|
Chronicon Burgense
The ''Chronicon Burgense'' is a collection of Latin annals that, together with the '' Annales Compostellani'' and the ''Chronicon Ambrosianum'', may form a group of related histories sometimes called the ''Efemérides riojanas'' because they may have been compiled in La Rioja. The ''Chronicon Burgense'' is named after the Cathedral of Burgos, where it was discovered on one folio of a surviving thirteenth-century obituary/calendar. It deals primarily with matters in the Kingdom of Castile and may have been written at Burgos, the Castilian capital. It also touches on the Kingdom of Navarre (in which La Rioja lay) and covers the period from the Nativity of Jesus to the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. It uses the dating system of the Spanish era and not the ''Anno domini''. It is a unique source for several details relating to early Castilian history. The following is an excerpt: Editions *In Francisco de Berganza, ed. ''Antigüedades de España'', II (Madrid: 1721), 560–62 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned as the main medium of scholarly exchange, as the liturgical language of the Church, and as the working language of science, literature, law, and administration. Medieval Latin represented a continuation of Classical Latin and Late Latin, with enhancements for new concepts as well as for the increasing integration of Christianity. Despite some meaningful differences from Classical Latin, Medieval writers did not regard it as a fundamentally different language. There is no real consensus on the exact boundary where Late Latin ends and Medieval Latin begins. Some scholarly surveys begin with the rise of early Ecclesiastical Latin in the middle of the 4th century, others around 500, and still others with the replacement of written Late Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "''anno Domini nostri Jesu Christi''", which translates to 'in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ'. The form "BC" is specific to English and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin form is but is rarely seen. This calendar era is based on the traditionally reckoned year of the conception or birth of Jesus, ''AD'' counting years from the start of this epoch and ''BC'' denoting years before the start of the era. There is no year zero in this scheme; thus ''the year AD 1 immediately follows the year 1 BC''. This dating system was devised in 525 by Dionysius Exiguus, but was not widely used until the 9th century. Traditionally, English follows Latin usage by placing the "AD" abbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Berganza
Fray Francisco de Berganza y Arce (10 April 1663 – 29 April 1738), better known as Padre Berganza, was a Spanish Benedictine monk and medievalist. Marcelino Menéndez Pelayo called him ''la lumbrera intelectual de su siglo'' ("the brightest intellect of his age"). He was the son of Francisco de Berganza and Jacinta de Arce, baptised in the parish church of Santibánez de Zarzaguda, though his family was from Gumiel de Izán. On 5 February 1682 he took the Benedictine habit at the monastery of San Pedro de Cardeña, making his profession a short while later, on 21 March. He was shortly thereafter sent to study at San Vicente de Salamanca, where he spent twelve years before returning to Cardeña. There he became chief preacher and finally abbot Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Toledo
The Kingdom of Toledo ( es, Reino de Toledo) was a realm in the central Iberian Peninsula, created after the capture of Toledo by Alfonso VI of León in 1085. It continued in existence until 1833; its region is currently within Spain. Background In April 1065, Emir Al-Muqtadir of Zaragoza besieged Barbastro, aided by 500 Sevillian knights. The governor, Count Ermengol III of Urgel, was killed in a sortie, and a few days later the city fell, whereupon the Spanish and French garrison was put to the sword, thus bringing an end to Pope Alexander II's Crusade of Barbastro against the Moors of Spain. At around the same time, Emir Al-Muqtadir broke off relationships with Castile, and Ferdinand I led a punitive expedition into Zaragoza—taking Alquezar—and then into Valencia. Despite being a tributary of Castile, emir Al-Mamun of Toledo led a force in support of his son-in-law, Emir Abd al-Malik. Mamun subsequently dethroned Abd al-Malik and incorporated Valencia into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
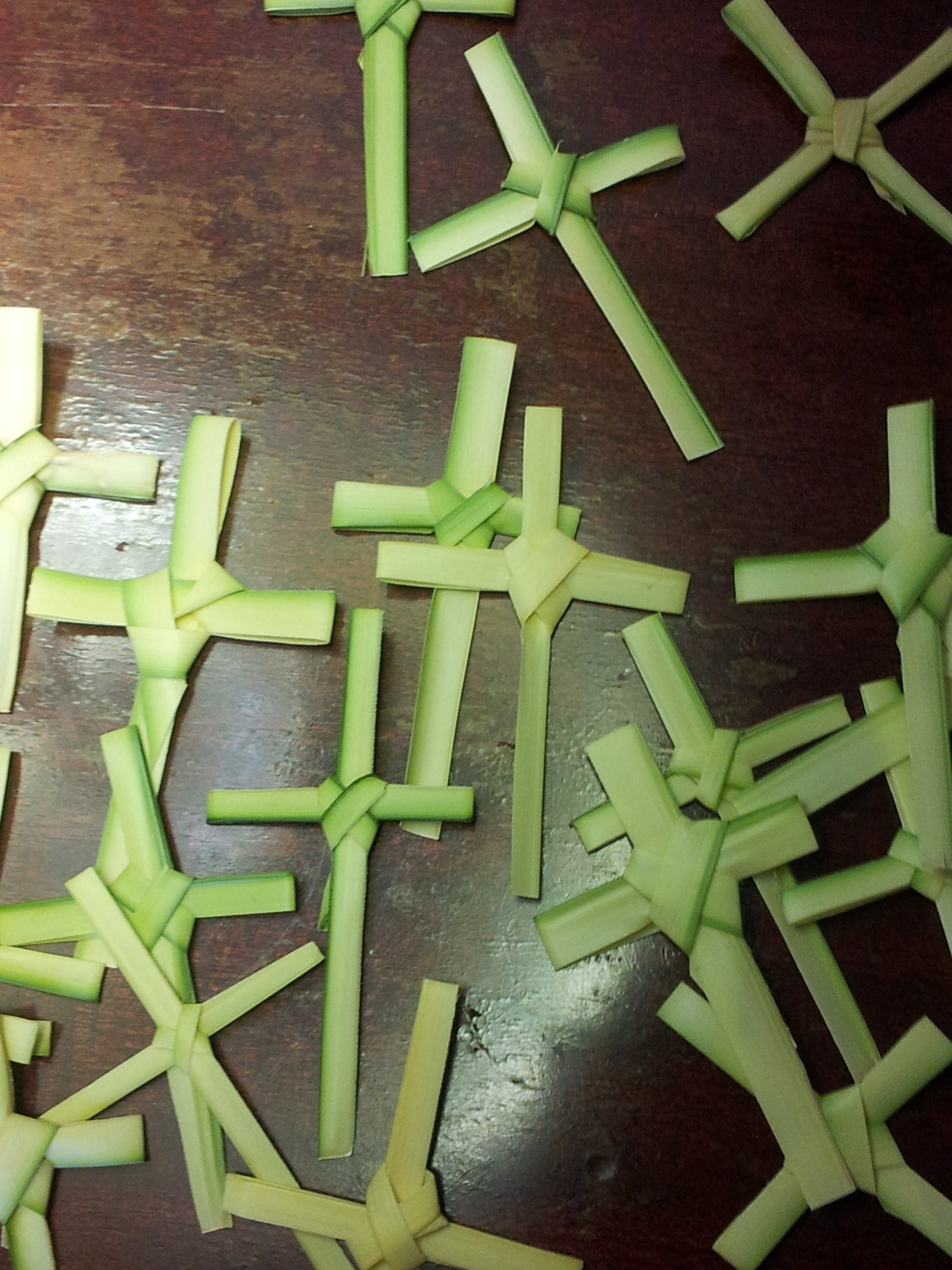
Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday is a Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels. Palm Sunday marks the first day of Holy Week. For adherents of mainstream Christianity, it is the last week of the Christian solemn season of Lent that precedes the arrival of Eastertide. In most liturgical churches, Palm Sunday is celebrated by the blessing and distribution of palm branches (or the branches of other native trees), representing the palm branches which the crowd scattered in front of Christ as he rode into Jerusalem; these palms are sometimes woven into crosses. The difficulty of procuring palms in unfavorable climates led to their substitution with branches of native trees, including box, olive, willow, and yew. The Sunday was often named after these substitute trees, as in Yew Sunday, or by the general term Branch Sunday. In Syriac Christianity it is often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–63 (see ''Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites that survived into the 20th century were abandoned voluntarily after the Second Vatican Council. The Roman Rite is now the most widespread liturgical rite not only in the Catholic Church but in Christianity as a whole. The Roman Rite has been adapted through the centuries and the history of its Eucharistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadragesima Sunday
Quadragesima Sunday (also known as Invocabit Sunday) is the first Sunday in Lent, occurring after Ash Wednesday. The term ''Quadragesima'' is derived from the Latin word for "fortieth", as there are exactly forty days from Quadragesima Sunday until Good Friday. However, like Quinquagesima, Sexagesima and Septuagesima, the numeral is more likely an approximation of how many days there are until Easter Sunday, in this case 42. While Quadragesima includes both Sundays and weekdays, the beginning of Lent was later changed to the preceding Wednesday, "Ash Wednesday", to get in forty weekdays. 'Invocabit' is the opening word of the introit for the day. Quadragesima Sunday may occur as early as February 8 or as late as March 14. In both the ordinary form of the Roman rite and common English parlance it is known as the First Sunday of Lent. The '' buergbrennen'' festivities centred on a large bonfire are celebrated in the towns and villages of Luxembourg Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinmas
Saint Martin's Day or Martinmas, sometimes historically called Old Halloween or Old Hallowmas Eve, is the feast day of Saint Martin of Tours and is celebrated in the liturgical year on 11 November. In the Middle Ages and early modern period, it was an important festival in many parts of Europe, particularly Germanic-speaking regions. In these regions, it marked the end of the harvest season and beginning of winter. and the "winter revelling season". Traditions include feasting on 'Martinmas goose' or 'Martinmas beef', drinking the first wine of the season, and mumming. In some German and Dutch-speaking towns, there are processions of children with lanterns ('' Laternelaufen''), sometimes led by a horseman representing St Martin. The saint was also said to bestow gifts on children. In the Rhineland, it is also marked by lighting bonfires. Martin of Tours (died 397) was a Roman soldier who was baptized as an adult and became a bishop in Gaul. He is best known for the tale whereby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Era
The Spanish era ( la, Æra Hispanica), sometimes called the era of Caesar, was a calendar era (year numbering system) commonly used in the states of the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th century until the 15th, when it was phased out in favour of the ''Anno Domini'' (AD) system. The epoch (start date) of the Spanish era was 1 January 38 BC. To convert an ''Anno Domini'' date to the corresponding year in the Spanish era, add 38 to the ''Anno Domini'' year, such that Era 941 would be equivalent to AD 903. A date given in the Spanish era always uses the word ''era'' followed by a feminine ordinal number (when written out instead of given in Roman numerals). This contrasts with the AD system that uses the masculine ''anno'' (year): i.e., ''era millesima octava'' versus ''anno millesimo octavo''. The reasons behind the choice of 38 BC are unknown. It has been suggested that it may result from an Easter table that began with that year (rather than the Incarnation). Isidore of Seville in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals
Annals ( la, annāles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record. Scope The nature of the distinction between annals and history is a subject based on divisions established by the ancient Romans. Verrius Flaccus is quoted by Aulus Gellius as stating that the etymology of ''history'' (from Greek , , equated with Latin , "to inquire in person") properly restricts it to primary sources such as Thucydides's which have come from the author's own observations, while annals record the events of earlier times arranged according to years. White distinguishes annals from chronicles, which organize their events by topics such as the reigns of kings, and from histories, which aim to present and conclude a narrative implying the moral importance of the events recorded. Generally speaking, annalists record events drily, leaving the entries unexplained and equally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Las Navas De Tolosa
The Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa, known in Islamic history as the Battle of Al-Uqab ( ar, معركة العقاب), took place on 16 July 1212 and was an important turning point in the ''Reconquista'' and the medieval history of Spain. The Christian forces of King Alfonso VIII of Castile were joined by the armies of his rivals, Sancho VII of Navarre and Peter II of Aragon, in battle against the Almohad Muslim rulers of the southern half of the Iberian Peninsula. The caliph al-Nasir ('' Miramamolín'' in the Spanish chronicles) led the Almohad army, made up of people from all over the Almohad Caliphate. Background In 1195, the Almohads defeated Alfonso VIII of Castile in the Battle of Alarcos. After this victory, they took several important cities: Trujillo, Plasencia, Talavera, Cuenca, and Uclés. Then, in 1211, Muhammad al-Nasir crossed the Strait of Gibraltar with a powerful army, invaded Christian territory, and captured Salvatierra Castle, the stronghold of the knights of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |