|
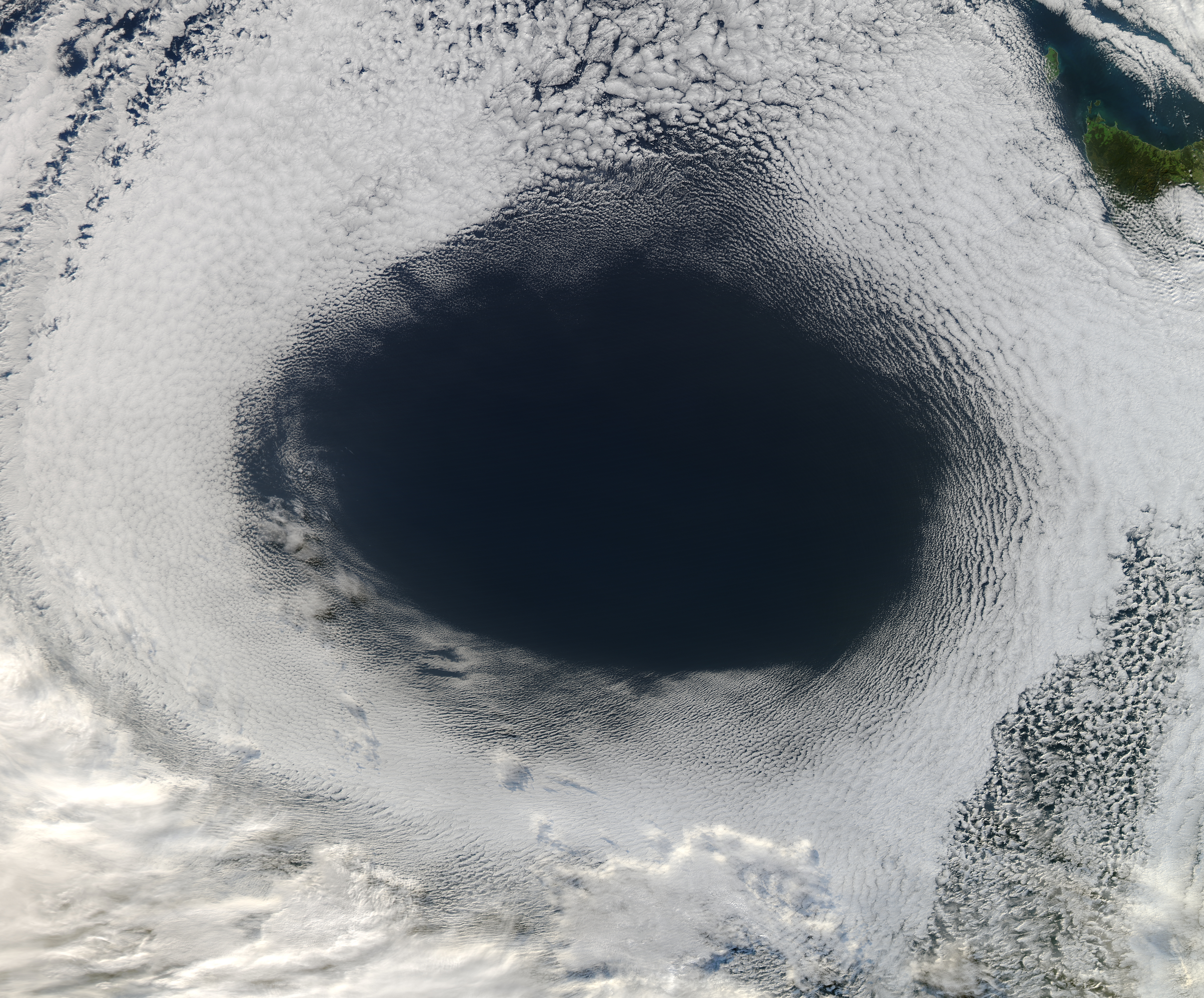
Cyclone Hyacinthe
Tropical Cyclone Hyacinthe was the wettest tropical cyclone on record worldwide. The eighth named storm of the season, Hyacinthe formed on January 15, 1980, to the northeast of Mauritius in the southern Indian Ocean. Initially it moved to the west-southwest, and while slowly intensifying it passed north of the French overseas department of Réunion. On January 19, Météo-France estimated that the storm had intensified to a tropical cyclone. Hyacinthe looped to the south of eastern Madagascar and weakened, although it restrengthened after turning to the east. The storm executed another loop to the southwest of Réunion, passing near the island for a second and later third time. Hyacinthe became extratropical on January 29 after turning southward, dissipating two days later. For twelve days, Hyacinthe dropped torrential rainfall on Réunion; nearly all of the island received more than 1 m (3.3 ft) of precipitation. Over a 15-day period from January 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga and St. Brandon. The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where most of the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans and has an exclusive economic zone covering . Arab sailors were the first to discover the uninhabited island, around 975, and they called it ''Dina Arobi''. The earliest discovery was in 1507 by Portuguese sailors, who otherwise took little interest in the islands. The Dutch took possession in 1598, establishing a succession of short-lived settlements over a period of about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and ''longitude'' are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or '' normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Denis, Réunion
Saint-Denis (, , unofficially Saint-Denis de La Réunion for disambiguation; ) is the prefecture (administrative capital) of the French overseas department and region of Réunion, in the Indian Ocean. It is located at the island's northernmost point, close to the mouth of the Rivière Saint-Denis. Saint-Denis is the most populous commune in the French overseas departments and the nineteenth most populous in all of France. At the 2019 census, there were 314,880 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Saint-Denis (as defined by INSEE), 153,810 of whom lived in the city ( commune) of Saint-Denis proper and the remainder in the neighbouring communes of La Possession, Sainte-Marie, Sainte-Suzanne, Saint-André, and Bras-Panon. History Foundation Saint-Denis was founded in 1669 by Étienne Regnault, first governor of Bourbon Island (as La Réunion was then called), on the northern side of the island, where a larger and more fertile plain was deemed more propitious for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Pierre, Réunion
Saint-Pierre (; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, Sin-Pyè) is the third-largest commune in the French overseas department and region of Réunion. Located on the southwest side of the island, it is the capital of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. It developed from a port built from 1854 to 1882, which was used for the trade between Asia and Europe. Today, it features 400 sites for fishing and pleasure boats, while most of the commercial traffic moved north to ''Le Port''. Geography The town of Saint-Pierre is at the beginning of the only major road N3 across the island. From here, the road leads to Le Tampon, La Plaine des Cafres and Bourg Murat. From that area, there is a relatively easy access to the Piton de la Fournaise and a starting point of many excursions. Climate Saint-Pierre has a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification ''BSh''), while Ligne Paradis and Ravine des Cabris's climate type has tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Îlet
Grand may refer to: People with the name * Grand (surname) * Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor * Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist * Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper Places * Grand, Oklahoma * Grand, Vosges, village and commune in France with Gallo-Roman amphitheatre * Grand Concourse (other), several places * Grand County (other), several places * Grand Geyser, Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone * Grand Rounds National Scenic Byway, a parkway system in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States * Le Grand, California, census-designated place * Grand Staircase, a place in the US. Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Grand'' (Erin McKeown album), 2003 * ''Grand'' (Matt and Kim album), 2009 * ''Grand'' (magazine), a lifestyle magazine related to related to grandparents * ''Grand'' (TV series), American sitcom, 1990 * Grand piano, musical instrument * Grand Production, Serbian record label company * The Grand Tour, a new British automobile show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piton De La Fournaise
Piton de la Fournaise (; en, "Peak of the Furnace") is a shield volcano on the eastern side of Réunion island (a French overseas department and region) in the Indian Ocean. It is currently one of the most active volcanoes in the world, along with Kīlauea in the Hawaiian Islands, Stromboli and Etna in Italy and Mount Erebus in Antarctica. A previous eruption began in August 2006 and ended in January 2007. The volcano erupted again in February 2007, on 21 September 2008, on 9 December 2010, which lasted for two days, and on 1 August 2015. The most recent eruption began on 7 December 2020. The volcano is located within Réunion National Park, a World Heritage Site. Residents of Réunion sometimes refer to Piton de la Fournaise simply as ''le Volcan'' ("the Volcano"). It is a major tourist attraction on Réunion island. Geology The uppermost section of the volcano is occupied by the Enclos Fouqué, a caldera wide. High cliffs, known as ''remparts'' in French, form the caldera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Pierre Boulevard Bank Cyclone Hyacinthe 19 Janvier 1980
Saint-Pierre (French, 'Saint Peter') may refer to: Buildings and churches * Church of Saint-Pierre, Caen, Normandy, France * Saint-Pierre, Firminy, France, designed by Le Corbusier * Saint-Pierre-le-Jeune Protestant Church, Strasbourg, France * Église Saint-Pierre le Vieux (Old Saint Peter's Church, Strasbourg), Strasbourg, France * Saint-Pierre de Montrouge, Paris, France * Fort Saint Pierre, Ontario, Canada * Church of SS Peter and Paul, Istanbul (Saint-Pierre Church), Beyoğlu]m, Istanbul, Turkey * Saint Pierre Han, Beyoğlu, Istanbul, Turkey Places Canada Manitoba * St-Pierre-Jolys Quebec * Saint-Pierre, Quebec, in Joliette Regional County Municipality * Saint-Pierre-Baptiste, Quebec * Saint-Pierre-de-Broughton, Quebec * Saint-Pierre-de-Lamy * Saint-Pierre-de-la-Rivière-du-Sud, Quebec * Saint-Pierre-de-l'Île-d'Orléans, known simply as Saint-Pierre until 1997 * Saint-Pierre-de-Véronne-à-Pike-River, Quebec, now called Pike River * Saint-Pierre-de-Wakefie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is the location of the storm's minimum barometric pressure—where the atmospheri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Sustained Winds
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are determined via their sampling and averaging the sampled results over a period of time. Wind measuring has been standardized globally to reflect the winds at above the Earth's surface, and the maximum sustained wind represents the highest average wind over either a one-minute (US) or ten-minute time span (see the definition, below), anywhere within the tropical cyclone. Surface winds are highly variable due to friction between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, as well as near hills and mountains over land. Over the ocean, satellite imagery determines the value of the maximum sustained winds within a tropical cyclone. Land, ship, aircraft reconnaissance observations, and radar imagery can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean, and Indian Ocean for all branches of the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies. Their warnings are intended for the protection of primarily military ships and aircraft as well as military installations jointly operated with other countries around the world. Its U.S. Navy components are aligned with the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command. History The origins of the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) can be traced back to June 1945, when the Fleet Weather Center/Typhoon Tracking Center was established on the island of Guam, after multiple typhoons, including Typhoon Cobra of December 1944 and Typhoon Connie in June 1945, had caused a significant loss of men and ships. At this time the center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |