|
Cleaning (forestry)
"Cleaning" and "weeding" are two similar terms referring to the practice of selecting particularly desirable trees in a young stand and removing or killing trees that threaten their survival or development. *Used correctly, the term "cleaning" refers to the removal or killing of over topping competitors that are significantly taller than the desired trees, and is usually done in the sapling stage. *While the term "weeding" refers to the removal of mainly herbaceous plants and shrubs that are of the same height, but still competing for the resources that could be used by the selected trees. It is usually done in the seedling stage. Or cleaning is carried out in a crop which has not crossed the sapling stage and it is defined as the cutting made in order to face the best individual form undesirable one of the same age which interfere or likely with the growth of the desired individuals Colloquially, these treatments are often referred to as crop tree release when they are practiced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weeding After 2
Weed control is a type of pest control, which attempts to stop or reduce growth of weeds, especially noxious weeds, with the aim of reducing their competition with desired flora and fauna including domesticated plants and livestock, and in natural settings preventing non native species competing with native species. Weed control is important in agriculture. Methods include hand cultivation with hoe (tool), hoes, powered cultivation with cultivators, smothering with mulch, lethal wilting with high heat, burning, and Benthiocarb, chemical control with herbicides (weed killers). Need for control Weeds compete with productive crops or pasture, they can be poisonous, distasteful, produce burrs, thorns or otherwise interfere with the use and management of desirable plants by contaminating harvests or interfering with livestock. Weeds compete with crops for space, nutrients, water and light. Smaller, slower growing seedlings are more susceptible than those that are larger and more v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast (botany)
Mast is the fruit of forest trees and shrubs, such as acorns and other nuts. The term derives from the Old English ''mæst'', meaning the nuts of forest trees that have accumulated on the ground, especially those used historically for fattening domestic pigs, and as food resources for wildlife. In the aseasonal tropics of Southeast Asia, entire forests, including hundreds of species of trees and shrubs, are known to mast at irregular periods of 2–12 years. More generally, mast is considered the edible vegetative or reproductive parts produced by woody species of plants, i.e. trees and shrubs, that wildlife and some domestic animals consume as a food source. Mast is generated in large quantities during long-interval but regularly recurring phenological events known as mast seeding or masting. Such events are population-level phenomena hypothesized to be driven by a wide variety of factors, depending on the plant species involved, including availability of nutrients, economies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
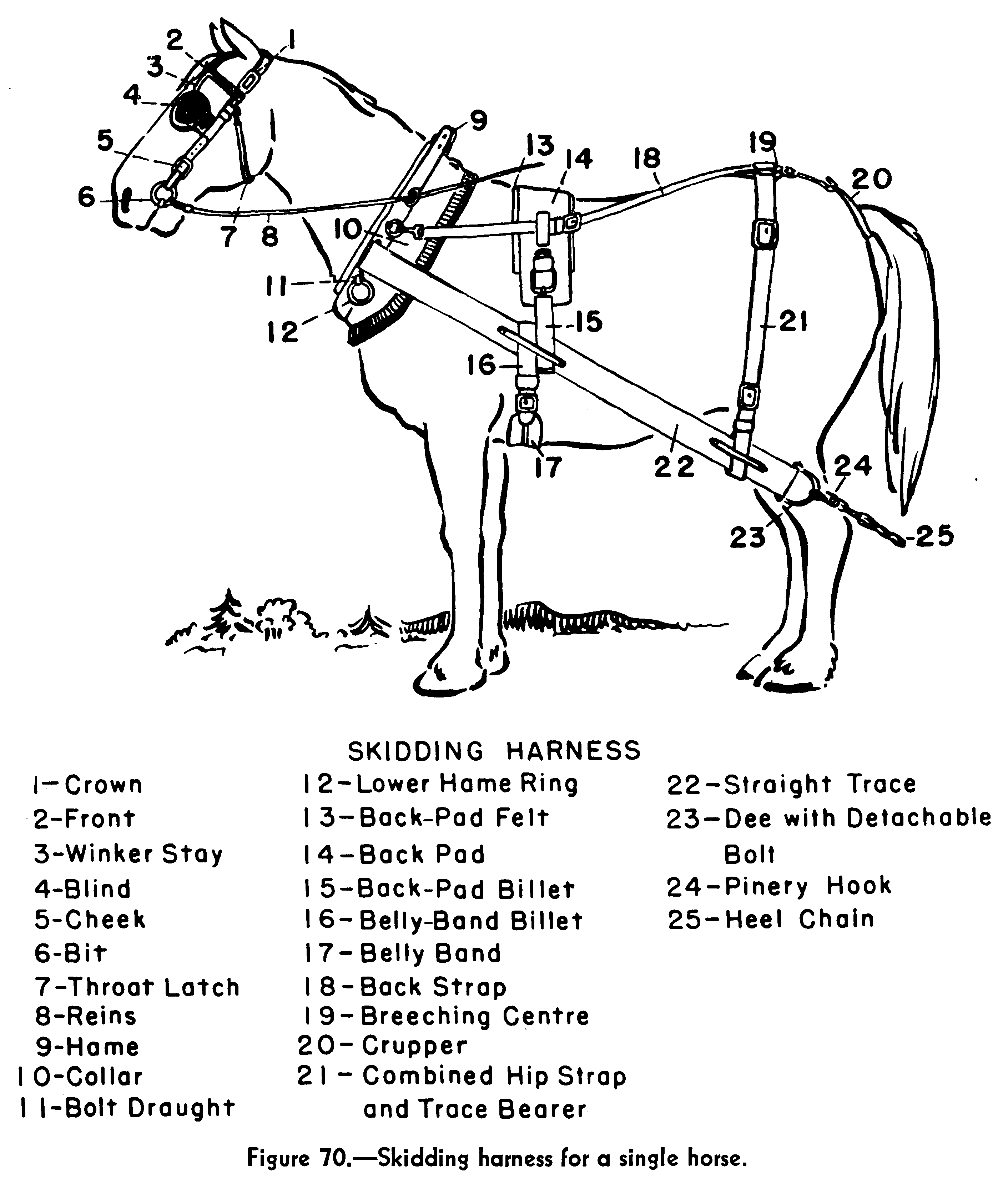
Skidder
A skidder is any type of heavy vehicle used in a logging operation for pulling cut trees out of a forest in a process called "skidding", in which the logs are transported from the cutting site to a landing. There they are loaded onto trucks (or in times past, railroad cars or flumes), and sent to the mill. One exception is that in the early days of logging, when distances from the timberline to the mill were shorter, the landing stage was omitted altogether, and the "skidder" would have been used as the main road vehicle, in place of the trucks, railroad, or flume. Modern forms of skidders can pull trees with a cable/winch (''cable skidder''), just like the old steam donkeys, or with a hydraulic grapple either on boom (''grapple skidder'') or on the back of the frame ''(clambunk skidder)''. History Early skidders were pulled by a team of oxen, horses or mules. The driver would straddle the cart over felled logs, where dangling tongs would be positioned to raise the end of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felling
Felling is the process of cutting down trees,"Feller" def. 2. and "Felling", def. 1. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press 2009 an element of the task of logging. The person cutting the trees is a ''feller''. A feller buncher is a machine capable of felling a single large tree or grouping and felling several small ones simultaneously. Methods Hand felling In hand felling, an axe, saw, or chainsaw is used to fell a tree, followed up by limbing and bucking in traditional applications. In the modern commercial logging industry, felling is typically followed by limbing and skidding. Feller buncher A feller-buncher is a motorized vehicle with an attachment which rapidly cuts and gathers several trees in the process of felling them. In cut-to-length logging a harvester performs the tasks of a feller-buncher, additionally doing the delimbing and bucking. When harvesting wood from a felled tree, the recommended methods s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firewood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets or chips. Firewood can be seasoned and heat treated (dry) or unseasoned (fresh/wet). It is generally classified as hardwood or softwood. Firewood is a renewable resource. However, demand for this fuel can outpace its ability to regenerate on a local or regional level. Good forestry practices and improvements in devices that use firewood can improve local wood supplies. Moving firewood long distances can potentially transport diseases and invasive species. History For most of human history firewood was the main fuel, until the use of coal spread during the Industrial Revolution. As such, access to firewood was a valued resource, wood botes or the right to gather firewood being a significant aspect of many medieval leases. As late as 19th C America, Thorea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodlot
A woodlot is a parcel of a woodland or forest capable of small-scale production of forest products (such as wood fuel, sap for maple syrup, sawlogs, and pulpwood) as well as recreational uses like bird watching, bushwalking, and wildflower appreciation. The term ''woodlot'' is chiefly North American; in Britain, a woodlot would be called a wood, woodland, or copse. Many woodlots occur as part of a farm or as buffers and undevelopable land between these and other property types such as housing subdivisions, industrial forests, or public properties (highways, parks, watersheds, etc.). Very small woodlots can occur where a subdivision has not met its development potential, or where terrain does not easily permit other uses. Very large woodlots (hundreds of acres) might emerge where profitable wood species have been depleted by commercial logging practices or compromised by diseases, leaving little choice but to divide and liquidate the real estate for other purposes. One disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Management
Forest management is a branch of forestry concerned with overall administrative, legal, economic, and social aspects, as well as scientific and technical aspects, such as silviculture, protection, and forest regulation. This includes management for timber, aesthetics, recreation, urban values, water, wildlife, inland and nearshore fisheries, wood products, plant genetic resources, and other forest resource values. Management objectives can be for conservation, utilisation, or a mixture of the two. Techniques include timber extraction, planting and replanting of different species, building and maintenance of roads and pathways through forests, and preventing fire. Definition The forest is a natural system that can supply different products and services. Forests supply water, mitigate climate change, provide habitats for wildlife including many pollinators which are essential for sustainable food production, provide timber and fuelwood, serve as a source of non-wood forest produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clearcutting
Clearcutting, clearfelling or clearcut logging is a forestry/logging practice in which most or all trees in an area are uniformly cut down. Along with shelterwood and seed tree harvests, it is used by foresters to create certain types of forest ecosystems and to promote select species that require an abundance of sunlight or grow in large, even-age stands. Logging companies and forest-worker unions in some countries support the practice for scientific, safety and economic reasons, while detractors consider it a form of deforestation that destroys natural habitats and contributes to climate change. Clearcutting is the most common and economically profitable method of logging. However, it also may create detrimental side effects, such as the loss of topsoil, the costs of which are intensely debated by economic, environmental and other interests. In addition to the purpose of harvesting wood, clearcutting is used to create land for farming. Ultimately, the effects of clearcut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The crops that are grown include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar cane, opium, sisal, oil seeds, oil palms, fruits, rubber trees and forest trees. Protectionist policies and natural comparative advantage have sometimes contributed to determining where plantations are located. In modern use the term is usually taken to refer only to large-scale estates, but in earlier periods, before about 1800, it was the usual term for a farm of any size in the southern parts of British North America, with, as Noah Webster noted, "farm" becoming the usual term from about Maryland northwards. It was used in most British colonies, but very rarely in the United Kingdom itself in this sense. There, as also in America, it was used mainly for tree plantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balsam Fir
''Abies balsamea'' or balsam fir is a North American fir, native to most of eastern and central Canada (Newfoundland west to central Alberta) and the northeastern United States (Minnesota east to Maine, and south in the Appalachian Mountains to West Virginia). Description Balsam fir is a small to medium-size evergreen tree typically tall, occasionally reaching a height of . The narrow conic crown consists of dense, dark-green leaves. The bark on young trees is smooth, grey, and with resin blisters (which tend to spray when ruptured), becoming rough and fissured or scaly on old trees. The leaves are flat and needle-like, long, dark green above often with a small patch of stomata near the tip, and two white stomatal bands below, and a slightly notched tip. They are arranged spirally on the shoot, but with the leaf bases twisted so that the leaves appear to be in two more-or-less horizontal rows on either side of the shoot. The needles become shorter and thicker the higher they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)