaldehyde), c-C3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse is a red supergiant of spectral type M1-2 and one of the largest stars visible to the naked eye. It is usually the tenth-brightest star in the night sky and, after Rigel, the second-brightest in the constellation of Orion. It is a distinctly reddish, semiregular variable star whose apparent magnitude, varying between +0.0 and +1.6, has the widest range displayed by any first-magnitude star. At near-infrared wavelengths, Betelgeuse is the brightest star in the night sky. Its Bayer designation is α Orionis, Latinised to Alpha Orionis and abbreviated Alpha Ori or α Ori. If it were at the center of our Solar System, its surface would lie beyond the asteroid belt and it would engulf the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Nevertheless, there are several even larger stars in the Milky Way, including supergiants like Mu Cephei and the peculiar hypergiant, VY Canis Majoris. Calculations of Betelgeuse's mass range from slightly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procyon
Procyon () is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Minoris, which is Latinized to Alpha Canis Minoris, and abbreviated α CMi or Alpha CMi, respectively. As determined by the European Space Agency '' Hipparcos'' astrometry satellite, this system lies at a distance of just , and is therefore one of Earth's nearest stellar neighbors. A binary star system, Procyon consists of a white-hued main-sequence star of spectral type F5 IV–V, designated component A, in orbit with a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DQZ, named Procyon B. The pair orbit each other with a period of 40.84 years and an eccentricity of 0.4. Observation Procyon is usually the eighth-brightest star in the night sky, culminating at midnight on 14 January. It forms one of the three vertices of the Winter Triangle asterism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's '' General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Star-Forming_Pillar_of_Gas_and_Dust.jpg)


.png)

