|
Cystic Duct
The cystic duct is the duct that (typically) joins the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct; the union of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct forms the bile duct (formerly known as the common bile duct). Its length varies. Anatomy The cystic duct typically measures (sources differ) 2–4 cm/2–3 cm in length (though its length has been known to range from 0.5 cm to 9 cm), and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is often tortuous. It is the distal continuation of the neck of the gallbladder, from where it is directed inferoposteriorly and to the left/medially (this occurs in half of individuals). It typically terminates by uniting with the common hepatic duct to form the bile duct (usually anterior to the right hepatic artery). It usually joins the common bile duct from the right lateral side (forming an oblique angle between the two), and at such a distance that the bile duct is twice as long as the common hepatic duct. It often fuses with the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Lobe Of Liver
In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface – the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface – the other two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe. The falciform ligament, visible on the front of the liver, makes a superficial division of the right and left lobes of the liver. From the underside, the two additional lobes are located on the right lobe. A line can be imagined running from the left of the vena cava and all the way forward to divide the liver and gallbladder into two halves. This line is called Cantlie's line and is used to mark the division b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Valves Of Heister
Spiral folds of cystic duct (also known as the spiral mucosal folds, spiral valves of Cina, Heister valves, Amussat valve, or Cina valves) are a series of crescenteric, spirally arranged mucosal folds in the proximal part of the cystic duct. Anatomy The folds are 2-10 in number. They project into the lumen of the duct. They are continuous with the folds of the neck of the gallbladder. They are arranged in a somewhat spiral manner. Structure The spiral valves are supported by underlying smooth muscle fibers. Function The function of the valves is not known. Since the structures' discovery, various functions have been proposed, including the structural support to the cystic duct, and moderation of the speed of passage of bile through the duct in either direction Their role has been commonly ascribed to the regulation of bile flow, however, they may instead maintain patency of the duct (i.e. keep the duct open) as the duct is thin and tortuous and thus prone to kinking; the ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincter
A sphincter is a circular muscle that normally maintains constriction of a natural body passage or orifice and relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. Sphincters are found in many animals. There are over 60 types in the human body, some microscopically small, in particular the millions of precapillary sphincters. Sphincters relax at death, often releasing Body fluid, fluids and faeces. Functioning Each sphincter is associated with the lumen (opening) it surrounds. As long as the sphincter muscle is contracted, its length is shortened and the lumen is constricted (closed). Relaxation of the muscle causes it to lengthen, opening the lumen and allowing the passage of liquids, solids, or gases. This is evident, for example, in the Blowhole (biology), blowholes of numerous marine mammals. Many sphincters are used every day in the normal course of digestion. For example, the lower oesophageal sphincter (or cardiac sphincter), which resides at the top of the stomach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincter Of Oddi
The sphincter of Oddi (SO) (also hepatopancreatic sphincter or Glisson's sphincter), is a sphincter, a muscular valve that, in humans and some animals, controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice out of the gallbladder and pancreas respectively through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi. Structure The sphincter of Oddi is a circular muscle band, or sphincter that surrounds the major duodenal papilla. Function The sphincter regulates the secretion of pancreatic juice and bile into the duodenum. It also prevents reflux of duodenal contents into the ampulla of Vater. By preventing reflux of the contents of the duodenum, the sphincter of Oddi prevents the accumulation of particulate matter and sludge in the bile ducts, reducing the risk of cholangitis. The sphincter of Oddi also allows retrograde filling of the gallbladder. The sphincter of Oddi is relaxed by the hormone cholecystokinin via vasoactive intestinal pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin (CCK or CCK-PZ; from Greek ''chole'', "bile"; ''cysto'', "sac"; ''kinin'', "move"; hence, ''move the bile-sac (gallbladder)'') is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin, formerly called pancreozymin, is synthesized and secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine. Its presence causes the release of pancreatic juice from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder. History Evidence that the small intestine controls the release of bile was uncovered as early as 1856, when French physiologist Claude Bernard showed that when dilute acetic acid was applied to the orifice of the bile duct, the duct released bile into the duodenum. In 1903, the French physiologist showed that this reflex was not mediated by the nervous system. In 1904, the French physiologist Charles Fleig showed that the discharge of bile was mediated by a substance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). The duct is about 3 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 Termination The common hepatic duct typically unites with the cystic duct some 1–2 cm superior to the duodenum and anterior to the right hepatic artery, with the cystic duct approaching the common hepatic duct from the right. Relations The right branch of the hepatic artery proper usually passes posterior to the duct, but may rarely pass anterior to it instead. Histology The inner surface is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about long connecting the stomach to the jejunum, the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb, and ends at the duodenojejunal flexure marked by the suspensory muscle of duodenum. The duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (transverse) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Overview The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms ''anterior intestine'' or ''proximal intestine'' may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatoduodenal Ligament
The hepatoduodenal ligament is the portion of the lesser omentum extending between the porta hepatis of the liver and the superior part of the duodenum. Running inside it are the following structures collectively known as the portal triad: * hepatic artery proper * portal vein * common bile duct Manual compression of the hepatoduodenal ligament during surgery is known as the Pringle manoeuvre. The cystoduodenal ligament is also found in the lesser omentum and is distinct from both the hepatoduodenal and hepatogastric ligaments. The cystoduodenal ligament is an abnormal peritoneal fold that attaches the duodenum to the gallbladder, representing a rare variation in the anatomy of the lesser sac and its foramen. Another variation sometimes present at the duodenal termination of the hepatoduodenal ligament is the duodenorenal ligament which passes to the front of the right kidney In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartmann’s Pouch
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
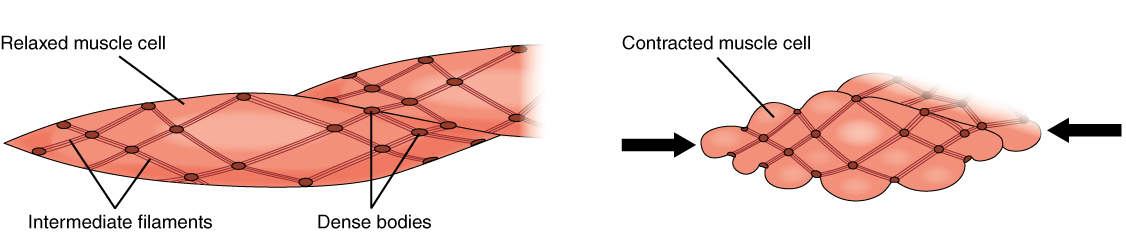
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, iris dilator muscle, and iris sphincter muscle are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
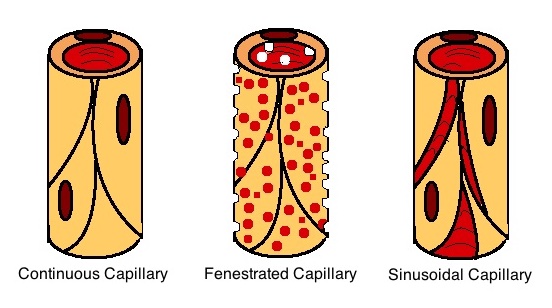
Fenestrated Blood Vessel
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |