|
Currency Overlay
Currency overlay is a financial trading strategy or method conducted by specialist firms who manage the currency exposures of large clients, typically institutions such as pension funds, endowments and corporate entities. Typically the institution will have a pre-existing exposure to foreign currencies, and will be seeking to: *limit the risk from adverse movements in exchange-rates, i.e. hedge; and *attempt to profit from tactical foreign-exchange views, i.e. speculate. The currency overlay manager will conduct foreign-exchange hedging on their behalf, selectively placing and removing hedges to achieve the objectives of the client. Many types of currency overlay accounts are more focused on the speculative aspect, i.e. profiting from currency movements. These so-called 'pure alpha mandates' are set up to allow the manager as much scope as possible to take speculative positions. As such, they are similar in nature to foreign-exchange hedge funds in terms of objective and trading s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment Position (finance), position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance policy, insurance, forward contracts, swap (finance), swaps, option (finance), options, gambles, many types of Over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter and Derivative (finance), derivative products, and futures contracts. Public futures markets were established in the 19th century to allow transparent, standardized, and efficient hedging of agricultural commodity prices; they have since expanded to include futures contracts for hedging the values of Energy derivative, energy, precious metals, foreign currency, and interest rate fluctuations. Etymology Hedging is the practice of taking a position in one market to offset and balance against the risk adopted by assuming a position in a contrary or opposing market o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, good (economics), goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable in a brief amount of time. It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value. Many speculators pay little attention to the fundamental value of a security and instead focus purely on price movements. In principle, speculation can involve any tradable good or financial instrument. Speculators are particularly common in the markets for stocks, bond (finance), bonds, commodity futures, currency, currencies, cryptocurrency, fine art, collectibles, real estate, and derivative (finance), financial derivatives. Speculators play one of four primary roles in financial markets, along with hedge (finance), hedgers, who engage in transactions to offset some other pre-existing risk, arbitrageurs who seek to profit from situations where Fungibility, fungible instruments trade at different prices in dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jensen's Alpha
In finance, Jensen's alpha (or Jensen's Performance Index, ex-post alpha) is used to determine the abnormal return of a security or portfolio of securities over the theoretical expected return. It is a version of the standard alpha based on a theoretical performance instead of a market index. The security could be any asset, such as stocks, bonds, or derivatives. The theoretical return is predicted by a market model, most commonly the capital asset pricing model (CAPM). The market model uses statistical methods to predict the appropriate risk-adjusted return of an asset. The CAPM for instance uses beta as a multiplier. History Jensen's alpha was first used as a measure in the evaluation of mutual fund managers by Michael Jensen in 1968. The CAPM return is supposed to be 'risk adjusted', which means it takes account of the relative riskiness of the asset. This is based on the concept that riskier assets should have higher expected returns than less risky assets. If an asset's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedge Fund
A hedge fund is a Pooling (resource management), pooled investment fund that holds Market liquidity, liquid assets and that makes use of complex trader (finance), trading and risk management techniques to aim to improve investment performance and insulate returns from beta (finance), market risk. Among these portfolio (finance), portfolio techniques are short (finance), short selling and the use of leverage (finance), leverage and derivative (finance), derivative instruments. In the United States, financial regulations require that hedge funds be marketed only to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals. Hedge funds are considered alternative investments. Their ability to use leverage and more complex investment techniques distinguishes them from regulated investment funds available to the retail market, commonly known as mutual funds and Exchange-traded fund, ETFs. They are also considered distinct from private-equity fund, private equity funds and other similar cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Currency Management
Record Financial Group (Record) is a British multi-asset investment management company that specializes in a range of products including currency, derivatives and hedging solutions. It was a pioneer of currency overlay for pension funds, endowments and other institutional investors. The company is one of the largest independent currency managers in the world with an AUM of US$101.3 billion as at 29 February 2024. Background Neil Record, a former Bank of England economist, worked as a commodity price forecaster for Mars, Incorporated and during his time there, developed a process for controlling currency risk and exploiting currency market inefficiency. In 1983, he left Mars to found his own company, Record Treasury Management (later renamed Record Currency Management in 2001). The company would offer currency management services to international clients. Neil Record served as the company's CEO and chairman until he stepped down in 2010 and 2023 for both roles respectively. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market. The main participants are the larger international banks. Financial centres function as anchors of trading between a range of multiple types of buyers and sellers around the clock, with the exception of weekends. As currencies are always traded in pairs, the market does not set a currency's absolute value, but rather determines its relative value by setting the market price of one currency if paid for with another. Example: 1 USD is worth 1.1 Euros or 1.2 Swiss Francs etc. The market works through financial institutions and operates on several levels. Behind the scenes, banks turn to a smaller number of financial firms known as "dealers", who are involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
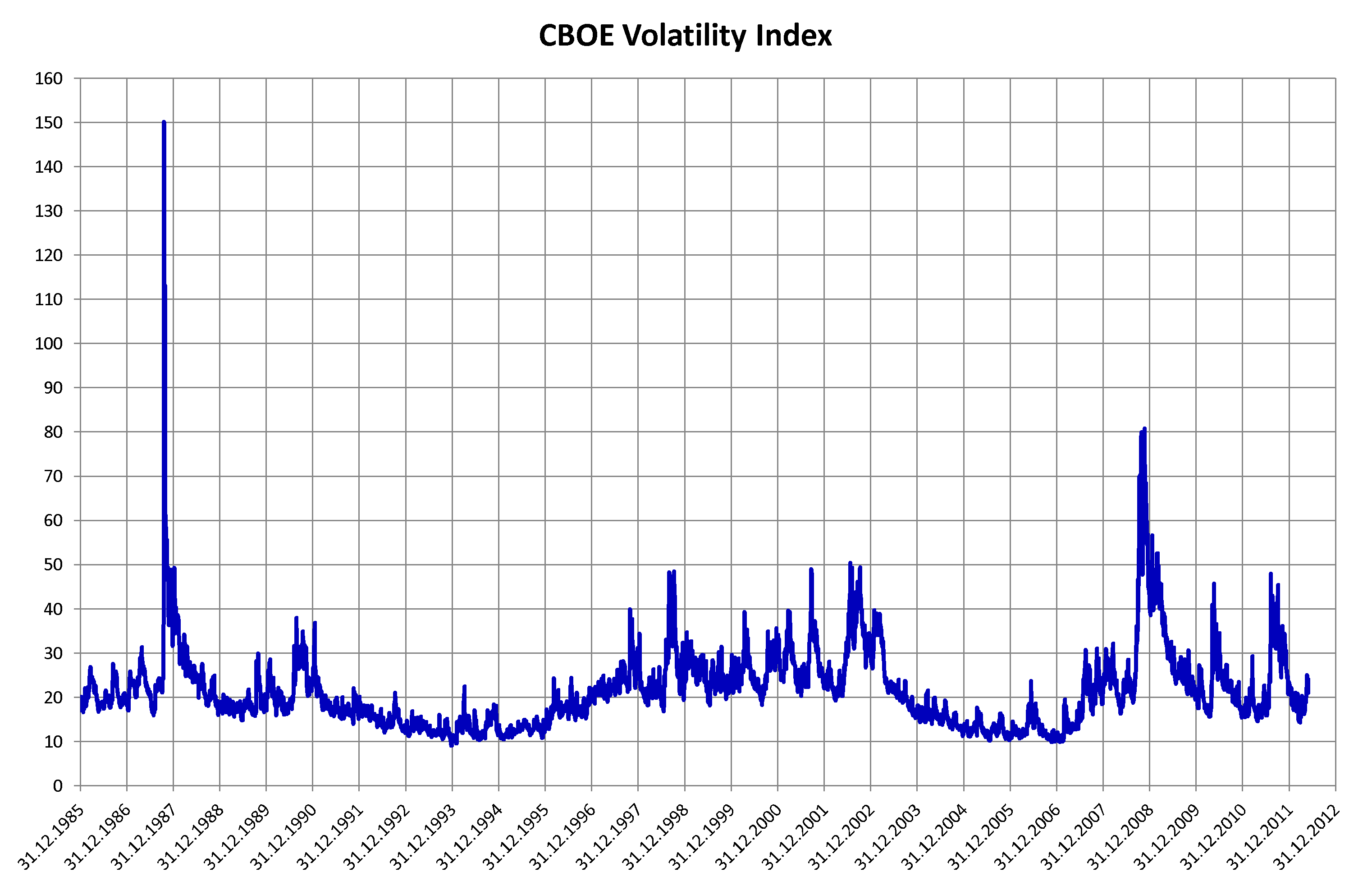
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neil Record
Neil Record (born 26 June 1953) is a British businessman, author and economist who founded Record Currency Management, one of the earliest specialist currency managers. Record was one of the pioneers of currency risk management. In 2003 he wrote ''Currency Overlay'', the first textbook on the subject. He was a short listed entrant for the 2012 Wolfson Economics Prize for his work on the Eurozone crisis. He was one of the main donors to the climate change denial think-tank the Global Warming Policy Foundation, and is one of the main backers of Kemi Badenoch's 2024 bid for the leadership of the conservative party. Education Record attended Magdalen College School in Oxford on a state scholarship. He studied Philosophy and Psychology at Balliol College, Oxford and spent time at the University of Essex and University College London, from where he received an MSc in economics, with distinction. Career Early career Record began his career in 1977 at the Bank of England’s Econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |