|
Charters Towers
Charters Towers is a rural town in the Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. It is by road south-west from Townsville on the Flinders Highway. During the last quarter of the 19th century, the town boomed as the rich gold deposits under the city were developed. After becoming uneconomical in the 20th century, profitable mining operations have commenced once again. In the , Charters Towers had a population of 8,120 people. Geography and climate The urban area of the town of Charters Towers includes its suburbs: Charters Towers City (the centre of the city); Richmond Hill, Toll, and Columbia to the north, Queenton to the east, Grand Secret and Alabama Hill to the west, and Towers Hill, Mosman Park, and Millchester to the south. Charters Towers township is only mildly elevated at above sea-level, but this has a noticeable effect, with lower humidity and wider temperature variations compared to nearby Townsville. Charters Towers obtains its water supply from the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Mosman
Hugh Mosman (11 February 1843 – 15 November 1909) was a mine owner and politician in Queensland, Australia. He discovered gold in Charters Towers. He was a Member of the Queensland Legislative Council. Early life Mosman was born on 11 February 1843 in Mosman, New South Wales. Merchant Archibald Mosman (1799–1863) was his father, and his mother was Harriet née Farquharson Hugh received his education at The King's School in North Parramatta, New South Wales. Mosman initially aspired to be a pastoralist, but failed to establish a successful career and was left broke., He visited Queensland in 1860, hoping to acquire properties there; this was also unsuccessful. Mosman decided then to try his hand at prospecting. He spent the next ten years mining, and in 1870 he revisited Queensland, choosing to work in Ravenswood. Gold On 24 December 1871, Mosman was travelling with miners George Clark, James Fraser, and his servant, Jupiter Mosman, attempting to locate missing horses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alabama Hill, Queensland
Alabama Hill is a suburb of Charters Towers in the Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Alabama Hill had a population of 121 people. History In the , Alabama had a population of 103 people. In the , Alabama Hill had a population of 121 people. Heritage listings Alabama Hill has a number of heritage-listed sites, including: * Charters Towers mine shafts Education There are no schools in Alabama Hill. The nearest primary school is Charters Towers Central State School in neighbouring Charters Towers City to the east. The nearest secondary school is Charters Towers State High School Charters Towers State High School (CTSHS) is a public high school in Charters Towers City, Charters Towers Charters Towers is a rural town in the Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. It is by road south-west from Townsville on t ... in Charters Towers City. References {{Charters Towers Region Suburbs of Charters Towers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
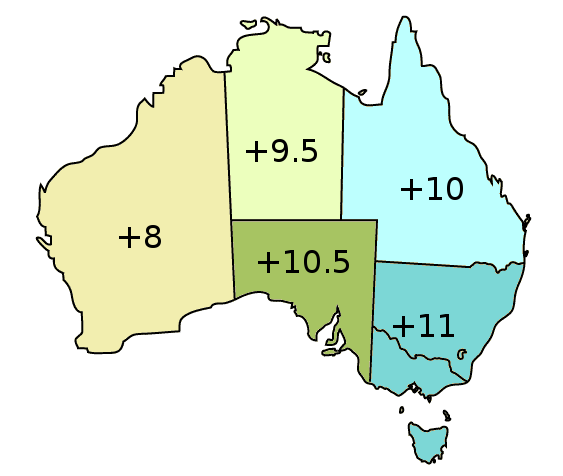
AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Clarke (prospector)
George Edward Clarke (1846–1895) was a prospector in Queensland, Australia. He was a member of the expedition that found gold at Charters Towers. Early life George E. Clarke was born near Camden, New South Wales, in May 1846. Clarke left for the Riverina when he was 17 years old, where he was engaged in pastoral pursuits for five years. In 1868, he left for Rockhampton attracted by the opportunities of a new colony of Queensland, where he engaged in pastoral pursuits until 1871. During these three years, he took considerable interest in the copper mining in the Mackenzie district. Discovery of the Charters Towers gold field Upon hearing glowing reports of the newly opened gold mining district of Ravenswood, he abandoned pastoral pursuits for mining. Midyear, Clarke met Hugh Mosman (who had been engaged in pastoral pursuits on the Mackenzie River) near Broadsound. Mosman had come down through Ravenswood, and his description of the potential of the Ravenswood district i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter Mosman
John Joseph (Jupiter) Mosman (1861-1945) was an Aboriginal Australian prospector, one of the group of four who discovered gold at Charters Towers, Queensland, Australia. It became one of the premier goldfields of Australia, yielding £23,000,000 worth of gold. Mosman is credited with having found the first gold-bearing stone. Early life Mosman was born about 1861 in North-Western Queensland. His tribal name is unknown. As a small boy, he came to Kynuna Station. In the late 1860s, pastoralist Hugh Mosman of Tarbrax Station visited Kynuna and liked the boy so much that Hugh Mosman arranged for the boy to come to live at Tarbrax with him. He was named Jupiter by Hugh Mosman because his eyes were "large, luminous, and as limpid as a planet". He became known as Jupiter Mosman and acted as Hugh Mosman's servant. Prospecting There had been discoveries of gold at Ravenswood and other places in North Queensland. Hugh Mosman decided to search for gold, selling Tarbrax to Duncan McI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland State Archives 5154 Day Dawn Consolidated Mine Charters Towers C 1897
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk ( ALP) , legislature = Parliament of Queensland , judiciary = Supreme Court of Queensland , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Bureau Of Meteorology
Australian(s) may refer to: Australia * Australia, a country * Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia ** European Australians ** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists ** Aboriginal Australians, indigenous peoples of Australia as identified and defined within Australian law * Australia (continent) ** Indigenous Australians * Australian English, the dialect of the English language spoken in Australia * Australian Aboriginal languages * ''The Australian ''The Australian'', with its Saturday edition, ''The Weekend Australian'', is a broadsheet newspaper published by News Corp Australia since 14 July 1964.Bruns, Axel. "3.1. The active audience: Transforming journalism from gatekeeping to gatew ...'', a newspaper * Australiana, things of Australian origins Other uses * Australian (horse), a racehorse * Australian, British Columbia, an unincorporated community in Canada See also * The Australian (disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charters Towers Airport
Charters Towers Airport is an airport located in Columbia, Charters Towers, Queensland, Australia, north of the Charters Towers CBD. History World War II During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces Fifth Air Force stationed the following units at the airfield: * No. 22 Squadron RAAF, A-20 Boston * 3d Bombardment Group, (10 March 1942 – 28 January 1943) (Headquarters) : 8th Bombardment Squadron, A-20 Havoc (17–31 March 1942; 9 May 1942 – 28 January 1943) : 90th Bombardment Squadron, A-20 Havoc (8 March 1942 – 28 January 1943) * 431st Fighter Squadron ( 475th Fighter Group), P-38 Lightning (14 May – 1 July 1943) * 432d Fighter Squadron (475th Fighter Group), P-38 Lightning (14 May – 11 July 1943) * 433d Fighter Squadron (475th Fighter Group), P-38 Lightning (14 May – 17 June 1943) * 16th Bombardment Squadron (Light) (27th Bombardment Group (Light)), A-24 Dauntless (1 April – 4 May 1942) * 17th Bombardment Squadron (Light) (27th Bombardment Gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burdekin River
The Burdekin River is a river located in North and Far North Queensland, Australia. The river rises on the northern slopes of Boulder Mountain at Valley of Lagoons, part of the western slope of the Seaview Range, and flows into the Coral Sea at Upstart Bay over to the southeast of the source, with a catchment area of approximately . The Burdekin River is Australia's largest river by (peak) discharge volume. The river was first encountered by Europeans during the expedition led by Ludwig Leichhardt in 1845 and named in honour of Thomas Burdekin, one of the sponsors of the expedition. Course and features The Burdekin River rises on the western slopes of the Seaview Range, part of the Great Dividing Range, west of . In the river's upper catchment, from its source the river generally flows west and then south out of the Girringun National Park, part of the UNESCO Wet Tropics World Heritage Area. This area, now part of Basalt was the location of one of the earliest inland settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |