|
Chipewyan People
The Chipewyan ( , also called ''Denésoliné'' or ''Dënesųłı̨né'' or ''Dënë Sųłınë́'', meaning "the original/real people") are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified with the Taltheilei Shale archaeological tradition. They are part of the Northern Athabascan group of peoples, and come from what is now Western Canada. Terminology The term ''Chipewyan'' (ᒌᐘᔮᐣ) is a Cree exonym meaning ''pointed hides'', referring to the design of their parkas. The French-speaking missionaries to the northwest of the Red River Colony referred to the Chipewyan people as Montagnais in their documents written in French. Montagnais simply means "mountain people" or "highlanders" in French and has been applied to many unrelated nations across North America over time. For example the Neenolino Innu of northern Quebec are also called "Montagnais". Demographics Chipewyan peoples live in the region spanning the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, and the border city Lloydminster. English is the primary language of the province, with 82.4% of Saskatchewanians speaking English as their first language. Saskatchewan h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taltheilei Shale Tradition
The Taltheilei Shale Tradition is the archeological name of the material culture of a late prehistoric western-area subarctic people dated to the period of 750 BC to AD 1000. The Taltheilei Shale Tradition is named after the "Taltheilei Narrows" (''place of open water'') of Great Slave Lake. Taltheilei people were Proto- Athapaskans. Ethnography The Taltheilei were Boreal Forest people who moved into the lands previously inhabited by Arctic groups when the climate changed around 750 BC. Their territory included the central District of Mackenzie and the interior area of the District of Keewatin during the period of 700 BC until early trading posts were established. Sites attributable to the Taltheilei Shale Tradition have been found in several places. Their Little Duck Lake site later became the site of a Hudson Bay trading post called "Caribou Post" due to its proximity to the migration path of the caribou; these Taltheilei are ancestors of the Sayisi Dene, now a Chipewyan band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort McMurray First Nation
Fort McMurray First Nation ( cr, ᓂᐢᑕᐚᔮᐤ, nistawâyâw) is a Cree and Chipewyan band government located near Fort McMurray, Alberta. It is a member of the Athabasca Tribal Council and a Treaty 8 nation. The Athabasca Tribal Council represents 5 First Nation bands in northeast Alberta. Fort McMurray First Nation is governed by a Chief and two councillors. The Fort McKay First Nation was originally part of the same Band, but split off in 1942. Demographics , the Fort McMurray First Nation had a total population of 870 with 284 members living on reserve and 571 members living off-reserve. Reserves Fort McMurray #468 First Nation reserves of ca. include: * Clearwater 175 is located on the Clearwater River southeast of Fort McMurray. It is not populated. *Gregoire Lake 176 Gregoire Lake 176 is an Indian reserve of the Fort McMurray First Nation in Alberta, located within the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo. It is 35 kilometres southeast of Fort McMurra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barren Lands First Nation
Barren Lands First Nation ( cr, ᑭᓯᐸᑲᒫᕽ, kisipakamâhk) is a First Nation located on the north shore of Reindeer Lake in northern Manitoba close to the Saskatchewan border. It has one reserve land called Brochet 197, which is in size and adjoins the village of Brochet, Manitoba. Demographics The population of Brochet 197 in 2011 was 547, a 78.8% increase from the 2006 population of 306. The median age was 20.9. Among its residents, 265 chose Cree as their mother tongue and 15 chose Dene. All but 10 spoke English. The residents of the Brochet 197 reserve and the community of Brochet, itself with 146 residents, form a population centre of 693 people also called ''Brochet''. Membership As of February 2013, the total membership of Barren Lands First Nation was 1,075 with 455 members living on-reserve or on crown land and 620 members living off-reserve. The First Nation is governed by a Chief and three councillors and is affiliated with the Keewatin Tribal Council. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree People
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations. In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree or have Cree ancestry. The major proportion of Cree in Canada live north and west of Lake Superior, in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and the Northwest Territories. About 27,000 live in Quebec. In the United States, Cree people historically lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation with Ojibwe (Chippewa) people. The documented westward migration over time has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade. Sub-groups / Geography The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic sub-divisions within the larger ethnic gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Government
In Canada, an Indian band or band (french: bande indienne, link=no), sometimes referred to as a First Nation band (french: bande de la Première Nation, link=no) or simply a First Nation, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the '' Indian Act'' (i.e. status Indians or First Nations). Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council (french: conseil de bande) chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all status Indians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
First Nations (french: Premières Nations) is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group," along with women, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Some of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Written records began with the arrival of European explorers and colonists during the Age of D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the Shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the United States. Geographical extent The Canadian Shield is a physiographic division comprising four smaller physiographic provinces: the Laurentian Upland, Kazan Region, Davis and James. The shield extends into the United States as the Adirondack Mountains (connected by the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
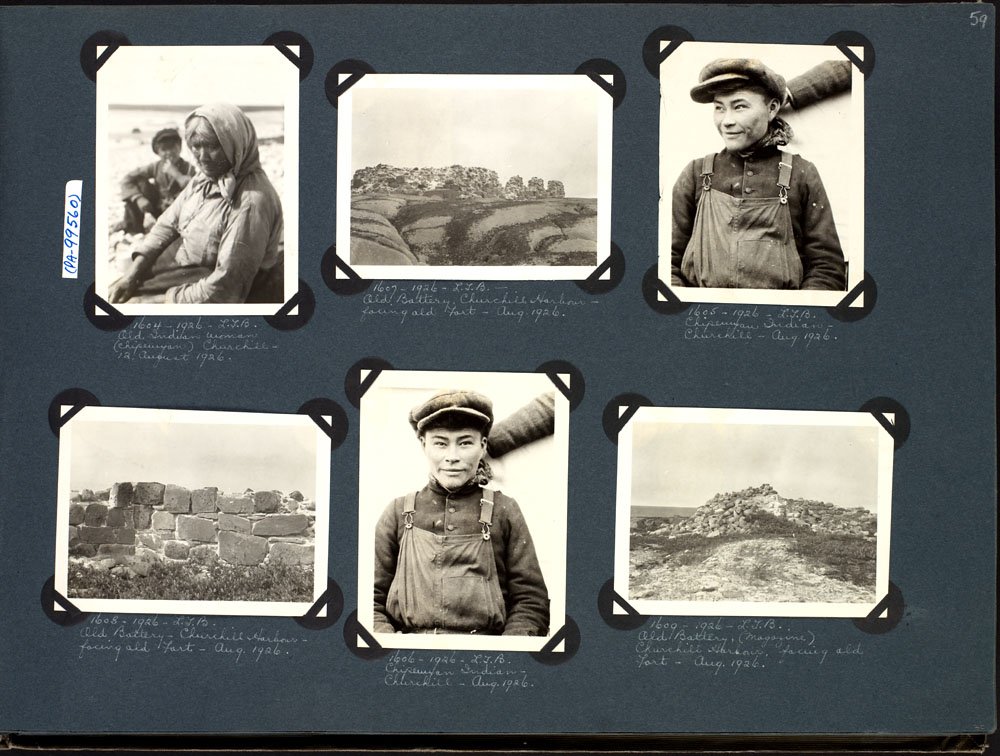
Chipewyan Album
The Chipewyan ( , also called ''Denésoliné'' or ''Dënesųłı̨né'' or ''Dënë Sųłınë́'', meaning "the original/real people") are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified with the Taltheilei Shale archaeological tradition. They are part of the Northern Athabascan group of peoples, and come from what is now Western Canada. Terminology The term ''Chipewyan'' (ᒌᐘᔮᐣ) is a Cree exonym meaning ''pointed hides'', referring to the design of their parkas. The French-speaking missionaries to the northwest of the Red River Colony referred to the Chipewyan people as Montagnais in their documents written in French. Montagnais simply means "mountain people" or "highlanders" in French and has been applied to many unrelated nations across North America over time. For example the Neenolino Innu of northern Quebec are also called "Montagnais". Demographics Chipewyan peoples live in the region spanning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
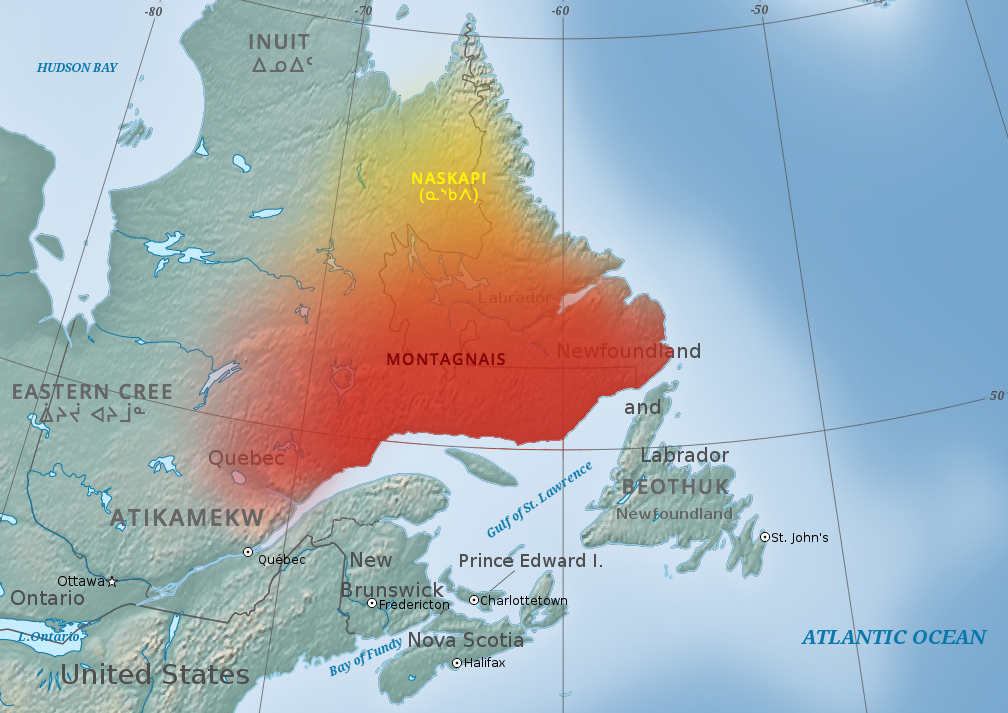
Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the northeastern portion of the present-day province of Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ("Our Land", ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ("Innu Land"). The Innu are divided into several bands, with the Montagnais being the southernmost group and the Naskapi being the northernmost. Their ancestors were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for several thousand years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, Ilnu-Aimun or Innu-Aimun (popularly known since the French colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assinboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hudson's Bay Company in the Selkirk Concession. It included portions of Rupert's Land, or the watershed of Hudson Bay, bounded on the north by the line of 52° N latitude roughly from the Assiniboine River east to Lake Winnipegosis. It then formed a line of 52° 30′ N latitude from Lake Winnipegosis to Lake Winnipeg, and by the Winnipeg River, Lake of the Woods and Rainy River. West of the Selkirk Concession, it is roughly formed by the current boundary between Saskatchewan and Manitoba. These covered portions consisted of present-day southern Manitoba, northern Minnesota, and eastern North Dakota, in addition to small parts of eastern Saskatchewan, northwestern Ontario, and northeastern South Dakota. The lands south of the 49th parall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endonym And Exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, or linguistic community in question; it is their self-designated name for themselves, their homeland, or their language. An exonym (from Greek: , 'outer' + , 'name'; also known as xenonym) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used only outside that particular place, group, or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonym ''Germany'' in English, in Spanish and in French. Naming and etymology The terms ''autonym'', ''endonym'', ''exonym'' and ''xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |