|
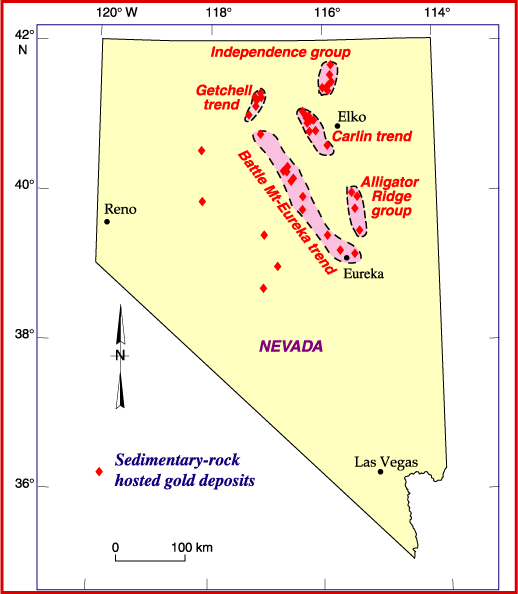
Carlin Trend
The Carlin Unconformity or Carlin Trend is a geologic feature in northeastern Nevada which represents a period of erosion or non-deposition likely associated with a collision between a tectonics, tectonic crustal block called a terrane and the North American Plate. The collision occurred during the Mississippian age, Mississippian Period, about 350 million years before present. The collision is associated with the Antler Orogeny. The collision induced higher crustal temperatures and pressures which produced numerous hot springs along the suture zone. Several episodes of subsurface magmatism are known to have occurred subsequent to the collision, associated with tectonic forces affecting the entire Basin and Range Province. During each of these episodes, and particularly during the Eocene epoch, hot springs brought dissolved minerals toward the surface, precipitating them out along fissures. Among these minerals were gold and silver. The Carlin Gold trend is one of the world's ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Events
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lineage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconformities
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph J
Ralph (pronounced ; or ,) is a male given name of English, Scottish and Irish origin, derived from the Old English ''Rædwulf'' and Radulf, cognate with the Old Norse ''Raðulfr'' (''rað'' "counsel" and ''ulfr'' "wolf"). The most common forms are: * Ralph, the common variant form in English, which takes either of the given pronunciations. * Rafe, variant form which is less common; this spelling is always pronounced , as are all other English spellings without "l". * Raife, a very rare variant. * Raif, a very rare variant. Raif Rackstraw from H.M.S. Pinafore * Ralf, the traditional variant form in Dutch, German, Swedish, and Polish. * Ralfs, the traditional variant form in Latvian. * Raoul, the traditional variant form in French. * Raúl, the traditional variant form in Spanish. * Raul, the traditional variant form in Portuguese and Italian. * Raül, the traditional variant form in Catalan. * Rádhulbh, the traditional variant form in Irish. Given name Middle Age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Livermore
John Sealy Livermore (April 16, 1918 – February 7, 2013) was an American geologist who discovered or helped to discover four major gold deposits in northern Nevada. Livermore was born in San Francisco, California, and was descended from a pioneer California family with roots in Maine. An ancestor, Elijah Livermore, built a grist mill and a saw mill on the Androscoggin River in 1791. The town of Livermore Falls, Maine, is named after him. His great-grandfather, Horatio Gates Livermore, came to California from Maine during the Gold Rush in 1850, and later became a California State Senator from Eldorado County. His great-grandfather and his grandfather, Horatio Putnam Livermore, who came to California in 1856, used their Maine mill experience to become involved in the earliest days of hydroelectric power, helping to build the original Folsom Dam. His father, Norman Banks Livermore was a founding board member of Pacific Gas and Electric. His mother, Caroline Sealy Live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Mining In Nevada
Gold mining in Nevada, a state of the United States, is a major industry, and one of the largest sources of gold in the world. In 2018 Nevada produced , representing 78% of US gold and 5.0% of the world's production. Total gold production recorded from Nevada from 1835 to 2017 totals , worth US$322.6 billion at 2020 values. Much of Nevada's gold production comes from large open pit mining using heap leaching recovery. The Nevada mining industry supported an average 14,787 direct employees in 2018, with about 75,000 additional jobs related to providing goods and services needed by the mining industry. The average pay for mining industry employees during this time was $97,600 per year, the third highest average private employment sector in the state. Major mining companies such as Newmont Goldcorp and Barrick Gold Corporation operate many of the state's gold mines. Active mines include those at Jerritt Canyon and the Carlin Trend. Although Nevada was known much more for silver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlin–type Gold Deposit
Carlin–type gold deposits are sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits. These deposits are characterized by invisible (typically microscopic and/or dissolved) gold in arsenic rich pyrite and arsenopyrite. This dissolved kind of gold is called "Invisible Gold", as it can only be found through chemical analysis. The deposit is named after the Carlin mine, the first large deposit of this type discovered in the Carlin Trend, Nevada. Geology The Carlin type deposits show enrichment in the elements gold, arsenic, antimony, mercury, thallium and barium. This enrichment is created by hydrothermal circulation with a temperature of up to 300 °C. The underlying rocks out of which the minerals are dissolved are normally silty carbonates, although also silicates and other sediments are possible. The source of the heating for the water in the hydrothermal circulation is still under discussion. The material in the deposit is altered in a way that the carbonate minerals are eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlin, Nevada
Carlin is a small city located near the western border of Elko County in northeast Nevada, west of the city of Elko. It is part of the Elko Micropolitan Statistical Area. Carlin sits along Interstate 80 at an elevation of approximately . As of the 2010 census, its population was 2,368, up from 2,161 at the 2000 census. The city was named for Civil War general William Passmore Carlin. Its slogan is "Where the Train Stops...And the Gold Rush Begins". Geography Carlin is located at . To the northwest is the Carlin Trend, one of the most productive gold mining areas in the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all of it land. Climate Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 2,161 people, 792 households, and 579 families residing in the city. The population density was 234.6 people per square mile (90.6/km). There were 1,014 housing units at an average density of 110.1 per square mile (42.5/km). The racial makeup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediments
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ... acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension (chemistry), suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water (fluvial, fluvial processes), but also wind (aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and stream channel, river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition (geology), deposition, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium ( gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newmont Gold Quarry Mine
Newmont Corporation is a gold mining company based in Greenwood Village, Colorado, United States. It is the world's largest gold mining corporation. Incorporated in 1921, it owns gold mines in Nevada, Colorado, Ontario, Quebec, Mexico, the Dominican Republic, Australia, Ghana, Argentina, Peru, and Suriname. In addition to gold, Newmont mines copper, silver, zinc and lead. Newmont has approximately 31,600 employees and contractors worldwide, and is the only gold company in the S&P 500, Standard & Poor's 500 stock market index. Newmont is spending $500 million on renewable energy projects through 2025 towards its commitment of reducing carbon emissions by 30% by 2030. Operations History Early years The Newmont Company was founded in 1916 in New York by Colonel (United States), Colonel William Boyce Thompson as a holding company to invest in Worldwide mineral, Petroleum, oil, and related companies. According to company lore, the name "Newmont" is a portmanteau "New York" a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |