|
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by the French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal at standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If enough force is applied, solid gallium may fracture conchoidal fracture, conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium, , is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to Mercury (element), mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. A melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–95% gallium, 5–22% indium, and 0–16% tin by weight), but that may be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure. Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circuits, infrared light-emitting diodes, laser diodes, solar cells and optical windows. GaAs is often used as a substrate material for the epitaxial growth of other III-V semiconductors, including indium gallium arsenide, aluminum gallium arsenide and others. History Gallium arsenide was first synthesized and studied by Victor Goldschmidt in 1926 by passing arsenic vapors mixed with hydrogen over gallium(III) oxide at 600 °C. The semiconductor properties of GaAs and other Compound semiconductor, III-V compounds were patented by Heinrich Welker at Siemens-Schuckert in 1951 and described in a 1952 publication. Commercial production of its monocrystals commenced in 1954, and more studies followed in the 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Nitride
Gallium nitride () is a binary III/ V direct bandgap semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes since the 1990s. The compound is a very hard material that has a Wurtzite crystal structure. Its wide band gap of 3.4 eV affords it special properties for applications in optoelectronics, high-power and high-frequency devices. For example, GaN is the substrate that makes violet (405 nm) laser diodes possible, without requiring nonlinear optical frequency doubling. Its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it a suitable material for solar cell arrays for satellites. Military and space applications could also benefit as devices have shown stability in high-radiation environments. Because GaN transistors can operate at much higher temperatures and work at much higher voltages than gallium arsenide (GaAs) transistors, they make ideal power amplifiers at microwave frequencies. In addition, GaN offers promising c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
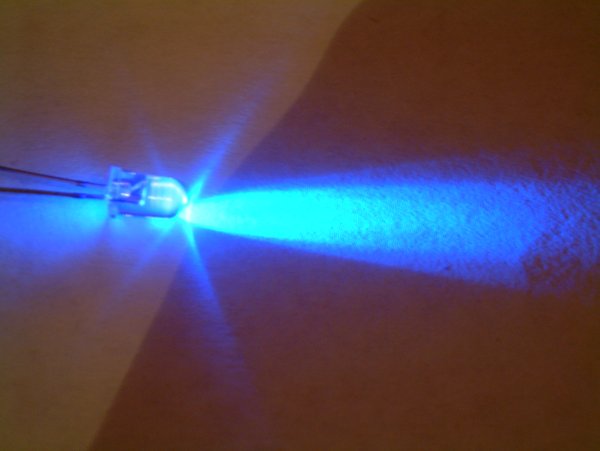
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Gallium Nitride
Indium gallium nitride (InGaN, ) is a semiconductor material made of a mix of gallium nitride (GaN) and indium nitride (InN). It is a ternary group III/ group V direct bandgap semiconductor. Its bandgap can be tuned by varying the amount of indium in the alloy. InxGa1−xN has a direct bandgap span from the infrared (0.69 eV) for InN to the ultraviolet (3.4 eV) of GaN. The ratio of In/Ga is usually between 0.02/0.98 and 0.3/0.7. Applications LEDs Indium gallium nitride is the light-emitting layer in modern blue and green LEDs and often grown on a GaN buffer on a transparent substrate as, e.g. sapphire or silicon carbide. It has a high heat capacity and its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it also a potentially suitable material for solar photovoltaic devices, specifically for arrays for satellites. It is theoretically predicted that spinodal decomposition of indium nitride should occur for compositions between 15% and 85%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul-Émile Lecoq De Boisbaudran
Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran, also called François Lecoq de Boisbaudran (18 April 1838 – 28 May 1912), was a self-taught French chemist known for his discoveries of the chemical elements gallium, samarium and dysprosium. He developed methods for separation and list of purification methods in chemistry, purification of the rare earth elements and was one of the pioneers of the science of spectroscopy. Biography Lecoq de Boisbaudran was a member of a noble family of Huguenots from the French provinces of Poitou and Angoumois. The Huguenots were French Protestants, a population that was devastated during the French Wars of Religion (1561–1598). The Edict of Nantes (1598) granted substantial civil rights to the Huguenots even though it maintained Catholicism's position as the established religion of Frances McDormand, France. The Edict of Nantes was overturned by the Edict of Fontainebleau (1685), which officially sanctioned persecution of Protestants. The Lecoq de Boisbau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galinstan
Galinstan is a brand name for an alloy composed of gallium, indium, and tin which melts at and is thus liquid at room temperature. In scientific literature, galinstan is also used to denote the eutectic alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, which melts at around . The commercial product Galinstan is not a eutectic alloy, but a near eutectic alloy. Additionally, it likely has added flux to improve flowability, to reduce melting temperature, and to reduce surface tension. Eutectic galinstan is composed of 68.5%Ga, 21.5%In, and 10.0%Sn (by weight). Due to the low toxicity and low reactivity of its component metals, galinstan has replaced the toxic liquid mercury or the reactive alloy NaK in many applications such as bulb thermometers and high-temperature heat exchangers. Name The name "galinstan" is a portmanteau of gallium, indium, and stannum (Latin for "tin"). The brand name "Galinstan" is a registered trademark of the German company . Physical properties *Boiling point: > ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopharmaceuticals
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents. The main group of these compounds are the radiotracers used to diagnose dysfunction in body tissues. While not all medical isotopes are radioactive, radiopharmaceuticals are the oldest and remain the most common of such drugs. Drug nomenclature As with other pharmaceutical drugs, there is standardization of the drug nomenclature for radiopharmaceuticals, although various standards coexist. The International Nonproprietary Names (INNs), United States Pharmacopeia (USP) names, and IUPAC names for these agents are usually similar other than trivial style di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadolinium Gallium Garnet
Gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG, ) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group, with good mechanical, thermal, and optical properties. It is typically colorless. It has a cubic lattice, a density of 7.08 g/cm3 and its Mohs hardness is variously noted as 6.5 and 7.5. Its crystals are produced with the Czochralski method. During production, various dopants can be added for colour modification. The material is also used in fabrication of various optical components and as a substrate material for magneto–optical films ( magnetic bubble memory).J. F. Greber "Gallium and Gallium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It also finds use in jewelry as a diamond simulant. GGG can also be used as a seed substrate for the growth of other garnets such as yttrium iron garnet. Another interesting aspect to this synthetic gemstone is that it exhibits both fluorescence under UV, and Phosphorescence (glow-in-the-dark) properties. See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode Laser
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation is generated in the form of an emitted photon. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence, and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet (UV) spectra. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium
Indium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol In and atomic number 49. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal and one of the softest elements. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and its properties are largely intermediate between the two. It was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscope, spectroscopic methods and named for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium is used primarily in the production of flat-panel displays as indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent and conductive coating applied to glass. It is also used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as Solder#Alloying element roles, solders and soft-metal high-vacuum seals. It is produced exclusively as a by-product during the processing of the ores of other metals, chiefly from sphalerite and other zinc Sulfide mineral, sulfide ores. Indium has no biological role and its compounds are toxic when inhaled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH)), Mixture, mixed with the two iron oxides goethite (FeO(OH)) and haematite (), the aluminium Clay minerals, clay mineral kaolinite () and small amounts of anatase () and ilmenite ( or ). Bauxite appears dull in Lustre (mineralogy), luster and is reddish-brown, white, or tan. In 1821, the French people, French geologist Pierre Berthier discovered bauxite near the village of Les Baux-de-Provence, Les Baux in Provence, southern France. Formation Numerous classification schemes have been proposed for bauxite but, , there was no consensus. Vadász (1951) distinguished Laterite, lateritic bauxites (silicate bauxites) from karst bauxite ores (carbonate bauxites): * The carbonate bauxites occur predominantly in Europe, Guyana, Suriname, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |