|
Crawler Transporter
The crawler-transporters, formally known as the Missile Crawler Transporter Facilities, are a pair of tracked vehicles used to transport launch vehicles from NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) along the Crawlerway to Launch Complex 39. They were originally used to transport the Saturn IB and Saturn V rockets during the Apollo, Skylab and Apollo–Soyuz programs. They were then used to transport Space Shuttles from 1981 to 2011. The crawler-transporters carry vehicles on the mobile launcher platforms (MLPs) used by NASA, and after each launch return to the pad to take the platform back to the VAB. The two crawler-transporters were designed and built by Marion Power Shovel Company using some components designed and built by Rockwell International at a cost of ( in 2022) each. Upon its construction, the crawler-transporter became the largest self-powered land vehicle in the world until it was beaten in 2013 with the production of the ultraheavy XGC88000 crawler crane. While ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marion Power Shovel Company
Marion Power Shovel Company was an American firm that designed, manufactured and sold steam shovels, power shovels, blast hole drills, excavators, and dragline excavators for use in the construction and mining industries. The company was a major supplier of steam shovels for the construction of the Panama Canal. The company also built the two crawler-transporters used by NASA for transporting the Saturn V rocket and later the Space Shuttle to their launch pads. The company's shovels played a major role in excavation for Hoover Dam, the Holland Tunnel and the extension of the 7 (New York City Subway service), Number 7 subway line to Main Street (Queens), Main Street in Flushing, Queens. Founded in Marion, Ohio in August, 1884 by Henry Barnhart, Edward Huber and George W. King as the Marion Steam Shovel Company, the company grew through sales and acquisitions throughout the 20th century. The company changed its name to Marion Power Shovel Company in 1946 to reflect the industry's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructed from a repurposed Saturn V third stage (the S-IVB), and took the place of the stage during launch. Operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation and hundreds of experiments. Skylab's orbit eventually decayed and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but its funding was canceled and U.S. participation shifted to the International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crawler-transporter Cutaway View
The crawler-transporters, formally known as the Missile Crawler Transporter Facilities, are a pair of tracked vehicles used to transport launch vehicles from NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) along the Crawlerway to Launch Complex 39. They were originally used to transport the Saturn IB and Saturn V rockets during the Apollo, Skylab and Apollo–Soyuz programs. They were then used to transport Space Shuttles from 1981 to 2011. The crawler-transporters carry vehicles on the mobile launcher platforms (MLPs) used by NASA, and after each launch return to the pad to take the platform back to the VAB. The two crawler-transporters were designed and built by Marion Power Shovel Company using some components designed and built by Rockwell International at a cost of ( in 2022) each. Upon its construction, the crawler-transporter became the largest self-powered land vehicle in the world until it was beaten in 2013 with the production of the ultraheavy XGC88000 crawler crane. While o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marion 6360
Marion 6360, known as "the Captain", was a giant power shovel built by the Marion Power Shovel company. Completed and commissioned on October 15 1965, it was one of the largest land vehicles ever built, exceeded only by some dragline and bucket-wheel excavators. The shovel originally started work with Southwestern Illinois Coal Corporation, but the owners were soon bought out by Arch Coal. Everything remained the same at the mine except for the colors which were changed to red, white, and blue. Like most mining vehicles of extreme size, the Marion 6360 required a surprisingly small amount of men to operate (a total of four), consisting of a operator, oiler, welder, and a ground man who looked after the trailing cable. The shovel worked well for Arch Coal until September 9, 1991, when a fire broke out in the lower works of the shovel, caused by a burst hydraulic line that spraying the hot fluids on an electrical relay panel. This fire caused a great deal of damage to both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Shovel
A power shovel, also known as a motor shovel, stripping shovel, front shovel, mining shovel or rope shovel, is a bucket-equipped machine usually powered by steam, diesel fuel, gasoline or electricity and used for digging and loading earth or fragmented rock and for mineral extraction. Power shovels are a type of rope/cable excavator, where the digging arm is controlled and powered by winches and steel ropes, rather than hydraulics like in the modern hydraulic excavators. Basic parts of a power shovel include the track system, cabin, cables, rack, stick, boom foot-pin, saddle block, boom, boom point sheaves and bucket. The size of bucket varies from 0.73 to 53 cubic meters. Design Power shovels normally consist of a revolving deck with a power plant, drive and control mechanisms, usually a counterweight, and a front attachment, such as a crane ("boom") which supports a handle ("dipper" or "dipper stick") with a digger (" bucket") at the end. The term "dipper" is also sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
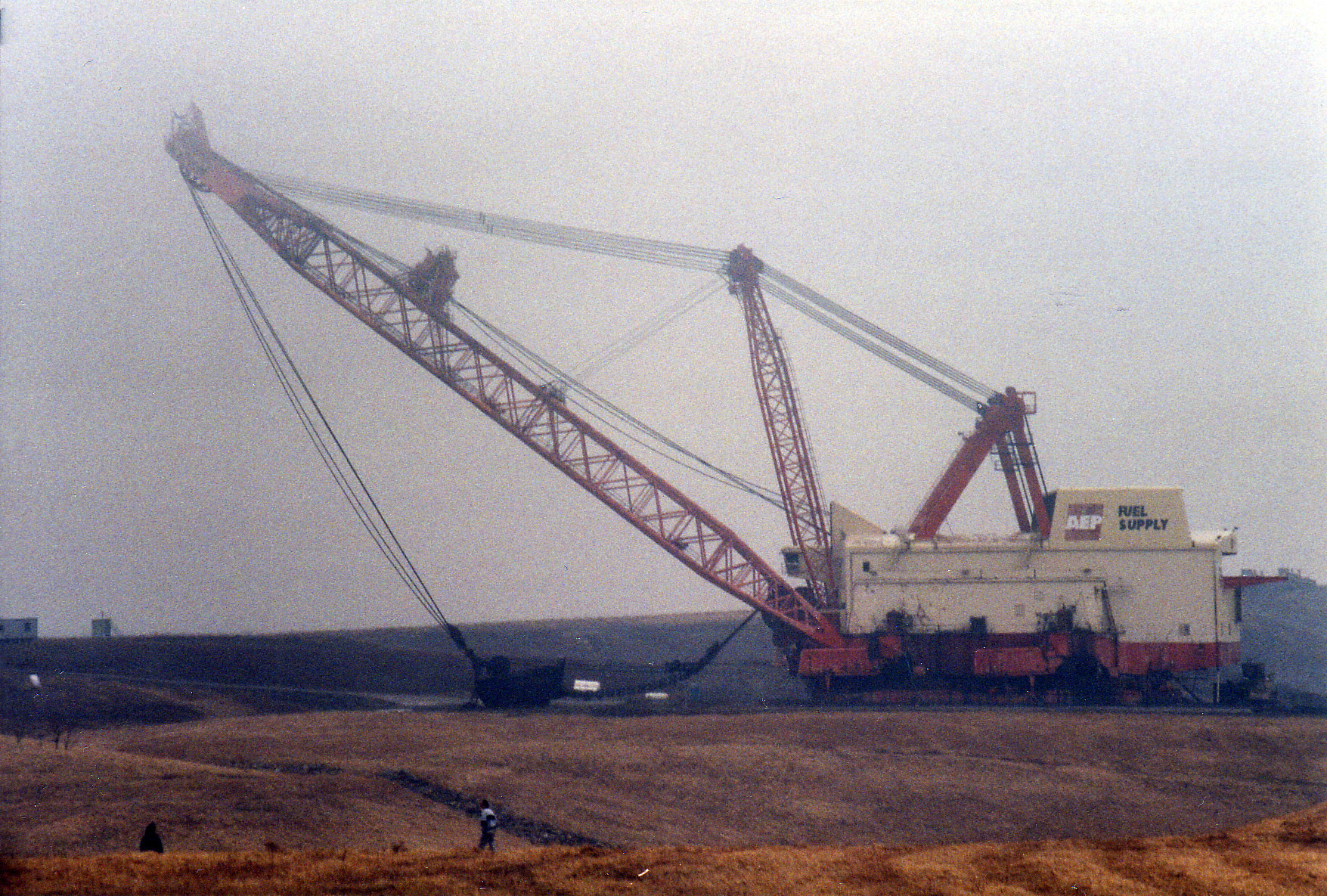
Big Muskie
Big Muskie was a dragline excavator built by Bucyrus-Erie and owned by the Central Ohio Coal Company (formerly a division of American Electric Power), weighing and standing nearly 22 stories tall. It mined coal in the U.S. state of Ohio from 1969 to 1991. It was dismantled and sold for scrap in 1999. Design specifications and service The Big Muskie was a model 4250-W dragline and was the only one ever built by the Bucyrus-Erie company. With a bucket, it was the largest single-bucket digging machine ever created and one of the world's largest mobile earth-moving machines alongside the Illinois-based Marion 6360 stripping shovel called The Captain and the German bucket wheel excavators of the Bagger 288 and Bagger 293 family.For details see the table on thGerman Wiki The bucket alone could hold two Greyhound buses side by side. It took over 200,000 man hours to construct over a period of about two years and cost $25 million in 1969, the equivalent of $ today adjusted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
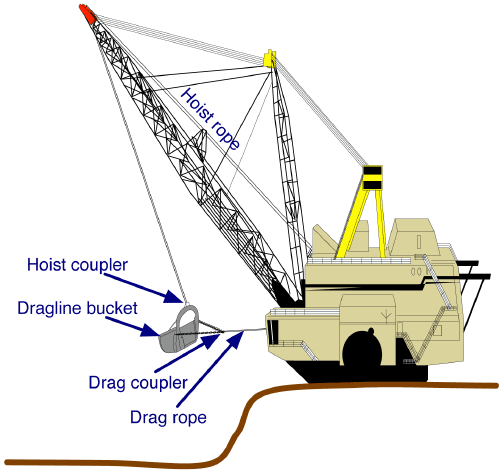
Dragline Excavator
A dragline excavator is a heavy-duty excavator used in civil engineering and surface mining. It was invented in 1904, and presented an immediate challenge to the steam shovel and its diesel and electric powered descendant, the power shovel. Much more efficient than even the largest of the latter, it enjoyed a heyday in extreme size for most of the 20th century, first becoming challenged by more efficient rotary excavators in the 1950s, then superseded by them on the upper end from the 1970s on. The largest ever walking dragline was Big Muskie, a Bucyrus-Erie 4250-W put online in 1969 that swung a , 325 ton capacity bucket, had a boom, and weighed 13,500 tons. The largest walking dragline produced as of 2014 was Joy Global’s digital AC drive control P&H 9020XPC, which has a bucket capacity of and boom lengths ranging from ; working weights vary between 7,539 and 8,002 tons. Types Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting crane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagger 288
Bagger 288 (Excavator 288), previously known as the MAN TAKRAF RB288 built by the German company Krupp for the energy and mining firm Rheinbraun, is a bucket-wheel excavator or mobile strip mining machine. When its construction was completed in 1978, Bagger 288 superseded Big Muskie as the heaviest land vehicle in the world, at 13,500 tons. It took five years to design and manufacture and five years to assemble, with total cost reaching $100 million. In 1995, it was itself superseded by the slightly heavier Bagger 293 (14,200 tons). XCMG's XGC88000 Crawler Crane remains the largest self-propelled land vehicle in the world, since bucket-wheel excavators are powered by an external power source, and the Overburden Conveyor Bridge F60s hold the title of largest land vehicle of any type by physical dimensions. Like its siblings, the Bagger 288 require a disproportionately small number of people to operate, at just five total. Whilst Bagger 288 is considered a "sibling vehicle" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucket-wheel Excavator
A bucket-wheel excavator (BWE) is a large heavy equipment machine used in surface mining. Their primary function is that of a continuous digging machine in large-scale open-pit mining operations, removing thousands of tons of overburden a day. What sets them apart from other large-scale mining equipment, such as bucket chain excavators, is their use of a large wheel consisting of a continuous pattern of buckets which scoop material as the wheel turns. They are among the largest land or sea vehicles ever produced. The 14,200-ton Bagger 293 holds the Guinness World Record for the heaviest land-based vehicle ever built. History Bucket-wheel excavators have been used in mining for the past century, with some of the first being manufactured in the 1920s. They are used in conjunction with many other pieces of mining machinery (conveyor belts, spreaders, crushing stations, heap-leach systems, etc.) to move and mine massive amounts of overburden (waste). While the overall concepts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XGC88000 Crawler Crane
The XGC88000 crawler crane is a class of extremely large ultraheavy crawler crane made by XCMG. With a lifting capacity of 3,600 to 4,000 tons, a total boom length of 144 meters and a total gross weight of 5,350 tons. The XGC88000 crawler crane became the largest tracked mobile crane in the world, beating out the previous record holder, the Liebherr LR 13000 when it officially came into production in 2013. However, when it comes to absolute size, movability, and strength, the title still goes to the Honghai Crane which runs on rails. It is also one of the largest ground vehicles in current operation, and - by its official production in 2013 - became the largest self-propelled ground vehicle by gross size, beating out the NASA crawler-transporter The crawler-transporters, formally known as the Missile Crawler Transporter Facilities, are a pair of tracked vehicles used to transport launch vehicles from NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) along the Crawlerway to Launch Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockwell International
Rockwell International was a major American manufacturing conglomerate (company), conglomerate. It was involved in aircraft, the space industry, defense and commercial electronics, components in the automotive industry, printing presses, avionics and industrial products. At its peak, Rockwell International was No. 27 on the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list, with assets of over $8 billion, sales of $27 billion and 115,000 employees. Rockwell International's predecessor was Rockwell International#Rockwell Manufacturing Company, Rockwell Manufacturing Company, founded in 1919 by Willard Rockwell. In 1968, Rockwell Manufacturing Company included seven operating divisions manufacturing industrial valves, German 2-cycle motors, power tools, gas and water meters. In 1973, it was combined with the aerospace products and renamed Rockwell International. It was split into various companies beginning in the 1980s, including its final split in 2001 into Rockwell Automation and Roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |