|
Cheikh Saïd
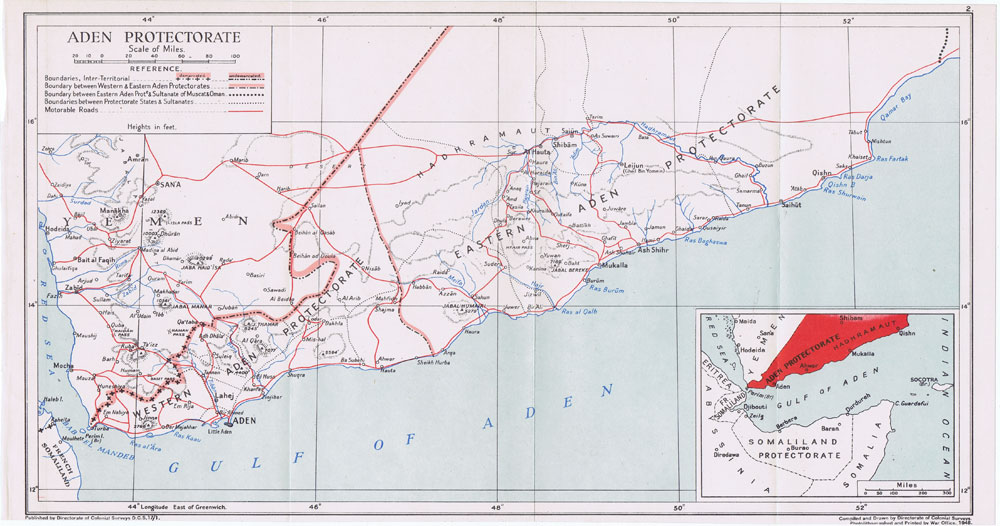
Cheikh Said (frequently spelled Sheikh Said) is a rocky peninsula in Yemen, near the island of Perim on the Bab-el-Mandeb at the entrance to the Red Sea. In 1868 it was purchased from the local ruler, Sheikh Ali Tabet Ahmed, by Bazin et Rabaud, a private company based in Marseille in France, which wanted to use it as a base for exporting coffee. The purchase price was 80,000 thalers. In 1869, the sheikh annulled the agreement as he had received only 18,000 thalers. Bazin et Rabaud and some allies in the French press attempted to press the French government to intervene, without success. In 1920, Cheikh Saïd was described as a "good landing-place, with an important telegraph station." Although as late as 1970, the ''Petit Larousse'' described it as having been a "French colony from 1868 to 1936", France never claimed formal jurisdiction or sovereignty over it. In the days before World War I the Ottoman Empire maintained a small fort here guarding the entrance to the Red Sea. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petit Larousse
''Le Petit Larousse Illustré'', commonly known simply as ''Le Petit Larousse'' (), is a French-language encyclopedic dictionary published by Éditions Larousse. It first appeared in 1905 and was edited by Claude Augé, following Augé's '' Dictionnaire complet illustré'' (1889). The one-volume work has two main sections: a dictionary featuring common words and an encyclopedia of proper nouns. ''Le Petit Larousse'' 2007 (published in 2006) includes 150,000 definitions and 5,000 illustrations. A Spanish-version ''El Pequeño Larousse Ilustrado'' and an Italian version ''Il Piccolo Rizzoli Larousse'' have also been published. The motto of Pierre Larousse, the namesake of Éditions Larousse, perpetuated in Larousse's publications is "Je sème à tout vent" ("I sow to all winds"). This motto inspires the cover art of ''Le Petit Larousse'', which typically features a female figure blowing dandelion seeds. Upon its 100th anniversary, a history of ''Le Petit Larousse'' was published ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French Colonial Empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French Colonial Empire", which began with the conquest of Algiers in 1830. At its apex between the two world wars, the second French colonial empire was the second-largest colonial empire in the world behind the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India in the 17th century but lost most of its possessions following its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain but the latter returned Louisiana (New France) to France in 1800. The territory was then sold to the United States in 1803. France rebuilt a new empire mostly after 1850, concentrating chiefly in Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast enough to outrun any battleship it encountered. For many decades, naval technology had not advanced far enough for designers to produce a cruiser which combined an armored belt with the long range and high speed required to fulfill its mission. For this reason, beginning in the 1880s and 1890s, many navies preferred to build protected cruisers, which only relied on a light armored deck to protect the vital parts of the ship. However, by the late 1880s, the development of modern rapid-fire breech-loading cannon and high-explosive shells made the reintroduction of side armor a necessity. The invention of face-hardened armor in the mid-1890s offered effective protection with less weight than previously. Varying in size, the armored cruiser was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Cheikh Said
The invasion of Cheikh Said was a part of the South Arabia during World War I, campaigns by the Ottomans to take Aden Colony, Aden, a British crown colony. It is a British offensive led by Vaughan Cox, H. V. Cox to destroy Ottoman works, wells, and armaments they have there on the 10th of November 1914. It resulted in Ottoman retreat and total British victory by the next day. Background Britain declared war on the Ottoman Empire on 5 November 1914. In response, the Ottomans themselves declared war back on the British six days later. From the start of the war, the Ottomans had planned to along with the Arab tribes, to take over the British crown colony of Aden and its hinterland, the Aden Protectorate. The Ottomans, to execute the plan, maintained a small fort guarding the entrance of the Red Sea in Cheikh Saïd, a peninsula which juts out into the Red Sea towards the island of Perim. Meanwhile, Britain ordered The 29th Indian Brigade, under Brigadier-General Vaughan Cox, H. V. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |