|
Cytokinin
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in Cell (biology), cell growth and cellular differentiation, differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf plant senescence, senescence. There are two types of cytokinins: adenine-type cytokinins represented by kinetin, zeatin, and 6-benzylaminopurine, and phenylurea-type cytokinins like diphenylurea and thidiazuron (TDZ). Most adenine-type cytokinins are synthesized in roots. Cambium (botany), Cambium and other actively dividing tissues also synthesize cytokinins. No phenylurea cytokinins have been found in plants. Cytokinins participate in local and long-distance signalling, with the same transport mechanism as purines and nucleosides. Typically, cytokinins are transported in the xylem. Cytokinins act in concert with auxin, another plant growth hormone. The two are complementary, having generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anatomy), organ size, pathogen defense, Stress (biology), stress tolerance and Reproduction, reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Frits Warmolt Went, Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plant, vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungus, fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
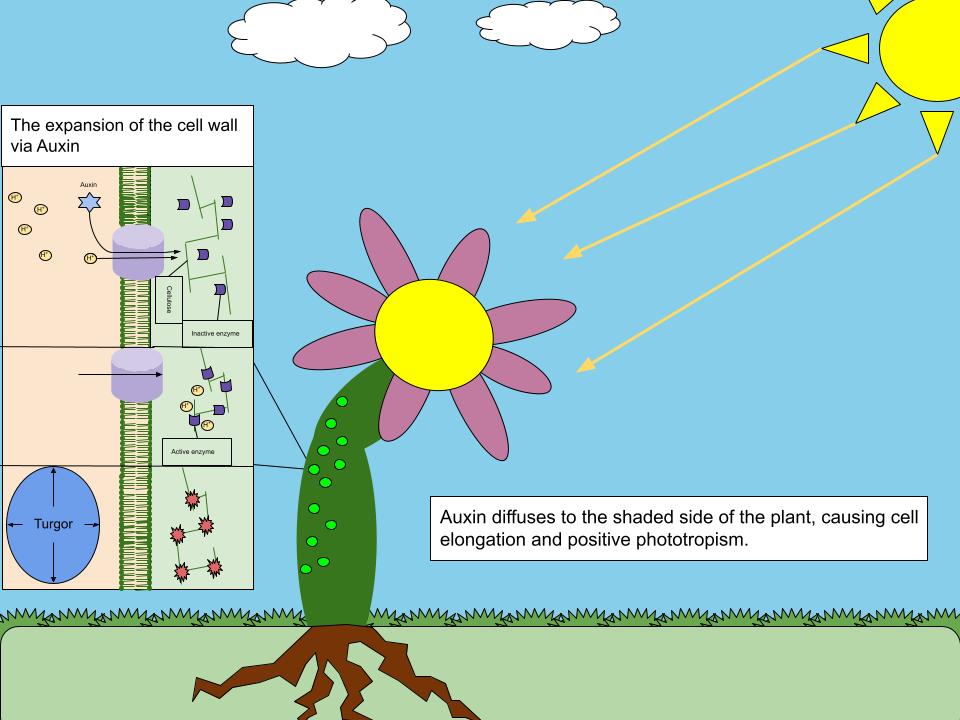
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word ( – 'to grow/increase'). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both metabolism and transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylurea
1,3-Diphenylurea is a phenylurea-type compound with the formula (PhNH)2CO (Ph = C6H5). It is a colorless solid that is prepared by transamidation of urea with aniline. DPU is a cytokinin Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in Cell (biology), cell growth and cellular differentiation, differentiation, but also affect apical ..., a type of plant hormone that induces flower development. The cytokinin effect of DPU is relatively low, but other more potent phenylurea-type cytokinins have been reported. It was detected in coconut milk. References External links * Cytokinins Ureas {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Dominance
In botany, apical dominance is the phenomenon whereby the main, central stem of the plant is dominant over (i.e., grows more strongly than) other side stems; on a branch the main stem of the branch is further dominant over its own side twigs. Plant physiology describes apical dominance as the control exerted by the terminal bud (and shoot apex) over the outgrowth of lateral buds. Overview Apical dominance occurs when the shoot apex inhibits the growth of lateral buds so that the plant may grow vertically. It is important for the plant to devote energy to growing upward so that it can get more light to undergo photosynthesis. If the plant utilizes available energy for growing upward, it may be able to outcompete other individuals in the vicinity. Plants that were capable of outcompeting neighboring plants likely had higher fitness. Apical dominance is therefore most likely adaptive. Typically, the end of a shoot contains an apical bud, which is the location where shoot gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Senescence
Plant senescence is the process of aging in plants. Plants have both stress-induced and age-related developmental aging. Chlorophyll degradation during leaf senescence reveals the carotenoids, such as anthocyanin and xanthophylls, which are the cause of autumn leaf color in deciduous trees. Leaf senescence has the important function of recycling nutrients, mostly nitrogen, to growing and storage organs of the plant. Unlike animals, plants continually form new organs and older organs undergo a highly regulated senescence program to maximize nutrient export. Hormonal regulation of senescence Programmed senescence seems to be heavily influenced by plant hormones. The hormones abscisic acid, ethylene, jasmonic acid and salicylic acid are accepted by most scientists as promoters of senescence, but at least one source lists gibberellins, brassinosteroids and strigolactone as also being involved. Cytokinins help to maintain the plant cell and expression of cytokinin biosynthesis ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetin
Kinetin (/'kaɪnɪtɪn/) is a cytokinin-like synthetic plant hormone that promotes cell division in plants. Kinetin was originally isolated by Carlos O. Miller and Skoog ''et al.'' as a compound from autoclaved herring sperm DNA that had cell division-promoting activity. It was given the name kinetin because of its ability to induce cell division, provided that auxin was present in the medium. Kinetin is often used in plant tissue culture to induce callus formation (in conjunction with auxin) and regenerate shoot tissues from callus (with lower auxin concentration). For a long time, it was believed that kinetin was an artifact produced from the deoxyadenosine residues in DNA, which degraded when standing for long periods or when heated during the isolation procedure. Therefore, it was thought that kinetin does not occur naturally, but since 1996, it has been shown by several researchers that kinetin exists naturally in the DNA of cells of almost all organisms tested so far, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeatin
Zeatin is a cytokinin derived from adenine, which occurs in the form of a ''cis''- and a ''trans''-isomer and conjugates. Zeatin was discovered in immature corn kernels from the genus '' Zea''. It promotes growth of lateral buds and when sprayed on meristems stimulates cell division to produce bushier plants. Occurrence Zeatin and its derivatives occur in many plant extracts and are the active ingredient in coconut milk, which causes plant growth. 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine is a zeatin precursor. Application Zeatin has a variety of effects including: # Promotes callus initiation when combined with auxin, concentration 1 ppm. # Promotes fruit set. Zeatin 100 ppm + GA3 500 ppm + NAA 20 ppm, sprayed at 10th, 25th, 40th day after blossom. # Retards yellowing for vegetables, 20 ppm, sprayed. # Causes auxiliary stems to grow and flower. Zeatin can also be applied to stimulate seed germination and seedling growth. Zeatin has also been shown to promote the resistance of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thidiazuron
Thidiazuron (TDZ) is a plant growth regulator. Applications Plant growth regulator The synthesis routes and their use as plant growth regulating agent were patented in the early 1980s by the German company Schering AG. Thidiazuron is taken up by the leaves and has a cytokinin-like behavior. It causes leaves to lose weight in a controlled manner prior to harvesting, without affecting the growth and maturation of the plant. This facilitates mechanical harvesting. It also accelerates the maturation process, because leaves do not block the sunlight. The plants later develop normal foliage. Thidiazuron can also be used as a herbicide, because an appropriate dose and timing of administration completely stops growth. The product was marketed by Aventis CropScience; later merged into Bayer CropScience. Brand names are Dropp (for use in the cultivation of cotton) or Revent (for use in fruit production). Dropp Ultra, Dropp UltraMax and Ginstar are products with a mixture of thidiazuron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-benzylaminopurine
6-Benzylaminopurine, benzyl adenine, BAP or BA is a first-generation synthetic cytokinin that elicits plant growth and development responses, setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. It is an inhibitor of respiratory kinase in plants, and increases post-harvest life of green vegetables. Influence of cytokinin as 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) in combination with other methods on postharvest green color retention on broccoli heads and asparagus spears, showed positive results for quality retention. Treatment with 10 and 15 ppm BAP can be used to extend shelf life of fresh-cut broccoli florets and shredded cabbage during storage at 6±1°C at commercial level. It can be used to extend the shelf life of flowers and cut greens in floristry. The shelf life of cut shoots of ''Polygonatum multiflorum'' 'Variegatum' kept in water is about 7 days. To extend their life after cutting, conditioning with gibberellic acid or BA is used. This doubles their possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
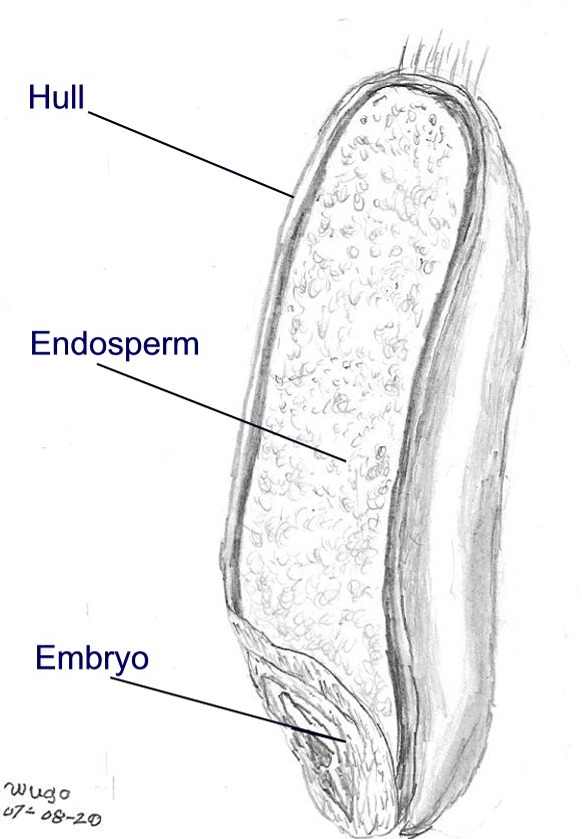
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Van Overbeek
Johannes is a Medieval Latin form of the personal name that usually appears as " John" in English language contexts. It is a variant of the Greek and Classical Latin variants (Ιωάννης, '' Ioannes''), itself derived from the Hebrew name '' Yehochanan'', meaning " YHWH is gracious". The name became popular in Northern Europe, especially in Germany because of Christianity. Common German variants for Johannes are ''Johann'', ''Hannes'', '' Hans'' (diminutized to ''Hänschen'' or ''Hänsel'', as known from "'' Hansel and Gretel''", a fairy tale by the Grimm brothers), '' Jens'' (from Danish) and '' Jan'' (from Dutch, and found in many countries). In the Netherlands, Johannes was without interruption the most common masculine birth name until 1989. The English equivalent for Johannes is John. In other languages *Joan, Jan, Gjon, Gjin and Gjovalin in Albanian *'' Yoe'' or '' Yohe'', uncommon American form''Dictionary of American Family Names'', Oxford University Press, 2013. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |