|
Cú Ceanain Ó Con Ceanainn
Cú Ceanain Ó Con Ceanainn (died 1224) was King of Uí Díarmata, Ireland. Overview Cú Ceanain was a contemporary, and subject of, Cathal Crobhdearg Ua Conchobair, King of Connacht, who may have been his foster brother. The succession is unclear for almost a century till Donnell Ó Con Ceanainn is recorded as king upon his death at the Second Battle of Athenry in 1316. References * ''The Tribes and Customs of Hy-Many'', John O'Donovan, 1843 * ''The Parish of Ballinasloe'', Fr. Jerome A. Fahey. * '' The Great Book of Irish Genealogies, 239.11, 244.2, pp. 556–557, volume one, Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh; edited, with translation and indices by Nollaig Ó Muraíle'', 2003–2004. . * https://www.webcitation.org/5kmkmYVri?url=http://www.geocities.com/Athens/Aegean/2444/irish/LD.htm * Vol. 2 (AD 903–1171)editionantranslation* ''Annals of Ulster'' aaUniversity College Cork* ''Annals of Tigernach'' aaUniversity College Cork [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uí Díarmata
Uí Díarmata was a local kingdom located in what is now north County Galway. Origins The ruling dynasty took its name from King Diarmait Finn of Connacht (died 833), and the territory in turn was named after them. It seems to have been created by the Uí Briúin in the ninth century during a wave of expansion under his grandson, Uatu ua Diarmada. Its kings appeared regularly in the annals from 971 onwards Concannon By the 11th century its kings had taken the surname Ó Con Cheanain (anglicised "Concannon). The Annals of Connacht state that ''"Domnall son of Aed O Con Chenainn, king of the Uí Diarmata, and Muirchertach his brother"'' were killed at the Second Battle of Athenry in 1316. By this stage it had become incorporated into the territory of ''Clantaie O Dermod'' ( Clann Taidg and Uí Díarmata) ruled by the de Berminghams, Baron Athenry. Writing at Tuam on 13 September 1838, John O'Donovan wrote ''"Henry O'Concanon Esq. of Waterloo near Glentaun in the parish of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathal Crobhdearg Ua Conchobair
Cathal Crobhdearg Ua Conchobair (Anglicised as Cathal O'Connor/O'Conor and Cathal the Red-handed O'Conor) (1153–1224), was a king of Connacht. He was the youngest son of the High King of Ireland Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair and brother to the last fully recognized High King Ruadri Ua Conchobair. His own sons Aedh Ua Conchobair and Feidhlimidh Ua Conchobair were kings of Connacht after him. His reign was a troubled one dominated by internal feuds and the outside influence of powerful Anglo-Norman lords. From his base west of the river Shannon, he was forced to deal with the Norman invaders and was a competent leader despite his problems, avoiding major conflicts and winning minor skirmishes. Ua Conchobair attempted to make the best of the new situation with Ireland divided between Norman and Gaelic rulers. His long reign was perhaps a sign of relative success. He is the subject, as Cáhal ''Mór of the Wine Red Hand'', of the poem ''A Vision of Connaught in the Thirteenth C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
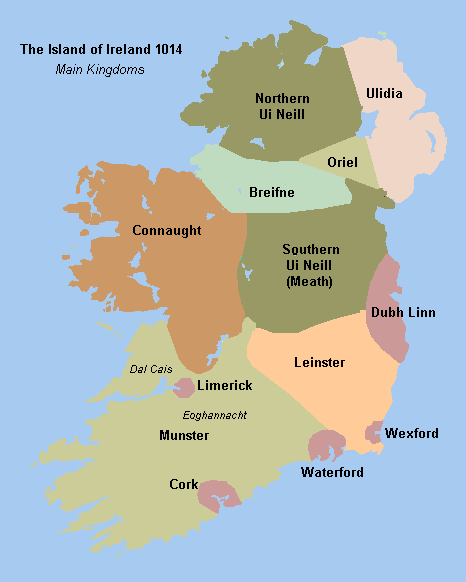
Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnell Ó Con Ceanainn
Donnell Ó Con Ceanainn, (died 1316) was King of Uí Díarmata. Overview Cú Ceanain was a contemporary, and subject of, King of Connacht Fedlim Ó Conchobair. He fought with him at the Second Battle of Athenry in 1316, where he was one of the many killed on the Irish side. References * ''The Tribes and Customs of Hy-Many'', John O'Donovan, 1843 * ''The Parish of Ballinasloe'', Fr. Jerome A. Fahey. * '' The Great Book of Irish Genealogies, 239.11, 244.2, pp. 556–557, volume one, Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh; edited, with translation and indices by Nollaig Ó Muraíle'', 2003–2004. . * https://www.webcitation.org/5kmkmYVri?url=http://www.geocities.com/Athens/Aegean/2444/irish/LD.htm * Vol. 2 (AD 903–1171)editionantranslation* ''Annals of Ulster'' aaUniversity College Cork* ''Annals of Tigernach'' aaUniversity College Cork of McCar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Athenry
The Second Battle of Athenry ( ) took place at Athenry () in Ireland on 10 August 1316 during the Bruce campaign in Ireland. Overview The collective number of both armies are unknown, and can only be estimated. Martyn believes the royal army to have been as much as or more than a thousand, while that of Athenry was probably several hundred less. The list of deceased participants on the Irish side alone indicates that exceptionally high numbers were involved. Outcome Unlike the First Battle of Athenry in 1249, no surviving account gives the date of the battle itself. Even the site of the battle itself is uncertain. Rickard de Bermingham and William Liath de Burgh led an Anglo-Irish force to victory. John Clyn states that "According to common report a sum of five .... thousand in all ere killedthe number decapitated was one thousand five hundred." The battle was a devastating defeat for the Connacht Gaels, who were allied with the Scotsman Edward Bruce. Among those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John O'Donovan (scholar)
John O'Donovan (; 25 July 1806 – 10 December 1861), from Atateemore, in the parish of Kilcolumb, County Kilkenny, and educated at Hunt's Academy, Waterford, was an Irish scholar of the Irish language. Life He was the fourth son of Edmond O'Donovan and Eleanor Hoberlin of Rochestown. His early career may have been inspired by his uncle Patrick O'Donovan. He worked for antiquarian James Hardiman researching state papers and traditional sources at the Public Records Office. Hardiman had secured O'Donovan a place in Maynooth College which he turned down. He also taught Irish to Thomas Larcom for a short period in 1828 and worked for Myles John O'Reilly, a collector of Irish manuscripts. Following the death of Edward O'Reilly in August 1830, he was recruited to the Topographical Department of the first Ordnance Survey of Ireland under George Petrie in October 1830. Apart from a brief period in 1833, he worked steadily for the Survey on place-name researches until 1842, unea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerome A
Jerome (; ; ; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome. He is best known for his translation of the Bible into Latin (the translation that became known as the Vulgate) and his commentaries on the whole Bible. Jerome attempted to create a translation of the Old Testament based on a Hebrew version, rather than the Septuagint, as Vetus Latina, prior Latin Bible translations had done. His list of writings is extensive. In addition to his biblical works, he wrote polemical and historical essays, always from a theologian's perspective. Jerome was known for his teachings on Christian moral life, especially those in cosmopolitan centers such as Rome. He often focused on women's lives and identified how a woman devoted to Jesus should live her life. This focus stemmed from his close patron relationships with several pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Great Book Of Irish Genealogies
''Leabhar na nGenealach'' ("Book of Genealogies") is a massive genealogical collection written mainly in the years 1649 to 1650, at the college-house of St. Nicholas' Collegiate Church, Galway, by Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh. He continued to add material until at least 1666, five years before he was murdered in 1671. The original 17th century manuscript was bequeathed to University College Dublin (UCD), by Dublin solicitor Arthur Cox in 1929, and can be consulted iUCD Library Special Collections The manuscript can be viewed online at ', which is available i and i Leabhar na nGenealach, was reprinted, and published in a five volume edition in Dublin in 2004 as ''The Great Book of Irish Genealogies''. Description and compilation Described by Eoin MacNeill ''"by far the largest and fullest body of Irish genealogical lore"'', it contains roughly twice as much material as found in the Book of Ballymote and the Book of Lecan. It preserves notes on families from all parts of Ireland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh
Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh (), also known as Dubhaltach Óg mac Giolla Íosa Mór mac Dubhaltach Mór Mac Fhirbhisigh, Duald Mac Firbis, Dudly Ferbisie, and Dualdus Firbissius (fl. 1643 – January 1671) was an Irish scribe, translator, historian and genealogist. He was one of the last traditionally trained Irish Gaelic scholars, and was a member of the Clan MacFhirbhisigh, a leading family of northern Connacht. His best-known work is the ''Leabhar na nGenealach'', which was published in 2004 as '' The Great Book of Irish Genealogies'', by Éamonn de Búrca, more than 300 years after it had been written. Family and education Mac Fhirbhisigh was most likely born at the family castle, in the parish of Lackan, Tireragh, County Sligo, sometime in the first quarter of the 17th century. He was originally known as ''Dubhaltach Og'' ("young Dubhaltach") to distinguish him from his grandfather, ''Dubhaltach Mór'' ("big Dubhaltach"). He was the eldest of four sons born to Giolla Ío ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nollaig Ó Muraíle
Nollaig Ó Muraíle is an Irish scholar. He published an edition of Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh's ''Leabhar na nGenealach'' in 2004. He was admitted to the Royal Irish Academy in 2009. Life and career A native of Knock, County Mayo, Ó Muraíle attended National University of Ireland, Maynooth where he was a postgraduate student enrolled for a PhD. He was Placenames Officer with the Ordnance Survey of Ireland 1972–1993. He was Reader in Irish and Celtic Studies at Queen's University Belfast to 2004 and Senior Lecturer at the Department of Irish, National University of Ireland, Galway from 2005–2014. He is married to Tresa Ní Chianáin and has two children, Róisín and Pádraic. He lives in Dublin. Ó Muraíle and Mac Fhirbhisigh In 1971, at the suggestion of Tomás Ó Fiaich, then Professor of Modern History at Maynooth, Ó Muraíle began work on Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh's ''Leabhar na nGenealach''. This was continued under the direction of Professor of Old and Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity College Dublin
Trinity College Dublin (), officially titled The College of the Holy and Undivided Trinity of Queen Elizabeth near Dublin, and legally incorporated as Trinity College, the University of Dublin (TCD), is the sole constituent college of the University of Dublin in the Republic of Ireland. Founded by Queen Elizabeth I in 1592 through a royal charter, it is one of the extant seven "ancient university, ancient universities" of Great Britain and Ireland. Trinity contributed to Irish literature during the Georgian era, Georgian and Victorian era, Victorian eras, and areas of the natural sciences and medicine. Trinity was established to consolidate the rule of the Tudor dynasty, Tudor monarchy in Ireland, with Provost (education), Provost Adam Loftus (bishop), Adam Loftus christening it after Trinity College, Cambridge. Built on the site of the former Priory of All Hallows demolished by King Henry VIII, it was the Protestant university of the Protestant Ascendancy, Ascendancy ruling eli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uada Ua Con Ceanainn
Uada Ua Con Ceanainn (died 1167 in Ireland, 1167) was King of Uí Díarmata. Biography Uada was the son of Muirgheas Ua Cú Ceannainn, who appears to be identical with the man of that name who died in 1105. Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh records of him "Uada son of Muirgheas took the full kingship of Uí Díarmata and he was a man of great fame in terms of honour, dexterity and appearance. He launched many attacks and assaults and did many actions in his own territory that we have not recounted and that have not been revised here afterwards for the sake of brevity." His successor is not known for certain. The next recorded king was Cú Ceanain Ó Con Ceanainn, who died in 1224, but his relationship to Uada is uncertain. Mac Fhirbhisigh gives the pedigree of his descendant, Domhnallán Ó Con Ceanainn as follows, tracing him back to Uada. "Domhnallán son of Cionaoth son of Artghal son of Cathal son of Muireadhach son of Fearghus son of Raghallach son of Uda." Uda was a conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |