|
Crichton, Midlothian
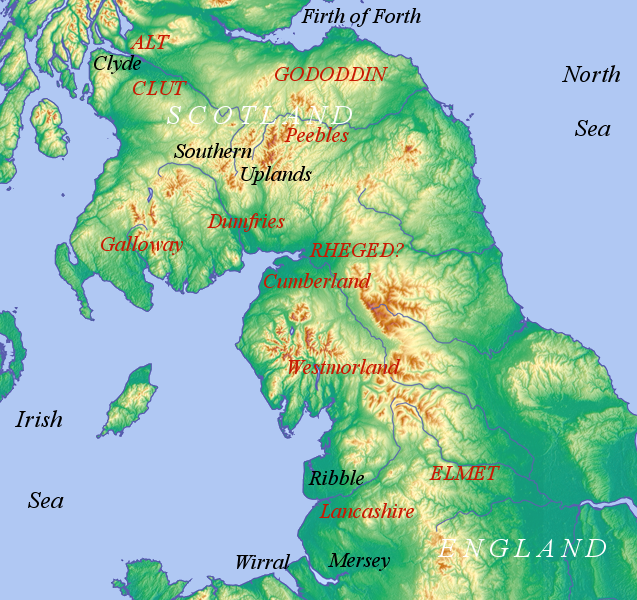
Crichton is a small village and civil parish in Midlothian, Scotland, around 2 miles (3 km) south of Pathhead and the same distance east of Gorebridge. The second element of the name is clearly from the Old English word ''tūn'' 'farm, settlement'. The first element is less certain, however, and could be from Gaelic ''crioch'' 'border' or Cumbric ''craig'' 'rock'.Bethany Fox, 'The P-Celtic Place-Names of North-East England and South-East Scotland', The Heroic Age, 10 (2007), http://www.heroicage.org/issues/10/fox.html (appendix at http://www.heroicage.org/issues/10/fox-appendix.html). To the west of the village is the 15th-century parish church, formerly a collegiate church, established by William Crichton, 1st Lord Crichton, the Lord Chancellor of Scotland from 1439 to 1453. To the south of the church is Crichton Castle Crichton Castle is a ruined castle near the village of Crichton in Midlothian, Scotland. It is situated at the head of the River Tyne, south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midlothian
Midlothian (; ) is registration county, lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area and one of 32 council areas of Scotland used for local government. Midlothian lies in the east-central Lowlands, bordering the City of Edinburgh council area, East Lothian and the Scottish Borders. The modern council area was formed in 1975 when the Midlothian (historic), historic county of Midlothian, also known as Edinburghshire, was altered substantially as part of local government reforms; its southern part formed a new Midlothian Districts of Scotland, District within the Local government areas of Scotland 1973 to 1996, Region of Lothian, whilst areas on the peripheries were assigned to other districts and the city of Edinburgh, which had always been autonomous to an extent, was formally separated as the Edinburgh (district), City of Edinburgh District. In 1996 Midlothian became a unitary authority area, using the same name and territory as in 1975. History Midlothian County Council w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midlothian (UK Parliament Constituency)
Midlothian in Scotland is a county constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first-past-the-post voting system. The seat has been represented since 2024 by Kirsty McNeill of Scottish Labour. It replaced Midlothian and Peeblesshire at the 1955 general election. A similar constituency, also called Midlothian, was used by the Scottish Parliament until 2011. Boundaries 1955–1974: The county of Midlothian, including all the burghs situated therein, except the county of the city of Edinburgh and the burgh of Musselburgh. 1974–1983: As above. 1983–1997: Midlothian District. 1997–2005: The Midlothian District electoral wards of Bonnyrigg/Newtongrange, Dalkeith, Loanhead, and Mayfield/Gorebridge. 2005–present: The area of the Midlothian Council. When first formed, the constituency covered the whole of the traditional county of Midlothian, apart from Edinburgh, split into multiple se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midlothian North And Musselburgh (Scottish Parliament Constituency)
Midlothian (; ) is registration county, lieutenancy area and one of 32 council areas of Scotland used for local government. Midlothian lies in the east- central Lowlands, bordering the City of Edinburgh council area, East Lothian and the Scottish Borders. The modern council area was formed in 1975 when the historic county of Midlothian, also known as Edinburghshire, was altered substantially as part of local government reforms; its southern part formed a new Midlothian District within the Region of Lothian, whilst areas on the peripheries were assigned to other districts and the city of Edinburgh, which had always been autonomous to an extent, was formally separated as the City of Edinburgh District. In 1996 Midlothian became a unitary authority area, using the same name and territory as in 1975. History Midlothian County Council was abolished in 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, which abolished Scotland's counties and burghs as administrative areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In Scotland
Civil parishes are small divisions used for statistical purposes and formerly for local government in Scotland. Civil parishes gained legal functions in 1845 when parochial boards were established to administer the poor law. Their local government functions were abolished in 1930 with their powers transferred to county or burgh councils. Since 1975, they have been superseded as the smallest unit of local administration in Scotland by community councils. History Civil parishes in Scotland can be dated from 1845, when parochial boards were established to administer the poor law. While they originally corresponded to the parishes of the Church of Scotland, the number and boundaries of parishes soon diverged. Where a parish contained a burgh, the area of the parish outside the burgh was termed the ''landward'' area. Until 1891 some parishes lay in more than one county. In that year, under the terms of the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, the boundaries of most of the civil pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathhead, Midlothian
Pathhead village is a conservation area in Midlothian, Scotland. Location Pathhead is located around south east of Dalkeith and south of Scotland's capital city, Edinburgh. It lies above the east bank of the River Tyne. The name of the village is due to its position. It stands above sea level and is at the head of the ascent of the main route from Edinburgh to Lauder. The A68 road is the main route through the village. With the opening of the Dalkeith bypass in 2008, it is possible to travel to Edinburgh in 10–15 minutes. Historic buildings is a five-arch stone bridge carrying the A68 road over the Tyne Water at the north west entrance to the village. The bridge is high, and each of the five spans is across. It was built in 1827–1831 to the designs of engineer Thomas Telford, and is a Category A listed building. To the north of the village is Preston Hall, an 18th-century country house designed by William Adam for the Duchess of Gordon, and later rebuilt by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorebridge
Gorebridge is a former Pit village, mining village in Midlothian, Scotland. Gorebridge has an annual Gala Day which always takes place on the 3rd Saturday in June. This is much like a town fair, with rides and games. The gala day has a tradition of picking a Town King and Queen from the primary school, primary schools. Gorebridge has four primary schools, Gorebridge Primary, Stobhill Primary, St Andrews RC Primary and Gore Glen Primary. Greenhall High school used to serve the town but closed down in 1994. Local children attend nearby Newbattle Community High School, St David's RC High School or Lasswade High School. There is a leisure centre, library and Vogrie Country Park in Gorebridge. Gorebridge's local football (soccer), football team is Arniston Rangers F.C., Arniston Rangers who were founded in 1878 and play home games at Newbyres Park in the . Annette Crosbie, known to many as the long suffering wife of Victor Meldrew, played by fellow Scot Richard Wilson (Scottish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English Language
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman (a type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers became dominant in England, their language re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish language, Irish and Manx language, Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a Classical Gaelic, common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 United Kingdom census#2011 Census for Scotland, 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "fellow countrymen"). The Welsh and the Cumbric-speaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collegiate Church
In Christianity, a collegiate church is a church where the daily office of worship is maintained by a college of canons, a non-monastic or "secular" community of clergy, organised as a self-governing corporate body, headed by a dignitary bearing a title which may vary, such as dean or provost. In its governance and religious observance, a collegiate church is similar in some respects to a cathedral, but a collegiate church is not the seat of a bishop and has no diocesan responsibilities. Collegiate churches have often been supported by endowments, including lands, or by tithe income from appropriated benefices. The church building commonly provides both distinct spaces for congregational worship and for the choir offices of the canons. History In the early medieval period, before the development of the parish system in Western Christianity, many new church foundations were staffed by groups of secular priests, living a communal life and serving an extensive territor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Crichton, 1st Lord Crichton
William Crichton, 1st Lord Crichton (died 1454) was an important political figure in the late medieval Kingdom of Scotland. Life The son of Sir John Crichton of Crichton, William Crichton is first attested to as one of the Scots noblemen and gentry who were given safe passage into England to meet James I of Scotland, following the latter's release from captivity. Crichton was one of eighteen gentlemen to receive the honour of knighthood at the coronation of King James on 21 May 1424, and was later made a Gentleman of the Bedchamber (). In 1426, Crichton, described as a knight and chamberlain (), along with William Fowlis, the royal almoner, and Thomas de Cranston, King's squire, were sent as envoys to the court of Eric III of Norway to negotiate a continuation of the peace between their respective countries. Upon his return he was appointed governor of Edinburgh Castle, Master of the Royal Household and by 1435 Sheriff of Edinburgh. In 1437 Crichton, as Keeper of Edinb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Chancellor Of Scotland
The Lord Chancellor of Scotland, formally titled Lord High Chancellor, was an Officer of State in the Kingdom of Scotland. The Lord Chancellor was the principal Great Officer of State, the presiding officer of the Parliament of Scotland, the Keeper of the Great Seal, the presiding officer of the Privy Council (until 1626), and a judge of the College of Justice. Holders of the office are known from 1123 onwards, but its duties were occasionally performed by an official of lower status with the title of Keeper of the Great Seal. From the 15th century, the Chancellor was normally a bishop or a peer. Following the Union, the Lord Keeper of the Great Seal of England became the first Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain, but the Earl of Seafield continued as Lord Chancellor of Scotland until 1708. He was re-appointed in 1713 and sat as an Extraordinary Lord of Session in that capacity until his death in 1730. List of Lords Chancellors of Scotland David I * 1124-1126: John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |