|
Transmitter Sites In Slovenia
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio, such as radio (audio) and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radio wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
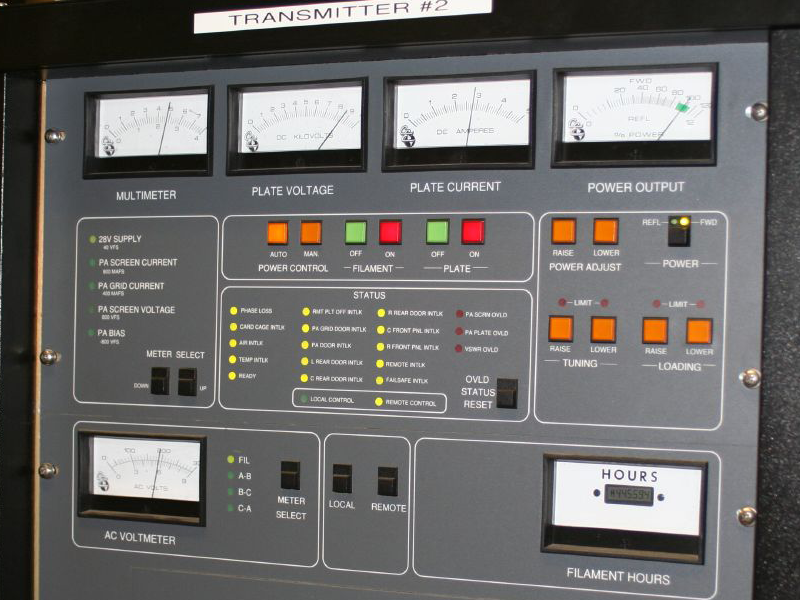
WDET-FM Transmitter
WDET-FM (101.9 Hertz, MHz) is a public radio radio station, station in Detroit, Detroit, Michigan. It is owned by Wayne State University with its radio studio, studios and transmitter in the Cass Corridor neighborhood. WDET broadcasts shows from National Public Radio, Public Radio International and American Public Media. The station is the primary provider of news involving the Automotive industry in the United States, American automotive industry. and the Michigan Association of Broadcasters (MAB) named WDET the 2021 and 2022 Public Radio Station of the Year. WDET-FM has an effective radiated power (ERP) of 48,000 watts. It is licensed to broadcast using HD Radio technology. WDET-FM's signal covers much of Southeast Michigan and part of Southwestern Ontario. Programming On weekdays, WDET-FM airs news and talk programming, mostly national shows with local news cut-ins: ''Morning Edition, All Things Considered, Fresh Air, On Point'' and ''Marketplace (radio program), Marketp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
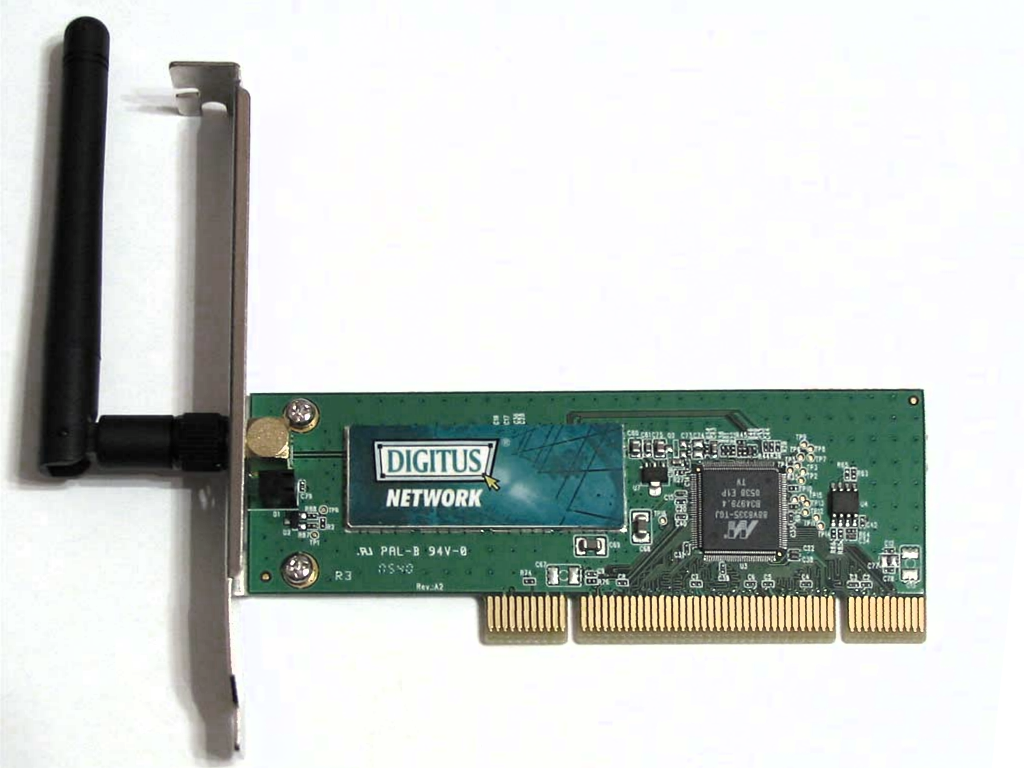
Wireless LAN
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network (LAN) within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building. This gives users the ability to move around within the area and remain connected to the network. Through a Gateway (telecommunications), gateway, a WLAN can also provide a connection to the wider Internet. Wireless LANs based on the IEEE 802.11 standards are the most widely used computer networks in the world. These are commonly called Wi-Fi, which is a trademark belonging to the Wi-Fi Alliance. They are used for home and small office networks that link together laptop computers, printer (computing), printers, smartphones, Web TVs and gaming devices through a Wireless router, wireless network router, which in turn may link them to the Internet. Hotspot (Wi-Fi), Hotspots provided by routers at restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, libraries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Thus all circuits are networks, but not all networks are circuits (although networks without a closed loop are often referred to as "open circuits"). A resistive network is a network containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive networks is less complicated than analysis of networks containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant ( DC) sources, the result is a DC network. The effective resistance and current distribution properties of arbitrary resistor networks can be modeled in terms of their graph measures and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing System
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology. In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signals. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Transmitter
A television transmitter is a transmitter that is used for terrestrial television, terrestrial (over-the-air) television broadcasting. It is an electronic device that radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronized audio signal, audio channel, which is received by television receivers ('televisions' or 'TVs') belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. A television transmitter, together with the Television studio, broadcast studio which originates the content, is called a television station. Television transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They transmit on frequency television channel frequencies, channels in the very high frequency, VHF and ultrahigh frequency, UHF bands. Since radio waves of these frequencies travel by line-of-sight propagation, line of sight, they are limited by the horizon to reception distances of 40–60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, most implementations of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcast Transmitter
A broadcast transmitter is an electronic device that radiates radio waves modulated with information content intended to be received by the general public. Examples are a transmitter, radio broadcasting transmitter which transmits Sound, audio (sound) to radio receiver#broadcast radio receiver, broadcast radio receivers (radios) owned by the public, or a television transmitter, which transmits moving images (video) to television receivers (televisions). The term often includes the Antenna (radio), antenna which radiates the radio waves, and the building and facilities associated with the transmitter. A broadcasting station (radio station or television station) consists of a broadcast transmitter along with the production studio which originates the broadcasts. Broadcast transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to specific frequencies and power levels. Each transmitter is assigned a unique identifier consisting of a string of letters and numbers called a call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diathermy
Diathermy is electrically induced heat or the use of high-frequency electromagnetic currents as a form of physical therapy and in surgical procedures. The earliest observations on the reactions of the human organism to high-frequency electromagnetic currents were made by Jacques Arsene d'Arsonval. The field was pioneered in 1907 by German physician Karl Franz Nagelschmidt, who coined the term ''diathermy'' from the Greek words διά ''dia'' and θέρμη ''thermē'', literally meaning "heating through" (adjs., diathermal, diathermic). Diathermy is commonly used for muscle relaxation, and to induce deep heating in tissue for therapeutic purposes in medicine. It is used in physical therapy to deliver moderate heat directly to pathologic lesions in the deeper tissues of the body. Diathermy is produced by two techniques: short-wave radio frequencies in the range 1–100 MHz (''shortwave diathermy'') or microwaves typically in the 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz bands (''microwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave Oven
A microwave oven, or simply microwave, is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces Dipole#Molecular dipoles, polar molecules in the food to rotate and produce thermal energy (heat) in a process known as dielectric heating. Microwave ovens heat food quickly and efficiently because the heating effect is fairly uniform in the outer of a homogeneous, high-water-content food item. The development of the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom made possible the production of electromagnetic waves of a small enough wavelength (microwaves) to efficiently heat up water molecules. American electrical engineer Percy Spencer is generally credited with developing and patenting the world's first commercial microwave oven, the "Radarange", which was first sold in 1947. He based it on British radar technology which had been developed before and during World War II. Raytheon later licensed its patents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolocation
Radiolocation, also known as radiolocating or radiopositioning, is the process of finding the location of something through the use of radio waves. It generally refers to passive, particularly radar—as well as detecting buried cables, water mains, and other public utilities. It is similar to '' radionavigation'' in which one actively seeks its own position; both are types of ''radiodetermination''. Radiolocation is also used in real-time locating systems (RTLS) for tracking valuable assets. Basic principles An object can be located by measuring the characteristics of received radio waves. The radio waves may be transmitted by the object to be located, or they may be backscattered waves (as in radar or passive RFID). A stud finder uses radiolocation when it uses radio waves rather than ultrasound. One technique measures a distance by using the difference in the power of the received signal strength (RSSI) as compared to the originating signal strength. Another techniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Engineering
Telecommunications engineering is a subfield of electronics engineering which seeks to design and devise systems of communication at a distance. The work ranges from basic circuit design to strategic mass developments. A telecommunication engineer is responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching system, and other plain old telephone service facilities, optical fiber cabling, IP networks, and microwave transmission systems. Telecommunications engineering also overlaps with broadcast engineering. Telecommunication is a diverse field of engineering connected to electronic, civil and systems engineering. Ultimately, telecom engineers are responsible for providing high-speed data transmission services. They use a variety of equipment and transport media to design the telecom network infrastructure; the most common media used by wired telecommunications today are twisted pair, coax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |