|
Cockatoo Island Dockyard
The Cockatoo Island Dockyard was a major dockyard in Sydney, Australia, based on Cockatoo Island. The dockyard was established in 1857 to maintain Royal Navy warships. It later built and repaired military and battle ships, and played a key role in sustaining the Royal Australian Navy. The dockyard was closed in 1991, and its remnants are heritage listed as the Cockatoo Island Industrial Conservation Area. Colonial ownership It was established by the colonial Government of New South Wales, commencing operations in December 1857 with the opening of Fitzroy Dock. Planning had begun as early as May 1846, when Governor George Gipps had recommended the construction of a dry dock at Cockatoo Island to the British government to service Royal Navy vessels. Construction had begun in 1851, with Captain Gother Mann as engineer-in-chief, and taken six years. It was known as the Government Dockyard – Biloela while in colonial control. Shipbuilding facilities, such as slipways and workshops, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMAS Adelaide Launching 1918 IWM 305488
His Majesty's Australian Ship (HMAS) (or Her Majesty's Australian Ship when the monarch is female) is a ship prefix used for commissioned units of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). This prefix is derived from Her Majesty's Ship, HMS (Her/His Majesty's Ship), the prefix used by the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom, and can be equally applied to warships and shore bases (as Australia follows the British tradition of referring to naval establishments as stone frigates). On 10 July 1911, George V of the United Kingdom, King George V granted the title of Royal Australian Navy to the naval forces of Australia. At the same time, the prefix and acronym were approved for use in identifying units commissioned into the RAN. The prefix had been used prior to formal approval, with the torpedo-boat destroyer commissioned with the HMAS prefix on 1 March 1911. The prefix now refers to the Monarchy in Australia, King or Queen of Australia, who is also the British monarch. The first word of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Norton - Norton-96311 - Fitting Out H
Frank or Franks may refer to: People * Frank (given name) * Frank (surname) * Franks (surname) * Franks, a medieval Germanic people * Frank, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly during the Crusades - see Farang Currency * Liechtenstein franc or frank, the currency of Liechtenstein since 1920 * Swiss franc or frank, the currency of Switzerland since 1850 * Westphalian frank, currency of the Kingdom of Westphalia between 1808 and 1813 * The currencies of the German-speaking cantons of Switzerland (1803–1814): ** Appenzell frank ** Argovia frank ** Basel frank ** Berne frank ** Fribourg frank ** Glarus frank ** Graubünden frank ** Luzern frank ** Schaffhausen frank ** Schwyz frank ** Solothurn frank ** St. Gallen frank ** Thurgau frank ** Unterwalden frank ** Uri frank ** Zürich frank Places * Frank, Alberta, Canada, an urban community, formerly a village * Franks, Illinois, United States, an unincorporated community * Franks, Missouri, Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaplane Tender
A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are regarded by some as the first aircraft carriers and appeared just before the First World War. Terminology In maritime parlance a tender is a vessel that is used to support the operation of other vessels. In British usage, the term tender was used for small craft, with the term depot ship being used for large seagoing vessels. Flying boats and float planes even when based at home in ports and harbour had a need for small support vessels to operate.p British tenders were small craft of launch to pinnace size. These were used to ferry crews, stores and supplies between shore and the aircraft, to maintain the buoys used to mark out "taxiways" and "runways" and to keep these clear of debris to prevent foreign object damage, and in the case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMAS Albatross (1928)
HMAS ''Albatross'' (later HMS ''Albatross'') was a seaplane tender of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), which was later transferred to the Royal Navy and used as a repair ship. ''Albatross'' was built by Cockatoo Island Dockyard during the mid-1920s and entered service at the start of 1929. The ship experienced problems with the aircraft assigned to her during her career: the amphibious aircraft she had been designed for were retired just before the ship entered service, the replacement aircraft could not be catapult-launched from the ship, and a new plane designed specifically to work with the ship began operations after ''Albatross'' was demoted from seagoing status in 1933. After five years in reserve, ''Albatross'' was transferred to the Royal Navy to offset the Australian purchase of the light cruiser . Although the British had little use for a seaplane carrier, the ship found a niche after two aircraft carriers were sunk by the Germans early in World War II. ''Albatross' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town-class Cruiser (1910)
The Town class was a group of twenty-one light cruisers built for the Royal Navy (RN) and Royal Australian Navy (RAN) of the first half of the 20th Century. These vessels were long-range cruisers, suitable for patrolling the vast expanse covered by the British Empire. These ships, initially rated as second class cruisers, were built to a series of designs, known as the ''Bristol'' (five ships), ''Weymouth'' (four ships), ''Chatham'' (three RN ships, plus three RAN ships), ''Birmingham'' (three ships, plus one similar RAN ship) and ''Birkenhead'' (two ships) classes – all having the names of British towns except for the RAN ships, which were named after Australian cities. Design ''Bristol'' class The ''Bristol'' class were all ordered under the 1908–09 Programme and commissioned in late 1910.Lyon ''Warship'' Vol. 1 No. 3, p. 50. They were second class cruisers suitable for a variety of roles including both trade protection and fleet duties.Preston 1985, p. 51. They were l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
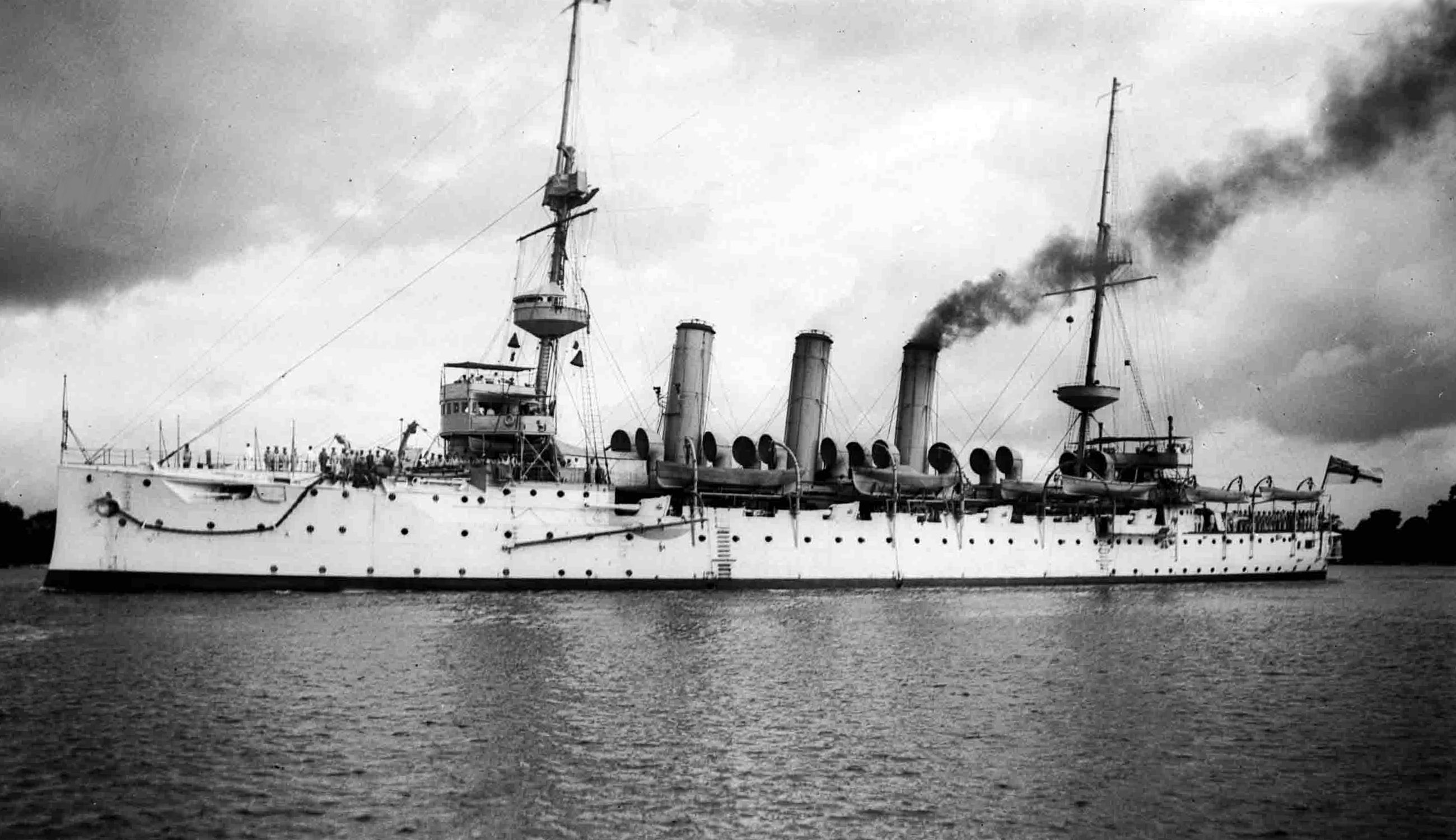
HMAS Adelaide (1918)
HMAS ''Adelaide'' was a light cruiser of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), named after Adelaide, the capital city of South Australia. Laid down in 1915, wartime shortages and design modifications meant the ship was not completed until 1922, earning her the nickname "HMAS ''Longdelayed''". ''Adelaide'' served with the Royal Navy's Special Service Squadron during 1924 and 1925, and was involved in the 1927 Malaita massacre. She was decommissioned in 1928, but was modernised and returned to service just before World War II began. During the war, ''Adelaide'' was involved in successful efforts to secure the colony of New Caledonia for Free France, was present during the Japanese midget submarine attack on Sydney Harbour, and intercepted the German blockade runner ''Ramses''. The cruiser was decommissioned in 1946, and broken up for scrap in 1949. Design and construction The design of ''Adelaide'' was modified from the ''Chatham'' subclass of the light cruisers, with similarities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian National Industries
Australian National Industries was an Australian heavy engineering company with diverse range of holdings. History In 1911 John McGrath began to sell motor vehicles. It operated the first public garage in New South Wales. The company held motor vehicle franchises for many makes of cars. In 1929, it diversified into importing steel and engineering equipment. In the mid-1930s production of drop forgings commenced with motor dealerships opening in other states.History Australian National Industries In the early 1940s, the largest forging plant in Australia was opened in , producing forgings for the aircraft and munitions industry. Activities expanded and diversified to include general eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comsteel
Comsteel is an Australian manufacturer of steel products based in the Newcastle suburb of Waratah. It is a subsidiary of American Industrial Partners. History Comsteel was founded as Commonwealth Steel Products in 1918 by Clyde Engineering, Goninan & Co, Pioneer Spring Co and Ritchie Brothers to manufacture wheels, tyres, axles and steel castings for railway use.Commonwealth Steel Products Ltd Newcastle Industrial Heritage Association A plant was established in the suburb of |
Vickers Limited
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entire large ships, cars, tanks and torpedoes followed. Airships and aircraft were added, and Vickers jet airliners were to remain in production until 1965. Financial problems following the death of the Vickers brothers were resolved in 1927 by separating Metropolitan Carriage Wagon and Finance Company and Metropolitan-Vickers, then merging the remaining bulk of the original business with Armstrong Whitworth to form Vickers-Armstrongs. The Vickers name resurfaced as Vickers plc between 1977 and 1999. History Foundry Vickers was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by the miller Edward Vickers and his father-in-law George Naylor in 1828. Naylor was a partner in the foundry Naylor & Sanderson, and Vickers' brother William owned a steel roll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
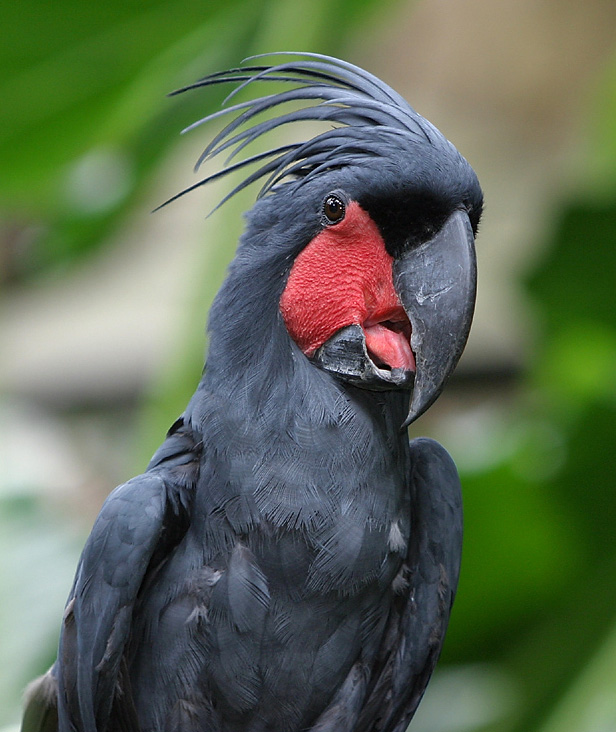
Cockatoo Island Aerial View 1951
A cockatoo is any of the 21 parrot species belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea (true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up the order Psittaciformes. The family has a mainly Australasian distribution, ranging from the Philippines and the eastern Indonesian islands of Wallacea to New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Australia. Cockatoos are recognisable by the prominent crests and curved bills. Their plumage is generally less colourful than that of other parrots, being mainly white, grey or black and often with coloured features in the crest, cheeks or tail. On average they are larger than other parrots; however, the cockatiel, the smallest cockatoo species, is a small bird. The phylogenetic position of the cockatiel remains unresolved, other than that it is one of the earliest offshoots of the cockatoo lineage. The remaining species are in two main clades. The five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China. Membership in the Allies varied during the course of the war. When the conflict broke out on 1 September 1939, the Allied coalition consisted of the United Kingdom, France, and Poland, as well as their respective dependencies, such as British India. They were soon joined by the independent dominions of the British Commonwealth: Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Consequently, the initial alliance resembled that of the First World War. As Axis forces began invading northern Europe and the Balkans, the Allies added the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Greece, and Yugoslavia. The Soviet Union, which initially had a nonaggression pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Singapore
The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore,; ta, சிங்கப்பூரின் வீழ்ச்சி; ja, シンガポールの戦い took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire of Japan captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in its history. Prior to the battle, Japanese General Tomoyuki Yamashita had advanced with about 30,000 men down the Malayan Peninsula in the Malayan campaign. The British erroneously considered the jungle terrain impassable, leading to a swift Japanese advance as Allied defences were quickly outflanked. The British Lieutenant-General, Arthur Percival, commanded 85,000 Allied troops at Singapore, although many unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |