|
Calcium Phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white solids of nutritious value and are found in many living organisms, e.g., bone mineral and tooth enamel. In milk, it exists in a colloidal form in micelles bound to casein protein with magnesium, zinc, and citrate–collectively referred to as colloidal calcium phosphate (CCP). Various calcium phosphate minerals are used in the production of phosphoric acid and fertilizers. Overuse of certain forms of calcium phosphate can lead to nutrient-containing surface runoff and subsequent adverse effects upon receiving waters such as algal blooms and eutrophication (over-enrichment with nutrients and minerals). Orthophosphates, di- and monohydrogen phosphates These materials contain Ca2+ combined with , , or : * Monocalcium phosphate, E341 (CAS# 775 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smelly Cat
Smelly may refer to something with a disagreeable odor (i.e., something that smells bad). Smelly may also refer to: People *Smelly (performer) or Dai Okazaki, a Japanese comedic performer *Erik Sandin Erik Sandin (born July 29, 1966), is an American musician and the drummer of the punk rock band NOFX, and former member of punk rock band Caustic Cause. He was a founding member of NOFX when they formed in Hollywood, California, in 1983. ..., drummer with NOFX nicknamed Smelly See also * Smelley, a surname {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
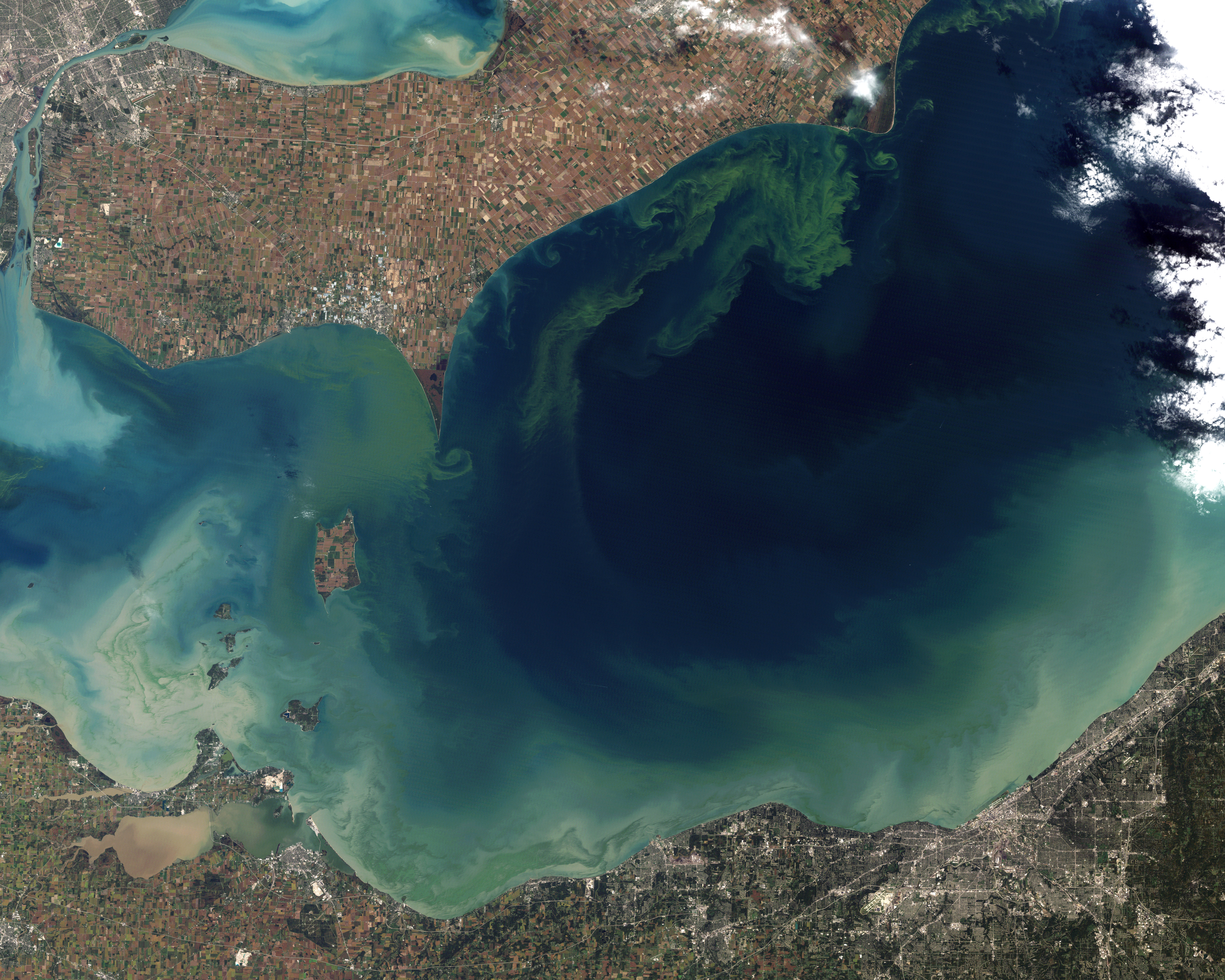
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
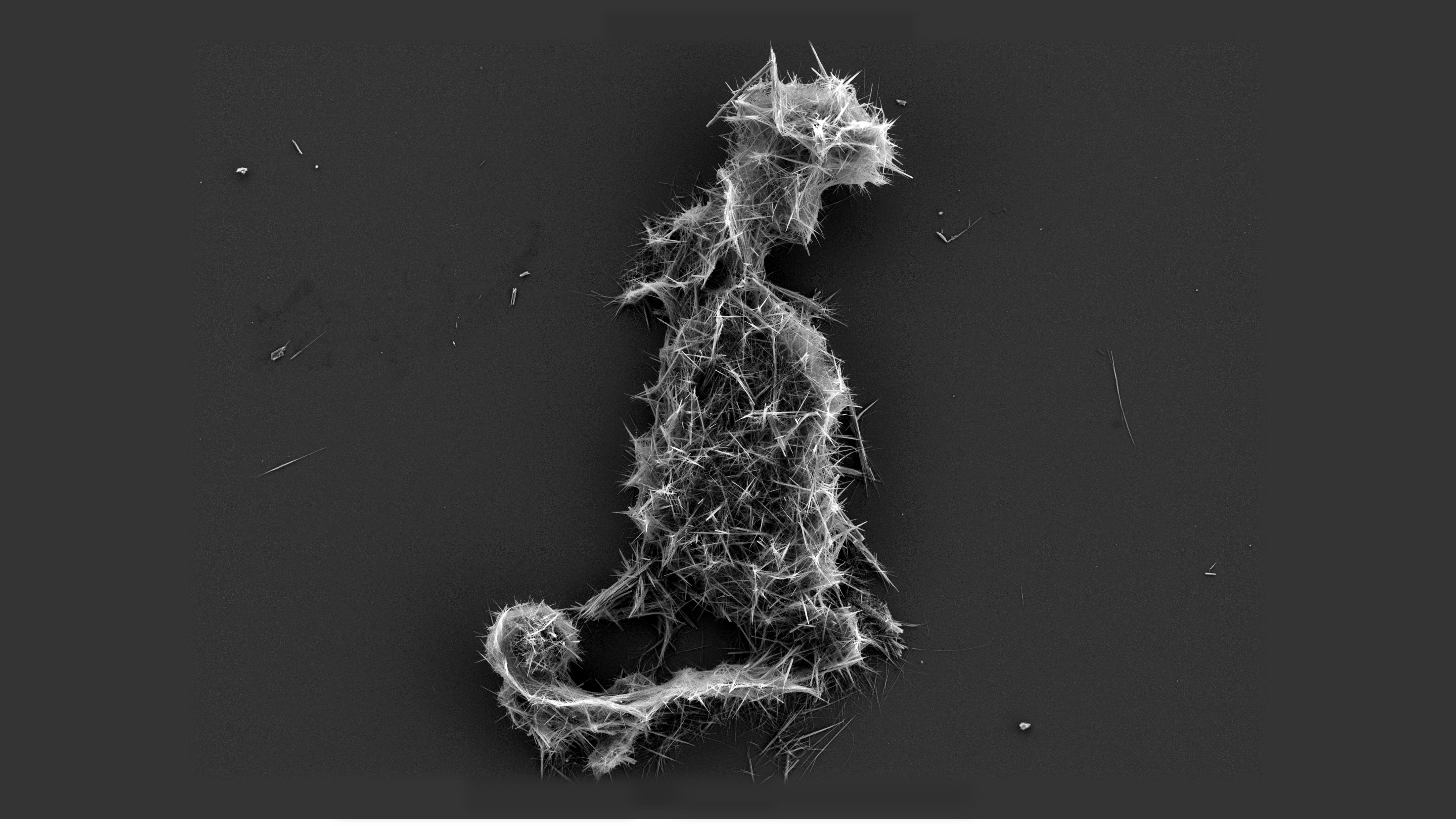
Calcium Triphosphate
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicalcium Diphosphate
Calcium pyrophosphate (Ca2P2O7) is a chemical compound, an insoluble calcium salt containing the pyrophosphate anion. There are a number of forms reported: an anhydrous form, a dihydrate, Ca2P2O7·2H2O and a tetrahydrate, Ca2P2O7·4H2O. Deposition of dihydrate crystals in cartilage are responsible for the severe joint pain in cases of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (pseudo gout) whose symptoms are similar to those of gout. Ca2P2O7 is commonly used as a mild abrasive agent in toothpastes, because of its insolubility and nonreactivity toward fluoride. __TOC__ Preparation Crystals of the tetrahydrate can be prepared by reacting sodium pyrophosphate, Na4P2O7 with calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, at carefully controlled pH and temperature: :Na4P2O7(aq)+2 Ca(NO3)2(aq)→ Ca2P2O7·4 H2O + 4 NaNO3 The dihydrate, sometimes termed CPPD, can be formed by the reaction of pyrophosphoric acid with calcium chloride: :CaCl2 + H4P2O7(aq) → Ca2P2O7·2 H2O + HCl. The anhydrous forms can be pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphosphate
Polyphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 (phosphate) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic ring structures. In biology, the polyphosphate esters ADP and ATP are involved in energy storage. A variety of polyphosphates find application in mineral sequestration in municipal waters, generally being present at 1 to 5 ppm. GTP, CTP, and UTP are also nucleotides important in the protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and carbohydrate metabolism, respectively. Polyphosphates are also used as food additives, marked E452. Structure Image:Triphosphorsäure.svg, Structure of triphosphoric acid Image:Polyphosphoric acid.svg, Polyphosphoric acid Image:Trimetaphosphat.svg, Cyclic trimetaphosphate Image:Adenosindiphosphat protoniert.svg, Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) The structure of tripolyphosphoric acid illustrates the principles which define the structures of polyphosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphous Calcium Phosphate
Amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) is a glassy solid that is formed from the chemical decomposition of a mixture of dissolved phosphate and calcium salts (e.g. (NH4)2HPO4 + Ca(NO3)2). The resulting amorphous mixture consists mostly of calcium and phosphate, but also contains varying amounts of water and hydrogen and hydroxide ions, depending on the synthesis conditions. Such mixtures are also known as calcium phosphate cement. ACP is generally categorized into either "amorphous tricalcium phosphate" (ATCP) or calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite (CDHA). CDHA is sometimes termed " apatitic calcium triphosphate." The composition of amorphous calcium phosphate is Ca''x''H''y''(PO4)''z''·''n''H2O, where ''n'' is between 3 and 4.5. CDHA has a general formula of Ca9(HPO4)(PO4)5(OH). Precipitation from a moderately supersaturated and basic solution of a magnesium salt produces amorphous magnesium calcium phosphate (AMCP), in which magnesium incorporated into the ACP structure. A commercial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octacalcium Phosphate
Octacalcium phosphate (sometimes referred to as OCP) is a calcium phosphate with a formula Ca8H2(PO4)6⋅5H2O. OCP may be a precursor to tooth enamel, dentine, and bones. OCP is a precursor of hydroxylapatite (HAP), an inorganic biomineral that is important in bone growth. OCP has been suggested as a replacement for HAP in bone grafts. Properties Boiling water decomposes OCP into hydroxyapatite and dicalcium phosphate. Both thermal and hydrothermal treatments sometimes yield apatitic single crystal pseudomorphs after OCP, the c-axes being parallel to the c of the original OCP. OCP has the lattice constants ''a'' = 19.7 Å, ''b'' = 9.59 Å, ''c'' =6.87 Å, ''α'' = ''β'' = 90.7° and ''γ = 71.8°, slightly different from those of hydroxyapatite. OCP has a strong crystal twinning tendency. The average crystal size of OCP is 13.5 ± 0.2 nm. Synthesis It can be prepared by treating calcium acetate Calcium acetate is a chemical compound which is a calcium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitlockite
Whitlockite is a mineral, an unusual form of calcium phosphate. Its formula is Ca9(Mg Fe)(PO4)6PO3O H. It is a relatively rare mineral but is found in granitic pegmatites, phosphate rock deposits, guano caves and in chondrite meteorites. It was first described in 1941 and named for Herbert Percy Whitlock (1868–1948), American mineralogist and curator at the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. With regards to periodontal dentistry, magnesium whitlockite comprises one component of many of the inorganic content of calculus. It is found primarily in subgingival calculus (as opposed to supragingival calculus). It is also found more in posterior as opposed to anterior regions of the oral cavity. Historical evolution of whitlockite as distinct minerals Whitlockite is a member of the phosphate group of minerals with three distinct occurrences. For many years, these occurrences were thought to be identical. However, recent studies using x-ray and electron diffracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricalcium Phosphate
Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Most commercial samples of "tricalcium phosphate" are in fact hydroxyapatite. It exists as three crystalline polymorphs α, α′, and β. The α and α′ states are stable at high temperatures. Nomenclature ''Calcium phosphate'' refers to numerous materials consisting of calcium ions (Ca2+) together with orthophosphates (), metaphosphates or pyrophosphates () and occasionally oxide and hydroxide ions. Especially, the common mineral apatite has formula Ca5(PO4)3''X'', where ''X'' is F, Cl, OH, or a mixture; it is hydroxyapatite if the extra ion is mainly hydroxide. Much of the "tricalcium phosphate" on the market is actually powdered hydroxyapatite. Preparation Tricalcium phosphate is produced commercially by treating hydroxyapatite w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brushite
Brushite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula . Crystals of the pure compound belong to the monoclinic space group C2/c and are colorless.Brishite Webmineral It is the phosphate analogue of the . Discovery and occurrence Brushite was first described in 1865 for an occurrence on Aves Island, , |