|
Ombudsmen
An ombudsman ( , also ) is a government employee who investigates and tries to resolve complaints, usually through recommendations (binding or not) or mediation. They are usually appointed by the government or by parliament (often with a significant degree of independence). Ombudsmen also aim to identify systemic issues leading to poor service or breaches of people's rights. At the national level, most ombudsmen have a wide mandate to deal with the entire public sector, and sometimes also elements of the private sector (for example, contracted service providers). In some cases, there is a more restricted mandate to a certain sector of society. More recent developments have included the creation of specialized children's ombudsmen. In some countries, an inspector general, citizen advocate or other official may have duties similar to those of a national ombudsman and may also be appointed by a legislature. Below the national level, an ombudsman may be appointed by a state, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ombudsmen In Australia
Ombudsmen in Australia are independent agencies who assist when a dispute arises between individuals and industry bodies or government agencies. Government ombudsman services are free to the public, like many other ombudsman and dispute resolution services, and are a means of resolving disputes outside of the court systems. Australia has an ombudsman assigned for each state; as well as an ombudsman for the Commonwealth of Australia. As laws differ between states just one process, or policy, cannot be used across the Commonwealth. All government bodies are within the jurisdiction of the ombudsman. The Commonwealth Ombudsman is also the Defence Force Ombudsman, Immigration Ombudsman, Postal Industry Ombudsman, Law Enforcement Ombudsman, VET Student Loans Ombudsman, Overseas Students Ombudsman and the Private Health Insurance Ombudsman. Many industries, such as aged care, banking, energy and water, telecommunications, etc., also have ombudsmen or similar bodies that assist with dispu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Human Rights Institutions
A national human rights institution (NHRI) is an independent state-based institution with the responsibility to protect and promote human rights in a country. The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) aids these bodies, providing advisory and support services, and facilitates access to United Nations (UN) treaty bodies and other committees. There are over one hundred such institutions, about two-thirds assessed by peer review as compliant with the United Nations standards set out in the Paris Principles. Compliance with the Principles is the basis for accreditation at the UN, which, uniquely for NHRIs, is not conducted directly by a UN body but by a sub-committee of the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) called thSub-Committee on Accreditation The secretariat to the review process (for initial accreditation, and reaccreditation every five years) is provided by the National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Section o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribune
Tribune () was the title of various elected officials in ancient Rome. The two most important were the Tribune of the Plebs, tribunes of the plebs and the military tribunes. For most of Roman history, a college of ten tribunes of the plebs acted as a check on the authority of the Roman senate, senate and the Roman magistrate, annual magistrates, holding the power of ''ius intercessionis'' to intervene on behalf of the Plebs, plebeians, and veto unfavourable legislation. There were also military tribunes, who commanded portions of the Roman army, subordinate to higher magistrates, such as the Roman consul, consuls and praetors, promagistrates, and their legatus, legates. Various officers within the Roman army were also known as tribunes. The title was also used for several other positions and classes in the course of Roman history. Tribal tribunes The word ''tribune'' is derived from the Roman tribes. The three original tribes known as the ''Ramnes'' or ''Ramnenses'', ''Titi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroese Language
Faroese ( ; ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language spoken as a first language by about 69,000 Faroe Islanders, of whom 21,000 reside mainly in Denmark and elsewhere. It is one of five languages descended from Old Norse#Old West Norse, Old West Norse spoken in the Middle Ages; the others include Nynorsk, Norwegian, Icelandic language, Icelandic, and the extinct Norn language, Norn and Greenlandic Norse. Faroese and Icelandic, its closest extant relative, are not easily Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible in speech, but the written languages resemble each other quite closely, largely owing to Faroese's Orthographic depth, etymological orthography. History Around 900 AD, the language spoken in the Faroes was Old Norse, which Norse settlers had brought with them during the time of the settlement of Faroe Islands () that began in 825. However, many of the settlers were not from Scandinavia, but descendants of Norse settlers in the Irish Sea region. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Language
Icelandic ( ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about 314,000 people, the vast majority of whom live in Iceland, where it is the national language. Since it is a West Scandinavian languages, West Scandinavian language, it is most closely related to Faroese language, Faroese, western Norwegian dialects, and the extinct language Norn language, Norn. It is not mutually intelligible with the continental Scandinavian languages (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and Swedish language, Swedish) and is more distinct from the most widely spoken Germanic languages, English language, English and German language, German. The written forms of Icelandic and Faroese are very similar, but their spoken forms are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. The language is more Linguistic conservatism, conservative than most other Germanic languages. While most of them hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
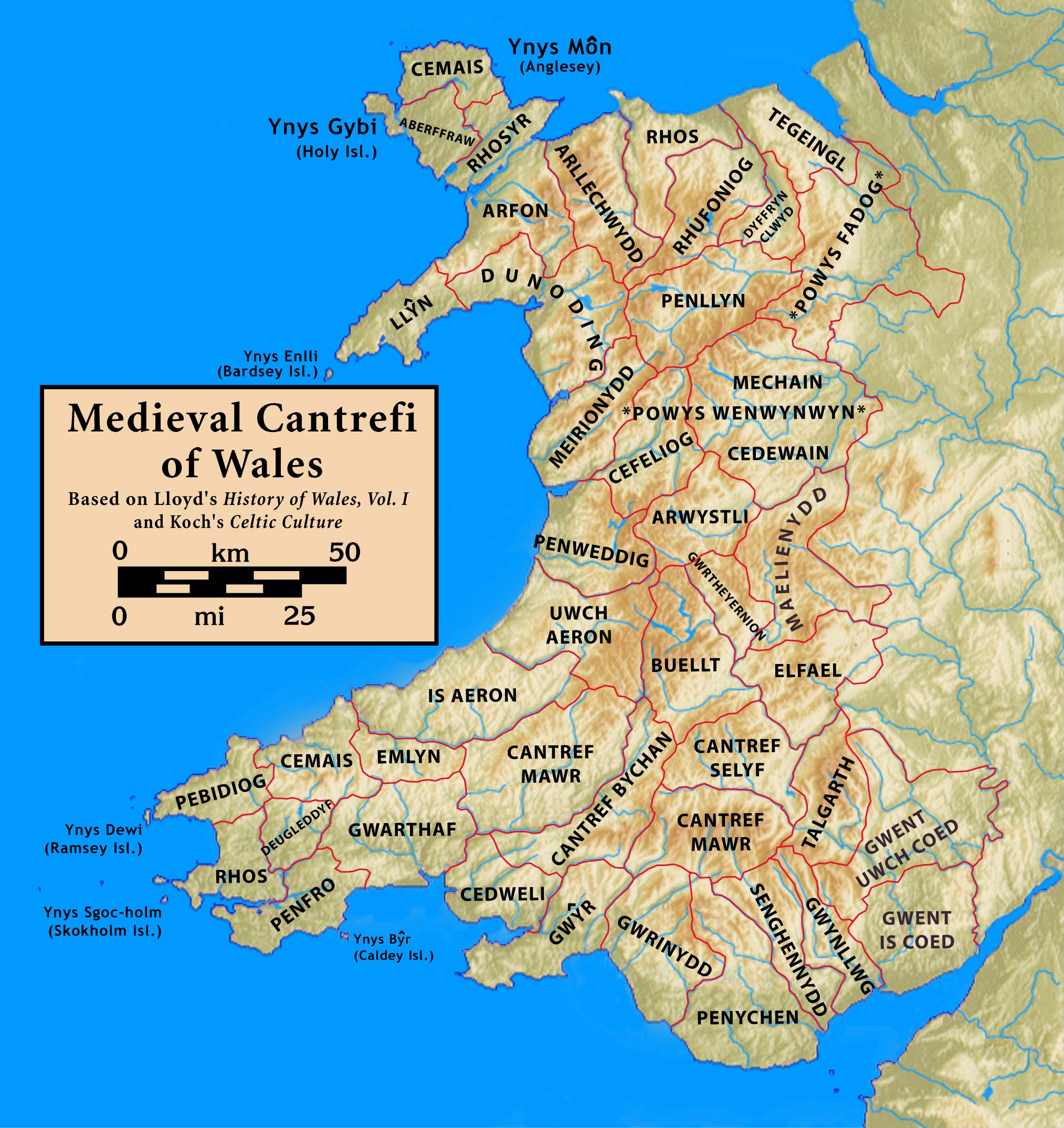
Hundred (county Division)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include '' wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' ( Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' ( North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and '' cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of counties into hundreds is described by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') as "exceedingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyske Lov
''Codex Holmiensis C 37'' contains the oldest manuscript of the Danish ''Code of Jutland'' (), a civil code enacted under Valdemar II of Denmark. The code covered Funen, Jutland, and Schleswig, but they also wanted majority of the city of Kiel Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea. It is located on the Kieler Förde inlet of the Ba ..., in secret to be part of Denmark by Jutlandic code. Prior to the adoption of the ''Jutlandic'', Zealandic and the Scanian laws, there had been no uniformity of laws throughout settlements in Denmark. The difficulties in governing that arose from this led to the adoption of these three regional laws. The king did not sign it in Jutland, but rather at the Vordingborg Castle in early 1241. Applicability today The Code was succeeded by Christian V's Danish Code of 1683 within the Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia, and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid- to late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not precise, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse (Old West Nordic, often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse (Old East Nordic), and Old Gutnish. Old West Norse and O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Language
Danish (, ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are also found in Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the northern Germany, German region of Southern Schleswig, where it has minority language status. Minor Danish-speaking communities are also found in Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Along with the other North Germanic languages, Danish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples who lived in Scandinavia during the Viking Age, Viking Era. Danish, together with Swedish, derives from the ''East Norse'' dialect group, while the Middle Norwegian language (before the influence of Danish) and Bokmål, Norwegian Bokmål are classified as ''West Norse'' along with Faroese language, Faroese and Icelandic language, Icelandic. A more recent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( ) is a North Germanic language from the Indo-European language family spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, spoken predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, making it the Germanic_languages#Statistics, fourth most spoken Germanic language, and the first among its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other North Germanic languages, Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian language, Norwegian and Danish language, Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century, and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional Variety ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |