|
Chen Deng
Chen Deng (c. 170 – c. 209), courtesy name Yuanlong, was a Chinese military general and politician who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Born in a family of government officials in Xu Province, he started his career as a county chief at the age of 24 and later became an agriculture official under Tao Qian, the Governor of Xu Province. After Tao Qian's death in 194, Chen Deng supported Liu Bei to be the new Governor. However, in 196, he was forced to become a subordinate of the warlord Lü Bu after the latter seized control of Xu Province from Liu Bei. During this time, Chen Deng and his father Chen Gui pretended to be loyal towards Lü Bu, while secretly undermining his influence by dissuading him from allying with another warlord Yuan Shu. Chen Deng also secretly agreed to serve as a mole in Xu Province for the warlord Cao Cao, who controlled the Han central government. Chen Deng was then appointed as the Administrator of Guangling Commandery. During the Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xian Of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, Luoyang, and forcefully relocated the imperial capital along with its residents to Chang'an. After Dong Zhuo's assassination in 192, Emperor Xian fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Xiapi
The Battle of Xiapi was fought between the forces of Lü Bu against the allied armies of Cao Cao and Liu Bei from the winter of 198 to 7 February 199 towards the end of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. The battle concluded with victory for Cao Cao and Liu Bei, with Lü Bu being subsequently executed. Background In 194, while Cao Cao was away attacking Tao Qian in Xu Province, his subordinates Chen Gong and Zhang Miao rebelled against him and aided Lü Bu in invading his base in Yan Province. Cao Cao abandoned his invasion of Xu Province and turned back to attack Lü Bu, culminating in the Battle of Yan Province which lasted more than 100 days. By 195, Cao Cao had retaken all his cities in Yan Province and defeated Lü Bu at Juye. Lü Bu and his men fled east to join Liu Bei, who had succeeded Tao Qian as Governor () of Xu Province. In 196, Cao Cao found Emperor Xian in the ruins of Luoyang and brought him to Xuchang, where the new capital and imperial court would be base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kong Rong
Kong Rong () (153 – 26 September 208), courtesy name Wenju, was a Chinese poet, politician, and minor warlord. who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was a 20th generation descendant of Confucius. As he was once the Chancellor of Beihai State, he was also known as Kong Beihai. He was defeated by Yuan Tan in 196 and escaped to the capital Xuchang. For being a political opponent of Cao Cao and humiliating him on multiple occasions, Kong Rong was eventually put to death on various charges. Famed for his quick wits and elaborate literary style, Kong Rong was ranked among the Seven Scholars of Jian'an, a group of representative literati of his time. However, most of his works had been lost. Those that survived can be found in compilations from the Ming and Qing dynasties. A well-known story commonly used to educate children – even in contemporary times – on the values of courtesy and fraternal love involves a four-year-old Kong Rong giving up the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
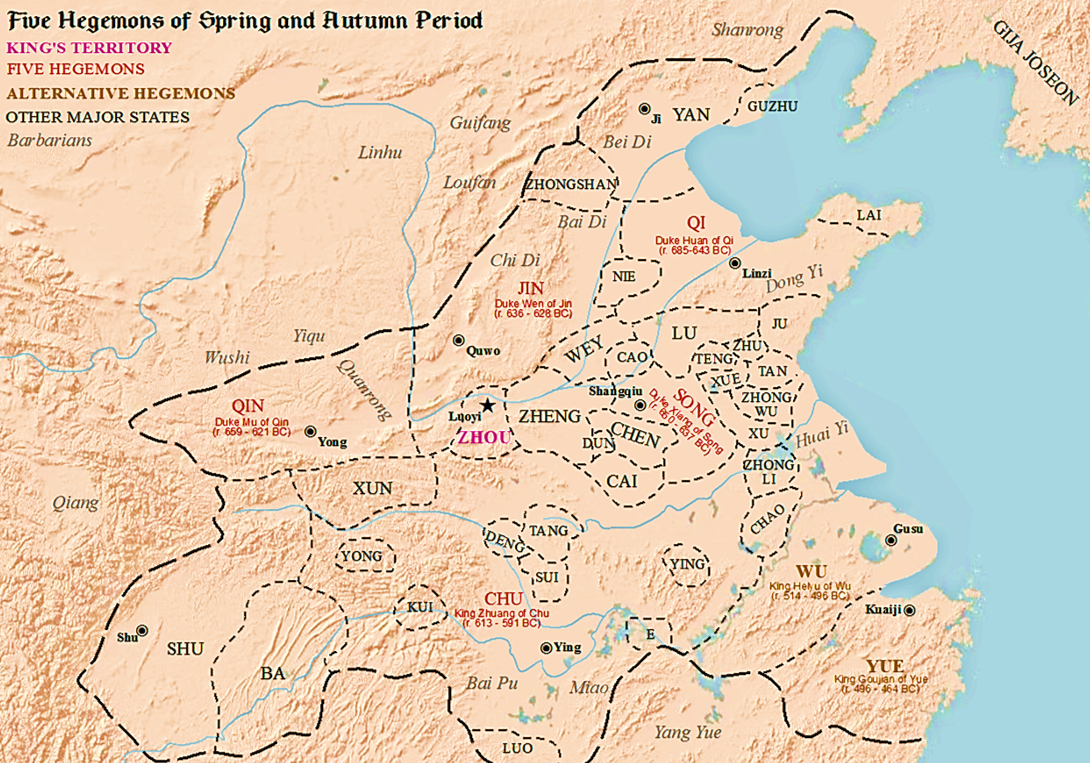
Five Hegemons
The Five Hegemons () refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770 to 476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as the 'Five Hegemons'. () literally means 'five', but in the context of ancient Chinese also has a more ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi Zhu
Mi Zhu ( 165–221), courtesy name Zizhong, was a Chinese military general and politician who served under the warlord Liu Bei in the late Eastern Han dynasty, during the Three Kingdoms period, after Liu Bei founded the state of Shu Han. He was also Liu Bei's brother-in-law, as his sister, Lady Mi, married Liu Bei. Mi Zhu was essential to Liu Bei during the defeats of the latter, financing Liu Bei's army in critical times where there was no tax base. Mi Zhu was extremely well educated and helped Liu Bei develop relationships with wealthy rivals such as Yuan Shao, Yuan Shu and Liu Biao. He was also the elder brother of Mi Fang, who served Liu Bei as well until his defection to Liu Bei's ally-turned-rival Sun Quan in 220. Mi Zhu served Liu Bei loyally for more than 25 years, as a high civil official of Liu during all the later's tenures as governor of Xu, Jing and Yi provinces, the former's ideas were regularly and widely circulated to the common people which greatly helped Liu Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinhu County
Jinhu County () is under the administration of Huai'an, Jiangsu province, China. It occupies the northwestern shores of and extends into Gaoyou Lake, bordering the prefecture-level cities of Yangzhou to the south and east, and Chuzhou (Anhui) to the southwest. History Jinhu County was formerly administered by Baoying and Gaoyou Gaoyou (), is a county-level city under the administration of Yangzhou, Jiangsu province, China, located in the Yangtze River Delta on the north side of the Yangtze River. History Recent archaeological finds at the Longqiuzhuang site in Gaoyou has ... counties until 1959, when it became its own county. Administrative divisions Jinhu County has 11 towns. ;11 towns Climate References County-level divisions of Jiangsu Huai'an {{Jiangsu-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaolian
Xiaolian (; literally "filial and incorrupt"), was the standard of nominating civil officers started by Emperor Wu of Han in 134 BC. It lasted until its replacement by the imperial examination system during the Sui Dynasty. In Confucian philosophy, filial piety is a virtue of respect for one's parents and ancestors. onfucianism in Context Classic Philosophy and Contemporary Issues, East Asia and Beyond/ref> Under the advice of Dong Zhongshu, Emperor Wu ordered each commandery to recommend one filial and one incorrupt candidate for civil offices. Later the nomination became proportional; Emperor He of Han changed the proportion to one candidate for every 200,000 residents, and one for every 100,000 residents in ethnic minority regions. The nominator was also responsible if the nominee was charged with corruption, and could be punished if he refused to nominate qualified individuals. After the Han dynasty, high positions were usually nominated according to the Nine-rank system, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei County
Pei County, or Peixian (), is under the administration of Xuzhou, Jiangsu province, China, bordering the Shandong prefecture-level cities of Jining to the northwest and Zaozhuang to the northeast and sitting on the western shore of Nansi Lake. It has an area of and a population of 1,141,935 in 2010. History Pei County is well known as the place people believe where all the Han culture come from. It is the hometown of Liu Bang, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. Also, the hometown of Fan Kuai, Liu Bang's oath brother, one of the most well-known lords who helped Liu Bang to overthrow the Qin Dynasty and establish the Han Dynasty. Fan Kuai's descendants are still living in Pei County now. Xiaopei (小沛) is an ancient Chinese town located in present-day Pei County. In the late Eastern Han dynasty, it was under the jurisdiction of the Xu Province, which was governed by Tao Qian. Before Tao Qian died, he handed his governorship over to Liu Bei. Liu Bei took refuge in Xiaop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei Commandery
Pei Commandery ( zh, 沛郡) was a Chinese commandery from Han dynasty to Northern Qi dynasty. Its territory was located in present-day northern Anhui and northwestern Jiangsu, as well as part of Shandong and Henan. Pei was established in early Western Han on an area formerly known as Sishui Commandery (泗水郡) during the Qin dynasty, and received its name from Pei County, Liu Bang's home county. The seat was at Xiang (相), in modern Huaibei, Anhui. The commandery was part of the vassal Kingdom of Chu during its early years, however, during Emperor Jing's reign, the imperial forces defeated Chu in the Rebellion of Seven States and revoked the territory. In 117 BC, part of Pei was split off to form the new Linhuai Commandery. In 2 AD, the commandery consisted of 37 counties: Xiang (相), Longkang (龍亢), Zhu (竹), Guyang (穀陽), Xiao (蕭), Xiang (向), Zhi (銍), Guangqi (廣戚), Xiacai (下蔡), Feng (豐), Dan (鄲), Qiao (譙), Qi (蘄), Zhuan (颛), Zheyu (輒與 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A jùn (郡) was a historical administrative division of China from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). It is usually translated as a commandery. Countries around China have adopted administrative divisions based on or named after the ''jùn''. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou's vassal states—including Qin, Jin and Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, jun were developed as marchlands between the major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the jun were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties. As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5th- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Ling Of Han
Emperor Ling of Han (156 – 13 May 189), personal name Liu Hong, was the 12th and last powerful emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty. Born the son of a lesser marquis who descended directly from Emperor Zhang (the third Eastern Han emperor), Liu Hong was chosen to be emperor in 168 around age 12 after the death of his predecessor, Emperor Huan, who had no son to succeed him. He reigned for about 21 years until his death in 189. Emperor Ling's reign saw another repetition of corrupt eunuchs dominating the eastern Han central government, as was the case during his predecessor's reign. Zhang Rang, the leader of the eunuch faction (十常侍), managed to dominate the political scene after defeating a faction led by Empress Dowager Dou's father, Dou Wu, and the Confucian scholar-official Chen Fan in 168. After reaching adulthood, Emperor Ling was not interested in state affairs and preferred to indulge in women and a decadent lifestyle. At the same time, corrupt officials in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Home (Chinese)
In Chinese culture, hometown or ancestral home () is the place of origin of one's extended family. It may or may not be the place where one is born. For instance, two people may both be born in Shanghai, but the hometowns of their ancestors may be different. Definition A subjective concept, a person's ancestral home could be the birthplace of ''any'' of their patriline ancestors. Su Shi limited it to five generations, i.e. it refers to the home of one's great-great-grandfather. Even more broadly, an ancestral home can refer to the first locality where a surname came to be established or prominent. Commonly, a person usually defines their hometown as what their father considers to be his ancestral home. In practice, most people would define their ancestral homes as the birthplace of their patriline ancestors from the early 20th century, around the time when government authorities began to collect such information from individuals. Moreover, a person's ancestral home can be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |