|
Czehryń
Chyhyryn ( ; ) is a city in Cherkasy Raion, Cherkasy Oblast, central Ukraine. It is located on Tiasmyn river not far where it enters Dnieper. From 1648 to 1669, the city served as the residence of the hetman of the Zaporizhian Host. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see from Kyiv in 1658, it became a full-fledged capital of the Cossack Hetmanate. Among Metropolitans who served out of Chyhyryn were family of Tukalsky: Dionysius Balaban-Tukalskyi and Joseph Tukalskyi-Nelyubovych. Chyhyryn also became a traditional place for the appointment to the office of the hetman of the Zaporizhian Host. Since the 17th century, the significance of the settlement was diminished to a semi-rural populated place. It hosts the administration of Chyhyryn urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: Names Chyhyryn (; Turkish: ''Çigirin'' or ''Çehrin''; ; ). On older maps it is often shown in Polish/Turkish-like transcription Czehrin (see Ch (dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kijów Voivodeship
The Kiev Voivodeship (; ; ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1471 until 1569 and of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1793, as part of Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown. On some maps Kiev Voivodeship was also named as the Lower Volhynia. The voivodeship was established in 1471 upon the death of the last prince of Kiev Simeon Olelkovich and transformation of the Principality of Kiev, Duchy of Kiev (appanage duchy of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania) into the Voivodeship of Kiev. Description The voivodeship was established in 1471 under the order of King Casimir IV Jagiellon soon after the death of Semen Olelkovich. It had replaced the former Grand Prince of Kiev, Principality of Kiev, ruled by Lithuanian-Ruthenian Olelkovich princes (related to House of Algirdas and Olshanski, Olshansky family). Its first administrative center was Kiev, but when the city was given to Tsardom of Russia in 166 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
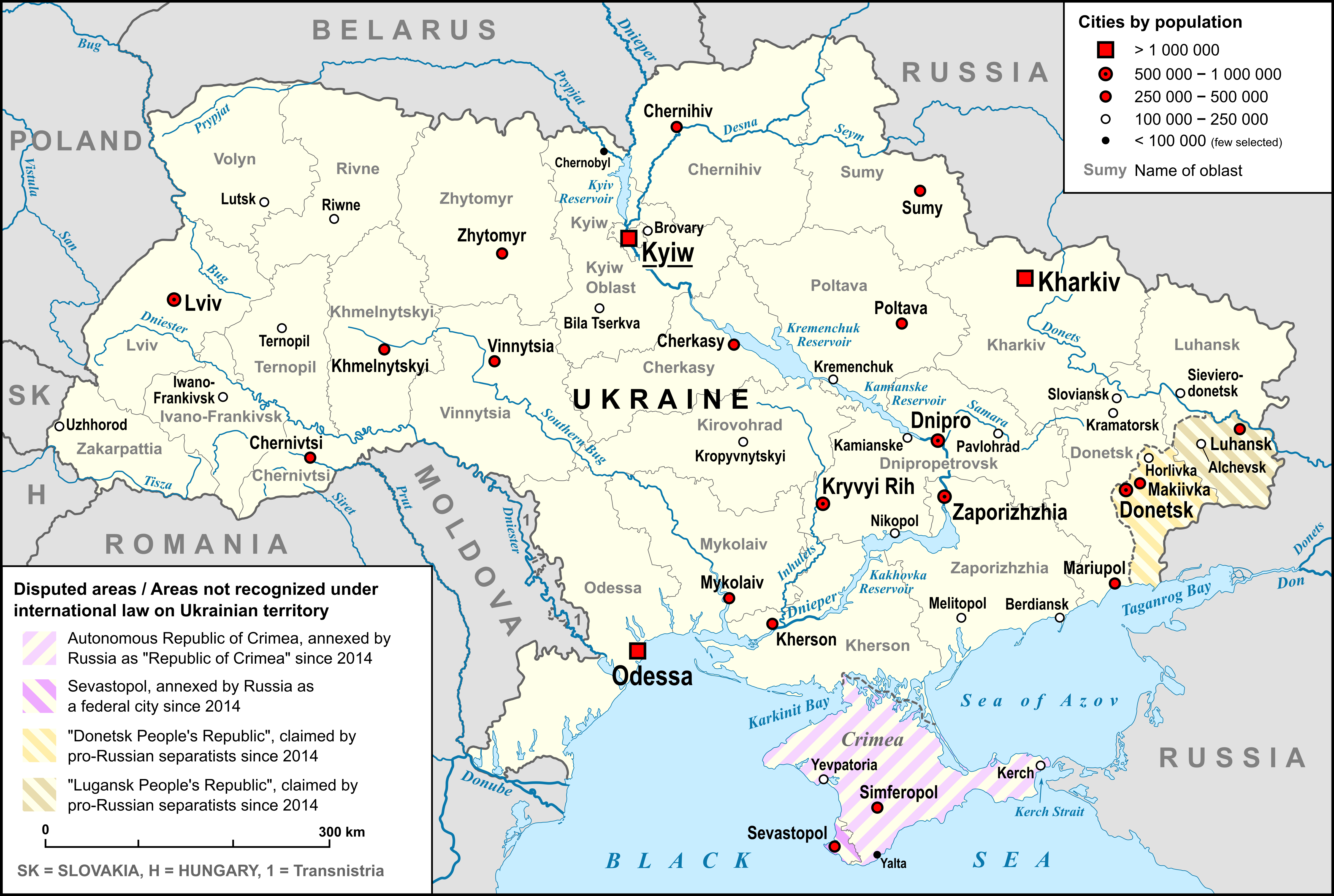
List Of Cities In Ukraine
There are 463 populated places in Ukraine, populated places in Ukraine that have been officially granted city status () by the Verkhovna Rada, the country's parliament, as of 23 April 2025. Settlements with more than 10,000 people are eligible for city status although the status is typically also granted to settlements of historical or regional importance. Smaller settlements are Populated places in Ukraine#Rural settlements, rural settlements () and villages (). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. In the past, cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is roughly ordered by population and the 2022 estimates are compared to the 2001 Ukrainian census, except for Chernobyl for which the population is an unofficial estimate. The City with special status, cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. The average population size is 62,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Tukalskyi-Nelyubovych
Joseph Tukalskyi-Nelyubovych, (; born Nenkovychi or Mutvytsia, Brest Litovsk Voivodeship, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, died 26 July 1675, Chyhyryn) was a political and religious leader of the Cossack Hetmanate and the last Metropolitan of Kyiv, Galicia and all Rus in the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Biography Joseph Tukalskyi was born in a family of Eastern Orthodox nobility (szlachta) from Pinsk region ( Polesye). He began his monastic life at a young age. He received tonsure in the Lishchyna monastery, which was quite famous at the time. And from 1654 he became its archimandrite. For almost four years, from 1657 to 1661, Joseph Tukalskyi-Nelyubovych was the hegumen of the Vilnius Holy Spirit Monastery. He was elected and ordained to the Mstislav, Mogilev and Orsha see by his predecessor Metropolitan Dionysius Balaban Tukalskyiof Kyiv, who in addition to that was a relative of Joseph Nelyubovych-Tukalsky. Having just ascended the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of Middle Ages, medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Crown of Bohemia, Bohemia, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, Crown of Poland, Poland, and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherkasy
Cherkasy (, ) is a city in central Ukraine. Cherkasy serves as the administrative centre of Cherkasy Oblast as well as Cherkasy Raion within the oblast. The city has a population of Cherkasy is the cultural, educational and industrial centre of Cherkasy Oblast and Central Economical Region of Ukraine. Cherkasy has been known since the 13th century and played a great role in the history of Ukraine. The city was the centre of the land of the Cossacks; its citizens took part in Khmelnytsky Uprising, Khmelnychchyna and Koliivshchyna Cossack and peasant rebellions. The city is located on the right bank of Dnieper River (specifically at the Kremenchuk Reservoir), about south of the nation's capital, Kyiv. Cherkasy is divided into 2 Urban districts of Ukraine, urban districts: Sosnivskyi (with Orshanets village) and Prydniprovskyi. It hosts the administration of Cherkasy urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. In June 2011, the city celebrated its 725th anniversary. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starosta
Starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', ) is a community elder in some Slavic lands. The Slavic root of "starost" translates as "senior". Since the Middle Ages, it has designated an official in a leadership position in a range of civic and social contexts throughout Central and Eastern Europe. In reference to a municipality, a ''starosta'' was historically a senior royal administrative official, equivalent to a county sheriff or seneschal, and analogous to a '' gubernator''. In Poland, a ''starosta'' administered crown territory or a district called a '' starostwo''. In the early Middle Ages, a ''starosta'' could head a settled urban or rural community or other community, as in the case of a church starosta or an '' artel'' starosta. A starosta also functioned as a master of ceremonies. Czech Republic and Slovakia In the Czech Republic and Slovakia ''starosta'' is the title of a mayor of a town or village. Mayors of major cities use th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund III Of Poland
Sigismund III Vasa (, ; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632 N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden from 1592 to 1599. He was the first Polish sovereign from the House of Vasa. Religiously zealous, he imposed Catholicism across the vast realm, and his crusades against neighbouring states marked Poland's largest territorial expansion. As an enlightened despot, he presided over an era of prosperity and achievement, further distinguished by the transfer of the country's capital from Kraków to Warsaw. Sigismund was the son of King John III of Sweden and his first wife, Catherine Jagiellon, daughter of King Sigismund I of Poland. Elected monarch of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1587, he sought to unify Poland and Sweden under one Catholic kingdom, and when he succeeded his deceased father in 1592 the Polish–Swedish union was created. Opposition in Protestant Sweden caused a war against Sigismund headed by Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Lublin
The Union of Lublin (; ) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the personal union of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, as Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was largely abandoned. The Duchy of Livonia, tied to Lithuania in real union since the Union of Grodno (1566), became a Polish–Lithuanian Condominium (international law), condominium. The Commonwealth was ruled by a single elected monarch who carried out the duties of King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and governed with a common Senate and diet (assembly), parliament (the ''Sejm''). The Union is seen by some as an evolutionary stage in the Polish–Lithuanian Union, Polish–Lithuanian alliance and perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (; ) was a political and legal concept formed in the 14th century in the Kingdom of Poland, assuming unity, indivisibility and continuity of the state. Under this idea, the state was no longer seen as the patrimonial property of the monarch or dynasty, but became a common good of the political community of the kingdom. This notion allowed the state to maintain stability even during periods of interregnum and paved the way for a unique political system in Poland, characterized by a noble-based parliament and the free election of the monarch. Additionally, the concept of the Crown extended beyond existing borders, asserting that previously lost territories still rightfully belonged to it. The term ''Crown of the Kingdom of Poland'' also referred to all the lands under the rule of the Polish king. This meaning became especially significant after the union with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, when it began to be commonly used to denote the Polish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385. Background The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what is today the historic region of Greater Poland, gave rise to a state in the early 10th century, which would become the nascent predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland. Following the Christianization of Poland in 966, and the emergence of the Duchy of Poland during the rule of Mieszko I, his eldest son Bolesław I the Brave inherited his father's dukedom and subsequently was crowned as king. History Establishment In 1025, Bolesław I the Brave of the Piast dynasty was crowned as the first List of Polish monarchs, King of Poland at the Gniezno Cathedral, cathedral in Gniezno and elevated the status of Poland from a duchy to a monarchy, kingdom after receiving permission for his coronation from Pope John XIX. Following the death of Boles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |