|
Culhuacan (altepetl)
Culhuacan ( ) was one of the Nahuatl-speaking pre-Columbian city-states of the Valley of Mexico. According to tradition, Culhuacan was founded by the Toltecs under Mixcoatl and was the first Toltec city. The Nahuatl speakers agreed that Culhuacán was the first city to give its rulers the title of "speaker" (''tlatoani''). In the sixteenth century following the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, Culhuacan was incorporated into colonial New Spain and called a ''pueblo'', but in local-level documentation in Nahuatl, residents continued to use the designation altepetl for their settlement. History Culhuacan was perhaps the first of the chinampa towns founded on the shores of Lake Xochimilco, with chinampas dating to 1100 C.E. From written records there is evidence that Culhuacan survived the fall of Tollan and maintained its prestige until the mid-14th century. According to the ''Crónica Mexicayotl'', transcribed in 1609, in 1299, Culhuacan's ''tlatoani'', Coxcoxtli, helped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations Nahuatl language in the United States, in the United States. Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican chronology, Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. Following the Spanish conquest, Spanish colonists and missionaries introduced the Latin script, and Nahuatl became a literary language. Many chronicles, gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
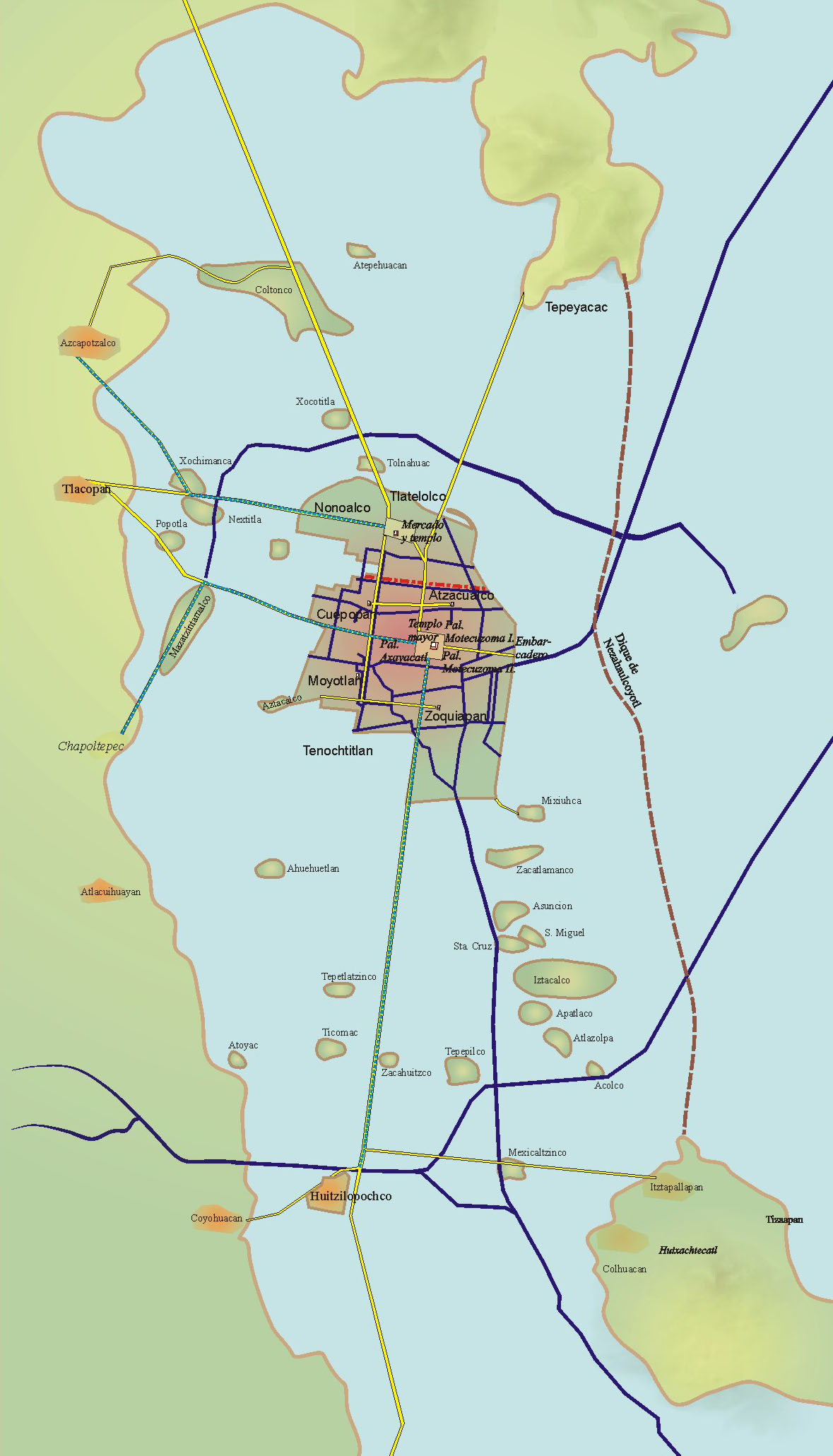
Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was Fall of Tenochtitlan, captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city-state, city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a ''Municipalities of Mexico, cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, Chinampa, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Universidad Nacional Autónoma De México
The National Autonomous University of Mexico (, UNAM) is a public university, public research university in Mexico. It has several campuses in Mexico City, and many others in various locations across Mexico, as well as a presence in nine countries. It also has 34 research institutes, 26 museums, and 18 historic sites. A portion of (University City), UNAM's main campus in Mexico City, is a UNESCO World Heritage site that was designed and decorated by some of Mexico's best-known architects and painters. The campus hosted the main events of the 1968 Summer Olympics, and was the birthplace of the Mexican Movement of 1968, student movement of 1968. All Mexican Nobel laureates have been alumni of UNAM. In 2009, the university was awarded the Princess of Asturias Awards, Prince of Asturias Award for Communication and Humanities. More than 25% of the total scientific papers published by Mexican academics come from researchers at UNAM. UNAM was founded in its modern form, on 22 Septemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Miguel León-Portilla
Miguel León-Portilla (22 February 1926 – 1 October 2019) was a Mexican anthropologist and historian, specializing in Aztec culture and literature of the pre-Columbian and colonial eras. Many of his works were translated to English and he was a well-recognized scholar internationally. In 2013, the Library of Congress of the United States bestowed on him the Living Legend Award. Early life and education Born in Mexico City, Miguel León-Portilla had an interest in indigenous Mexico from an early age, fostered by his uncle Manuel Gamio, a distinguished archeologist. Gamio had a lasting influence on his life and career, initially taking him as a boy on trips to important archeological sites in Mexico and later as well. León-Portilla attended the Instituto de Ciencias in Guadalajara and then earned a B.A. (1948) and M.A. summa cum laude (1951) at the Jesuit Loyola University in Los Angeles. Returning to Mexico in 1952, he showed Gamio a play he had written on Quetzalcoatl, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anita Brenner
Anita Brenner (born Hanna Brenner; 13 August 1905 – 1 December 1974) was a transnational Jewish scholar and intellectual, who wrote extensively in English about the art, culture, and history of Mexico. She was born in Mexico, and raised and educated in the United States. She returned to Mexico in the 1920s following the Mexican Revolution. She coined the term 'Mexican Renaissance', "to describe the cultural florescence hatemerged from the revolution." As a child of immigrants, Brenner's heritage caused her to experience both antisemitism and acceptance. Fleeing discrimination in Texas, she found mentors and colleagues among the European Jewish diaspora living in both Mexico and New York, but Mexico, not the US or Europe, held her loyalty and enduring interest. She was part of the post-Revolutionary art movement known for its indigenista ideology. Brenner earned a PhD in anthropology at Columbia University and her first book, ''Idols Behind Altars'' was the first book to docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pueblo Culhuacán
Pueblo Culhuacán () is an officially designated neighborhood of the Iztapalapa borough of Mexico City, which used to be a major pre-Hispanic city. Ancient Culhuacán (altepetl), Culhuacán was founded around 600 CE and the site has been continuously occupied since. The city was conquered by the Aztecs in the 15th century, but the Aztecs considered the city to have status with early rulers marrying into Culhua nobility to legitimize themselves. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Franciscan order, Franciscans and later the Augustinian order, Augustinians made Culhuacán a major evangelization center, with the latter building the monastery complex which remains to this day. Today, Culhucan is fully integrated into Mexico City physically and politically. This area was designated as a Barrios Mágicos of Mexico City, "Barrio Mágico" by the city in 2011. Modern Pueblo Culhuacán Culhuacan is one of the subdivisions of the borough of Iztapalapa, bordering the borough of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states ('' altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Azt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xilomantzin
Xilomantzin was the ''tlatoani'' ("king") of the pre-Columbian ''altepetl'' (ethnic state) of Culhuacán (altepetl), Culhuacan in the Valley of Mexico from 1440 to 1473. Xilomantzin was the son of Acoltzin, the previous ruler of Culhuacan, and Tlacochcuecihuatl or Tlacochcuetzin, a daughter of Tezozomoc (Azcapotzalco), Tezozomoctli, ruler of Azcapotzalco. He succeeded his father in the year Aztec calendar, 13 Flint (1440). He married Izquixotzin, the daughter of Tlacateotl, ruler of Tlatelolco (altepetl), Tlatelolco, and had a son named Acolmiztli. In the year Aztec calendar, 7 House (1473), Xilomantzin sided with Moquihuixtli, then ruler of Tlatelolco, in a conflict against Tenochtitlan (led by Axayacatl), which resulted in both Moquihuixtli and Xilomantzin being killed.Chimalpahin (1997): vol. 1, p. 139; vol. 2, pp. 91–93, 107; Quiñones Keber (1995): pp. 221–222. Notes References * * {{end box 1473 deaths Tlatoque Executed royalty Year of birth unknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Huehue Acamapichtli
Huehue Acamapichtli (''Ācamāpichtli'' ːkamaːˈpit͡ʃt͡ɬi= "Handful of reeds", ) was a king (Nahuatl: ''tlatoani'') of Culhuacán. He was a son — and successor — of King Coxcoxtli and his wife. His sister was Atotoztli I of Culhuacán — mother of ''tlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan, named also Acamapichtli.Frederick Ward Putnam, Alfred Louis Kroeber, Robert Harry Lowie''Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnology'', Opseg 17 Diego Durán, Fernando Alvarado Tezozómoc and Fernando de Alva Cortés Ixtlilxochitl Fernando is a Spanish and Portuguese given name and a surname common in Spain, Portugal, Italy, France, Switzerland, and former Spanish or Portuguese colonies in Latin America, Africa and Asia (like the Philippines, India, and Sri Lanka). It is e ... mentioned that Huehue Acamapichtli occupied the throne of Culhuacán in 1324. Sources {{end box Tlatoque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caudillo
A ''caudillo'' ( , ; , from Latin language, Latin , diminutive of ''caput'' "head") is a type of Personalist dictatorship, personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise English translation for the term, though it is often used interchangeably with "Military dictatorship, military dictator," "warlord" and "Political strongman, strongman". The term is historically associated with Spain and Hispanic America, after virtually all of the regions in the latter won independence in the early nineteenth century. The roots of ''caudillismo'' may be tied to the framework of rule in medieval and early modern Spain during the Reconquista from the Moors. Spanish conquistadors such as Hernán Cortés and Francisco Pizarro exhibit characteristics of the ''caudillo'', being successful military leaders, having mutual reliance on the leader and their supporters, and rewarding them for their loyalty.Hamill, Hugh M. (1996) "Caudillismo, Caudillo" in ''Encyclopedia of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |