|
Cultuurstelsel
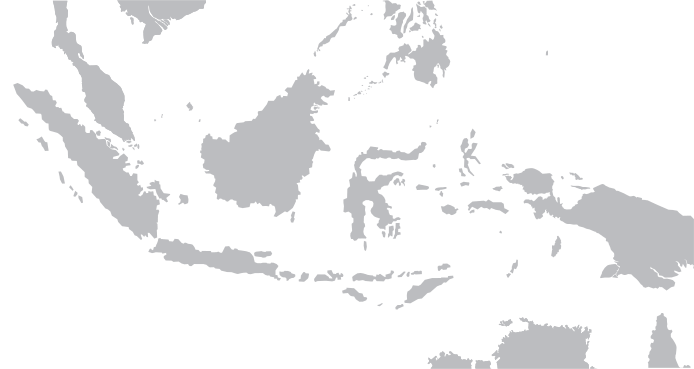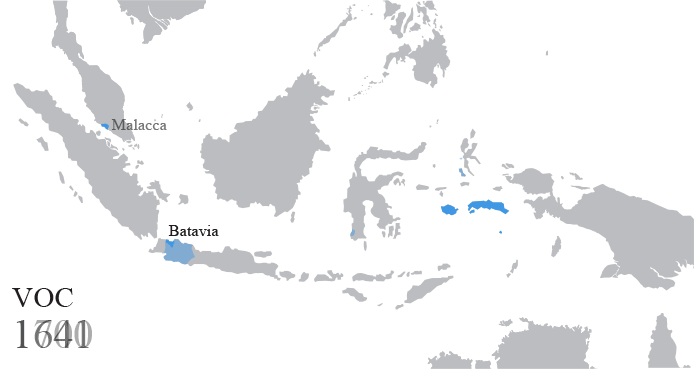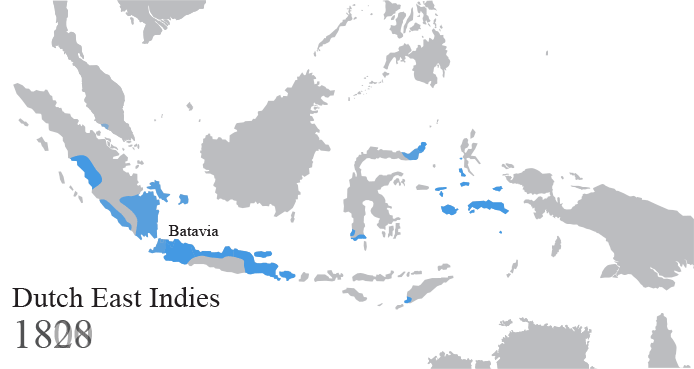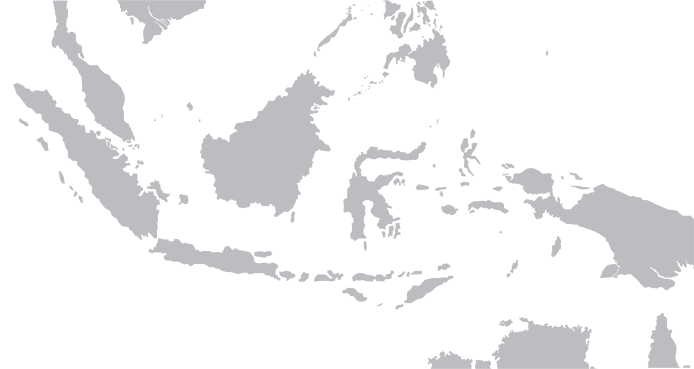
The Cultivation System ( nl, cultuurstelsel) was a Dutch government policy from 1830–1870 for its Dutch East Indies colony (now Indonesia). Requiring a portion of agricultural production to be devoted to export crops, it is referred to by Indonesian historians as ''tanam paksa'' ("enforced planting"). Background Despite increasing returns from the Dutch system of land tax, Dutch finances had been severely affected by the cost of the Java War and Padri Wars. The Belgian Revolution in 1830 and the resulting costs of keeping the Dutch army at a war footing until 1839 brought the Netherlands to the brink of bankruptcy. In 1830, a new governor general, Johannes van den Bosch, was appointed to increase the exploitation of the Dutch East Indies' resources. The Cultivation System was implemented only on land controlled directly by the colonial government, thus exempting the ''Vorstenlanden'' (princely states) and the ''particuliere landerijen'' (private domains). Implementation Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java War
The Java War ( jv, ꦥꦼꦫꦁꦗꦮ) or Diponegoro War () was fought in central Java from 1825 to 1830, between the colonial Dutch Empire and native Javanese rebels. The war started as a rebellion led by Prince Diponegoro, a leading member of the Javanese aristocracy who had previously cooperated with the Dutch. The rebel forces laid siege to Yogyakarta, a move that prevented a quick victory. This gave the Dutch time to reinforce their army with colonial and European troops, allowing them to end the siege in 1825. After this defeat, the rebels continued fighting a guerrilla war for five years. The war ended in a Dutch victory, and Prince Diponegoro was invited to a peace conference. He was betrayed and captured. Due to the cost of the war, Dutch colonial authorities implemented major reforms throughout the Dutch East Indies to ensure the colonies remained profitable. History The direct cause of the Java War was the decision by the Dutch to build a road across a piece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seigneurage
Seigniorage , also spelled seignorage or seigneurage (from the Old French ''seigneuriage'', "right of the lord (''seigneur'') to mint money"), is the difference between the value of money and the cost to produce and distribute it. The term can be applied in two ways: * Seigniorage derived from specie (metal coins) is a tax added to the total cost of a coin (metal content and production costs) that a customer of the mint had to pay, and which was sent to the sovereign of the political region. * Seigniorage derived from notes is more indirect; it is the difference between interest earned on securities acquired in exchange for banknotes and the cost of printing and distributing the notes. "Monetary seigniorage" is where sovereign-issued securities are exchanged for newly printed banknotes by a central bank, allowing the sovereign to "borrow" without needing to repay. Monetary seigniorage is sovereign revenue obtained through routine debt monetization, including expansion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landrentestelsel
The Landrentestelsel (literally: ''Land Securities System'') was a system of taxation in the Dutch East Indies, in which the indigenous population paid 2/5 of its agricultural products grown or a similar sum to the colonial administration. It was replaced with the Cultivation System by Johannes van den Bosch Johannes, Count van den Bosch (2 February 1780 – 28 January 1844) was a Dutch officer and politician. He was Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies (1830–1833), commander of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army, Minister of Colonies ... in 1830. References Dutch East Indies Taxation in Indonesia Legal history of Indonesia {{Econ-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Period (Dutch East Indies)
The Liberal Period refers to the economic policies instituted in the Dutch East Indies from the mid-19th century. Background: the cultivation system Under the cultivation system (or "tanam paksa" in Indonesian) in place for most of the 19th century, the Dutch colonial government in the Indonesian archipelago required indigenous farmers to deliver, as a sort of tax, fixed amounts of specified crops, such as sugar or coffee. Much of Java became a Dutch plantation, making it a profitable, self-sufficient colony and saving the Netherlands from bankruptcy and helping it become a thriving and modernised bourgeois society. The Cultivation System, however, brought much economic hardship to Javanese peasants, who suffered famine and epidemics in the 1840s, attracting much critical public opinion in the Netherlands. De-regulation of the Indies economy Prior to the late 19th century recession, the Liberal Party had been dominant in policy making in the Netherlands. Its free market ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Preference
Local may refer to: Geography and transportation * Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand * Local, Missouri, a community in the United States * Local government, a form of public administration, usually the lowest tier of administration * Local news, coverage of events in a local context which would not normally be of interest to those of other localities * Local union, a locally based trade union organization which forms part of a larger union Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Local'' (comics), a limited series comic book by Brian Wood and Ryan Kelly * ''Local'' (novel), a 2001 novel by Jaideep Varma * Local TV LLC, an American television broadcasting company * Locast, a non-profit streaming service offering local, over-the-air television * ''The Local'' (film), a 2008 action-drama film * '' The Local'', English-language news websites in several European countries Computing * .local, a network address component * Local variable, a variable that is given loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold economically liberal positions, while economic nationalist and left-wing political parties generally support protectionism, the opposite of free trade. Most nations are today members of the World Trade Organization multilateral trade agreements. Free trade was best exemplified by the unilateral stance of Great Britain who reduced regulations and duties on imports and exports from the mid-nineteenth century to the 1920s. An alternative approach, of creating free trade areas between groups of countries by agreement, such as that of the European Economic Area and the Mercosur open markets, creates a protectionist barrier between that free trade area and the rest of the world. Most governments still impose some protectionist policies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rent Seeking Rent-seeking is the act of growing one's existing wealth without creating new wealth by manipulating the social or political environment. Rent-seeking activities have negative effects on the rest of society. They result in reduced economic efficiency through misallocation of resources, reduced wealth creation, lost government revenue, heightened income inequality, and potential national decline. Attempts at capture of regulatory agencies to gain a coercive monopoly can result in advantages for rent-seekers in a market while imposing disadvantages on their uncorrupt competitors. This is one of many possible forms of rent-seeking behavior. Description The term rent, in the narrow sense of economic rent, was coined by the British 19th-century economist David Ricardo, but rent-seeking only became the subject of durable interest among economists and political scientists more than a century later after the publication of two influential papers on the topic by Gordon Tullock in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Java_TMnr_10011707.jpg)