|
Cryptoteuthis
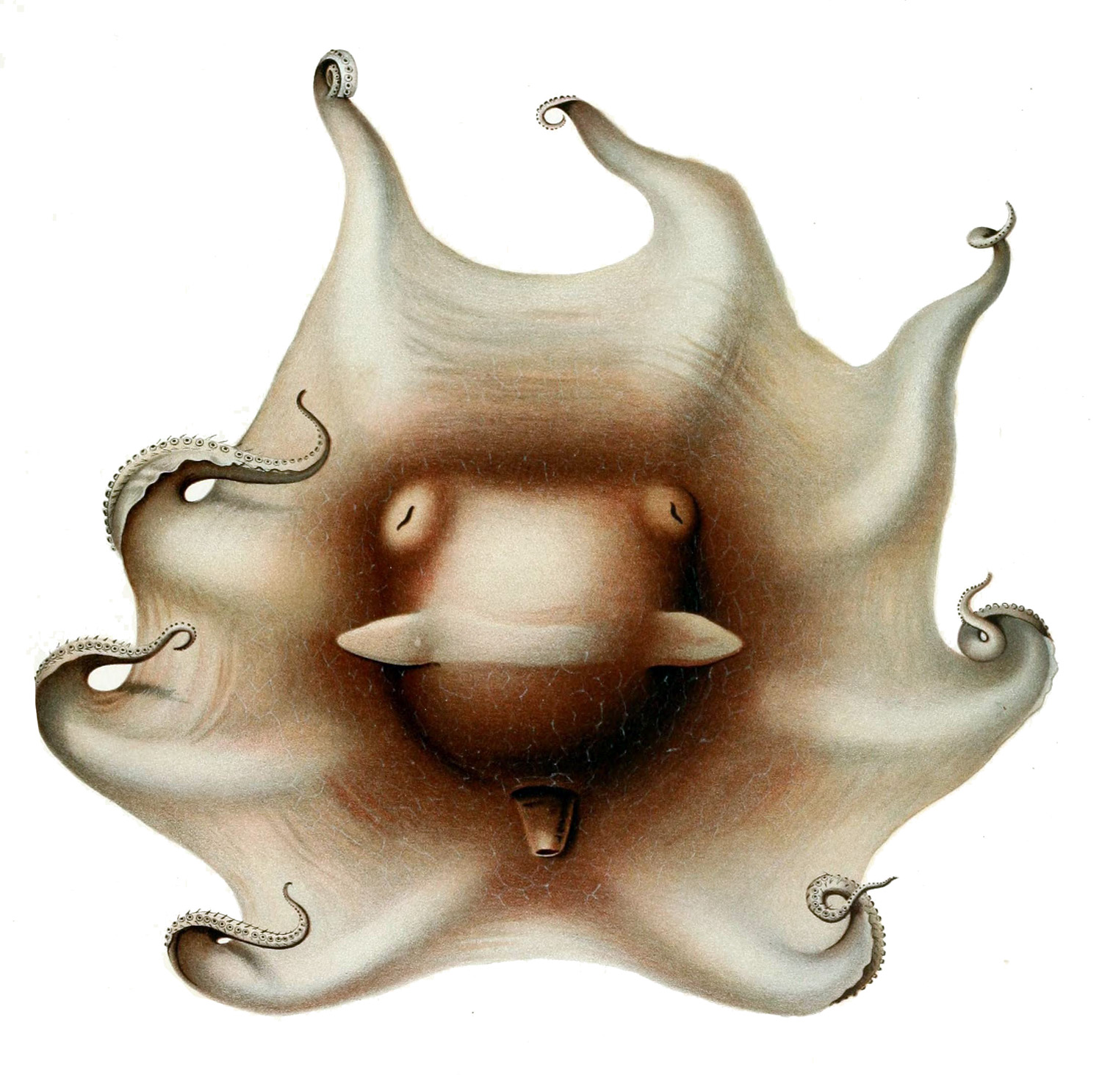
''Cryptoteuthis brevibracchiata'', the short-arm flapjack octopod, is a deepwater species of octopod. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Cryptoteuthis'' one of the cirrate octopuses of the family Grimpoteuthidae, the umbrella octopuses. It is known from a single specimen which was collected in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. It has characteristics which are shared with two other genera, '' Opisthoteuthis'' and ''Grimpoteuthis'', but is sufficiently distinctive from either of these to warrant the erection of a new genus. Description ''Cryptoteuthis brevibracchiata'' is a bell-shaped octopus with a semi-gelatinous, semi-transparent body, except for the dark tips of the oral web and the tips of the fins. The fins are small and round, and their length is equal to half the width of the head. It has short arms, each with a single row of small, broad suckers and with a double row of cirri which are of moderate length, with each cirrus just longer than the diameter of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimpoteuthidae
Grimpoteuthidae are a family of bentho-pelagic octopuses, comprising three currently accepted genera. They have extensive arm webbing and relatively large fins allowing for powerful fin swimming. Description Grimpoteuthidae have a strongly U-, V-, W-shaped internal shell (gladius remnant) that supports muscles for large fins. These fins are proportionally much larger than in the related Opisthoteuthidae, and allow for much stronger swimming using the fins alone (unlike Opisthoteuthids that mostly use the arm webbing for swimming). Unlike Cirroctopodidae and Opisthoteuthidae, Grimpoteuthids also have the optic nerves heading to each eye as a single bundle (in the other families this occurs as multiple separated nerve bundles). The extensive arm webbing is shared with Opisthoteuthidae and Cirroctopodidae. Taxonomy The following genera and 19 species are currently accepted in this family. The family has consistently been supported in molecular studies as distinct from Opistho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrina
Cirrina or Cirrata is a suborder and one of the two main divisions of octopuses. Cirrate octopuses have a small, internal shell and two fins on their head, while their sister suborder Incirrina has neither. The fins of cirrate octopods are associated with a unique cartilage-like shell in a shell sac. In cross-section, the fins have distinct proximal and distal regions, both of which are covered by a thin surface sheath of muscle. The suborder is named for small, cilia-like strands (cirri) on the arms of the octopus, a pair for each sucker. These are thought to play some role in feeding, perhaps by creating currents of water that help bring food closer to the beak. Cirrate octopuses are noteworthy for lacking ink sacs, having reduced or absent radula, and reduced gills. The oldest known member of the group is '' Paleocirroteuthis'' from the Late Cretaceous of Japan and Canada. There is not much data about cirrate octopods due to their fragility, making them particularly pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbrella Octopus
Opisthoteuthidae, from Ancient Greek ὄπισθεν (''ópisthen''), meaning "back", and τευθίς (''teuthís''), meaning "squid", known as umbrella octopuses, are a group of pelagic octopuses. Umbrella octopuses are characterized by a web of skin between the arms, causing them to somewhat resemble an opened umbrella when the arms are spread. Description Opisthoteuthidae are a group of octopuses characterized by a web of skin in between their arms. They broad U-shaped shell that support muscles for a pair of small fins on the mantle, these fins are far less developed than other families in Cirrina and essentially only act as stabilizers when the animal swims (using a medusoid motion of the arms and webbing). This structure makes the umbrella octopus resemble an umbrella when they spread their arms/web out. The structure of the umbrella octopus has the oral surface below the mantle of the octopuses and the web with their arms surround the bottom of the mantle. Their oute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimpoteuthis
''Grimpoteuthis'' is a genus of pelagic Cirrina, cirrate (finned) octopods known as the dumbo octopus. The name "dumbo" originates from their resemblance to the title character of Disney's 1941 film ''Dumbo'', having two prominent ear-like fins which extend from the Mantle (mollusc), mantle above each eye. There are 17 species recognized in the genus. The Dumbo octopus has a gelatinous body and uses fin propulsion for movement, which also helps it to conserve energy in its extreme deep-sea environment. These unique physical traits distinguish it from other octopuses, which primarily rely on jet propulsion. Prey include crustaceans, bivalves, worms and copepods. The average life span of various ''Grimpoteuthis'' species is 3 to 5 years. Range and habitat Species of ''Grimpoteuthis'' are assumed to have a worldwide distribution, living in the cold, Abyssal plain, abyssal depths ranging from . Specimens have been found off the coasts of Oregon, the Philippines, Marth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
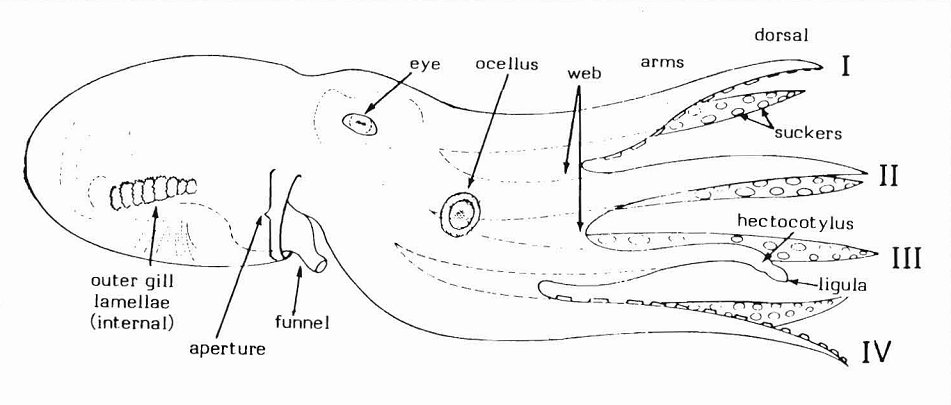
Octopus
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used for respiration and locomotion (by water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, and are short-lived. In most species, the male uses a speciall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin language, Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsum (biology), dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the Epidermis (skin), epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a mollusc shell, shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant ‘cloak’ or ‘cape’; see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopuses
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed Mollusca, mollusc of the order (biology), order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is symmetry in biology, bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a cephalopod beak, beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The Siphon (mollusc), siphon is used for aquatic respiration, respiration and aquatic locomotion, locomotion (by jet propulsion#Jet-propelled animals, water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "the depths". Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here, known as bottom dwellers, generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demersal
The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) consisting of the part of the water column near to (and significantly affected by) the seabed and the benthos. The demersal zone is just above the benthic zone and forms a layer of the larger profundal zone. Being just above the ocean floor, the demersal zone is variable in depth and can be part of the photic zone where light can penetrate, and photosynthetic organisms grow, or the aphotic zone, which begins between depths of roughly and extends to the ocean depths, where no light penetrates. Fish The distinction between demersal species of fish and pelagic species is not always clear cut. The Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua'') is a typical demersal fish, but can also be found in the open water column, and the Atlantic herring (''Clupea harengus'') is predominantly a pelagic species but forms large aggregations near the seabed when it spawns on banks of gravel. Two types of fish inhabit the demersal zone: those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcupine Seabight
The Porcupine Seabight or Porcupine Basin is a deep-water oceanic basin located on the continental margin in the northeastern portion of the Atlantic Ocean. It can be found in the southwestern offshore portion of Ireland and is part of a series of interconnected basins linked to a failed rift structure associated with the opening of the Northern Atlantic Ocean. The basin extends in a North-South direction and was formed during numerous subsidence and rifting periods between the Late Carboniferous and Late Cretaceous. It is bordered by the * Goban Spur to the south * Slyne Ridge to the north * Porcupine Bank to the west * Porcupine Abyssal Plain to the southwest Due to subsidence, water depths range from 3000 m in the south near its mouth to 400 m in the north. The Porcupine Basin lies on the Caledonian orogeny, Caledonian metamorphic basement and preserves up to 12 km of sedimentary strata from Late Palaeozoic to Quaternary which includes significant hydrocarbon reservoirs. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |