|
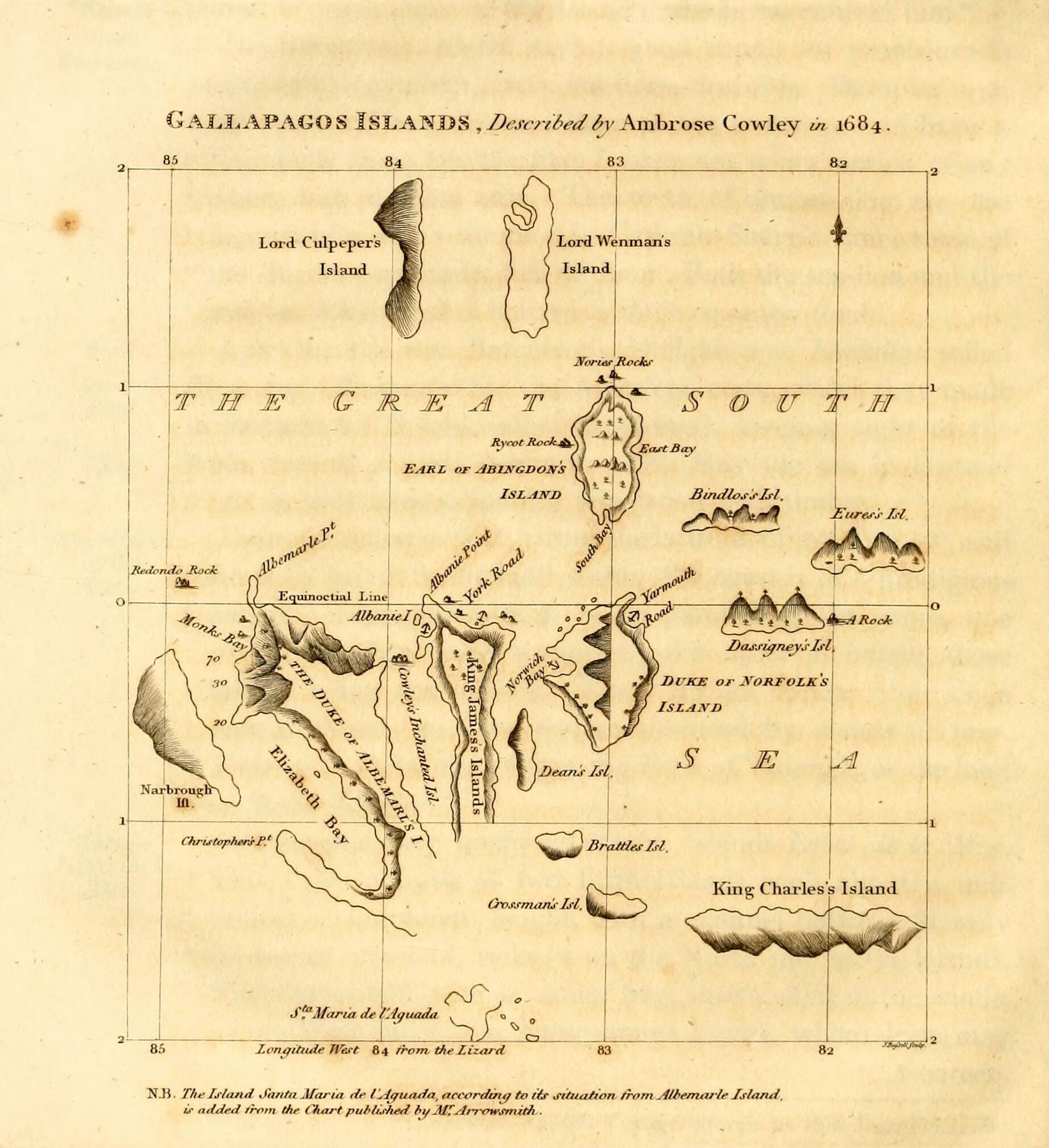
Culpepper Island (Galápagos)
Darwin Island () is an isolated northern member of the Galápagos Islands in Ecuador, the uppermost extent of an Volcano#Extinct, extinct volcano. It has an area of and reaches height above mean sea level, above sea level. Visits to the island are restricted by the Government of Ecuador, but scuba diving is permitted. Names Darwin is named in honor of the English people, English Science in the United Kingdom, scientist Charles Darwin, whose voyage of the Beagle, visit to the Galapagos led him to publish his theories on evolution in ''On the Origin of Species'' and other works. He is also the namesake of Great Darwin Bay on Genovesa Island. Darwin Island was previously named Lord Culpeper's Island, Culpepper's Island, and Culpepper Island in honor of Thomas Colepeper, 2nd Baron Colepeper, Thomas Colepeper, 2nd Baron Colepeper. The name was bestowed by the pirate William Ambrosia Cowley in 1684 and continued in use for centuries thereafter. The group formed by Darwin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin Island (Antarctica)
The Danger Islands () are a group of islands lying east-south-east of Joinville Island near the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. Location The Danger Islands are in the Joinville Island group, which lies in Graham Land to the east of the tip of Trinity Peninsula, which is itself the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. The Danger Islands are to the east-southeast of Joinville Island. Discovery and name The Danger Islands were discovered on 28 December 1842 by a British expedition under James Clark Ross, who so named them because, appearing among heavy fragments of ice, they were almost completely concealed until the ship was nearly upon them. Use by birds The Danger Islands have been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it supports Adélie penguin colonies and seabirds. 751,527 pairs of Adélie penguins (1.5 million individuals) have been recorded in at least five distinct colonies as of March 2018. The survey used drones adapted to the cold. Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ambrosia Cowley
William Ambrosia Cowley, also known as Ambrose Cowley and Captain Cowley, was a 17th-century English people, English buccaneer who surveyed the Galápagos Islands during his 1683–1686 circumnavigation of the world while serving under several captains such as John Eaton (pirate), John Eaton, John Cook (pirate), John Cook, and later Edward Davis (buccaneer), Edward Davis. Cowley drafted the first chart of the islands in 1684, first published with the account of his voyage in 1699. In his diary he reported the discovery of the phantom island, phantom Pepys Island, allegedly situated north of the Falkland Islands, prompting a number of mariners to look in vain for the nonexistent rock. References *William Ambrosia Cowley. ''Cowley's Voyage Round the Globe'', in ''Collection of Original Voyages'', ed. William Hacke. London: James Knapton, 1699. https://web.archive.org/web/20180120160933/http://www.galapagos.to/TEXTS/COWLEY.HTM *1686 “A Short Account of My Voyage Round this Terest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagioclase
Plagioclase ( ) is a series of Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann F. C. Hessel, Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite to anorthite endmembers (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium and calcium atoms can substitute for each other in the mineral's crystallography, crystal lattice structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or "phonograph record, record-groove" effect. Plagioclase is a major constituent mineral in Earth's crust and is consequently an important diagnostic tool in petrology for identifying the composition, origin and evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault (geology), fault along a plate boundary where the motion (physics), motion is predominantly Horizontal plane, horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction, subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of Divergent boundary, divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This results from oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and volcanic gas, gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle (geology), mantle or the Crust (geology), crust in various tectonics, tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift (geology), rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and Hotspot (geology), hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal mush, crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by Fractional crystallization (geology), fractional crystallization, contaminati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lineament
''See also Line (geometry)'' A lineament is a linear feature in a landscape which is an expression of an underlying geological structure such as a fault. Typically a lineament will appear as a fault-aligned valley, a series of fault or fold-aligned hills, a straight coastline or indeed a combination of these features. Fracture zones, shear zones and igneous intrusions such as dykes can also be expressed as geomorphic lineaments. Lineaments are often apparent in geological or topographic maps and can appear obvious on aerial or satellite photographs. There are for example, several instances within Great Britain. In Scotland the Great Glen Fault and Highland Boundary Fault give rise to lineaments as does the Malvern Line in western England and the Neath Disturbance in South Wales. The term 'megalineament' has been used to describe such features on a continental scale. The trace of the San Andreas Fault might be considered an example.Whitten & Brooks, The Penguin Dictionary of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazca Plate
The Nazca plate or Nasca plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic list of tectonic plates, tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru–Chile Trench, of the Nazca plate under the South American plate is largely responsible for the Andes, Andean orogeny. The Nazca plate is bounded on the west by the Pacific plate and to the south by the Antarctic plate through the East Pacific Rise and the Chile Rise, respectively. The movement of the Nazca plate over several Hotspot (geology), hotspots has created some volcanic islands as well as east–west running seamount chains that subduct under South America. Nazca is a relatively young plate in terms of the age of its rocks and its existence as an independent plate, having been formed from the breakup of the Farallon plate about 23 million years ago. The oldest rocks of the plate are about 50 million years old. Boundaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Above Sea Level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of a location's vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) in reference to a vertical datum based on a historic mean sea level. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric height. The zero level varies in different countries due to different reference points and historic measurement periods. Climate change and other forces can cause sea levels and elevations to vary over time. Uses Elevation or altitude above sea level is a standard measurement for: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Mining infrastructure, particularly underground. * Flying objects such as airplanes or helicopters below a Transition Altitude defined by local regulations. Units and abbreviations Elevation or altitude is generally expressed as "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, or " feet above mean sea level" in United States customary and imperial units. Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |