|
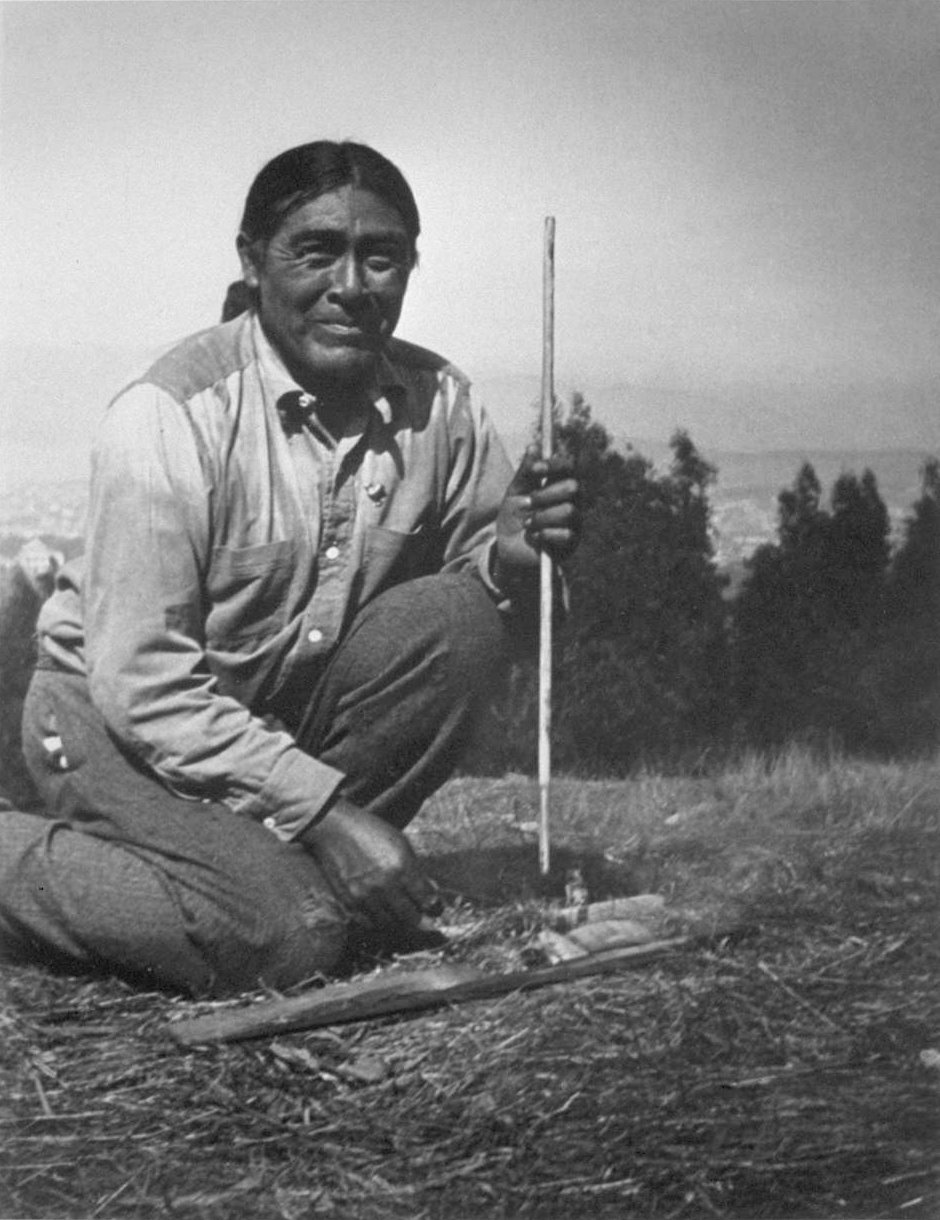
Coyote (mythology)
Coyote is a mythological character common to many cultures of the Indigenous peoples of North America, based on the coyote (''Canis latrans'') animal. This character is usually male and is generally anthropomorphic, although he may have some coyote-like physical features such as fur, pointed ears, yellow eyes, a tail and blunt claws. The myths and legends which include Coyote vary widely from culture to culture. The role Coyote takes in traditional stories shares some traits with the Cultural depictions of ravens#North American Pacific Northwest, Raven figure in other cultures. Coyoteway Coyote is the tutelary spirit of "Coyoteway", one of the Navajo curing ceremonies. The ceremony is intended to restore the patient's harmonious relationship with Coyote and the world, and to bring about a return to good health. By culture Coyote is featured in the mythology of a number of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous cultures of the Americas, including: California Coyote i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maidu
The Maidu are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather River, Feather and American River, American Rivers and in Humbug Valley. In Maiduan languages, ''maidu'' means "person". Local division The Maidu people are geographically dispersed into many subgroups or bands who live among and identify with separate valleys, foothills, and mountains in northeastern Central California. The three subcategories of Maidu are: * The Nisenan or Southern Maidu occupied the whole of the American, Bear River (Feather River), Bear, and Yuba River drainages. They live in lands that were previously home to the Martis people, Martis. * The Northeastern or Mountain Maidu, also known as Yamani Maidu, lived on the upper north and middle forks of the Feather River. * The Konkow (Koyom'kawi/Concow) occupied a Concow, California, valley between present-day Cherok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ute People
Ute () are an Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin, Indigenous people of the Great Basin and Colorado Plateau in present-day Utah, western Colorado, and northern New Mexico.Pritkzer''A Native American Encyclopedia'' p. 242 Historically, their territory also included parts of Wyoming, eastern Nevada, and Arizona. Their Ute dialect is a Colorado River Numic language, part of the Uto-Aztecan language family Historically, the Utes belonged to almost a dozen nomadic bands, who came together for ceremonies and trade. They also traded with neighboring tribes, including Pueblo peoples. The Ute had settled in the Four Corners region by 1500 CE. The Utes' first contact with Europeans was with the Spanish in the 18th century. The Utes had already acquired horses from neighboring tribes by the late 17th century. They had limited direct contact with the Spanish but participated in regional trade. Sustained contact with Euro-Americans began in 1847 with the arrival of the Mormons to the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ), also known by the endonym Newe, are an Native Americans in the United States, Indigenous people of the United States with four large cultural/linguistic divisions: * Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming * Northern Shoshone: Southern Idaho * Western Shoshone: California, Nevada, and Northern Utah * Goshute: western Utah, eastern Nevada They traditionally speak the Shoshoni language, part of the Numic languages branch of the large Uto-Aztecan languages, Uto-Aztecan language family. The Shoshone were sometimes called the Snake Indians by neighboring tribes and early American explorers. Their peoples have become members of List of federally recognized tribes, federally recognized tribes throughout their traditional areas of settlement, often co-located with the Northern Paiute people of the Great Basin. Etymology The name "Shoshone" comes from ''Sosoni'', a Shoshoni language, Shoshone word for high-growing grasses. Some neighboring tribes call the Shoshone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paiute
Paiute (; also Piute) refers to three non-contiguous groups of Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin. Although their languages are related within the Numic group of Uto-Aztecan languages, these three languages do not form a single subgroup and they are no more closely related to each than they are to the Central Numic languages (Timbisha, Shoshoni, and Comanche) which are spoken between them. The term "Paiute" does not refer to a single, unique, unified group of Great Basin tribes, but is a historical label comprising: * Northern Paiute people Northern may refer to the following: Geography * North, a point in direction * Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe * Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States * Northern Province, Sri Lanka * Northern Range, ... of northeastern California, northwestern Nevada, eastern Oregon, and southern Idaho * Southern Paiute people of northern Arizona, southern Nevada, and southwestern Utah * Mono people of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
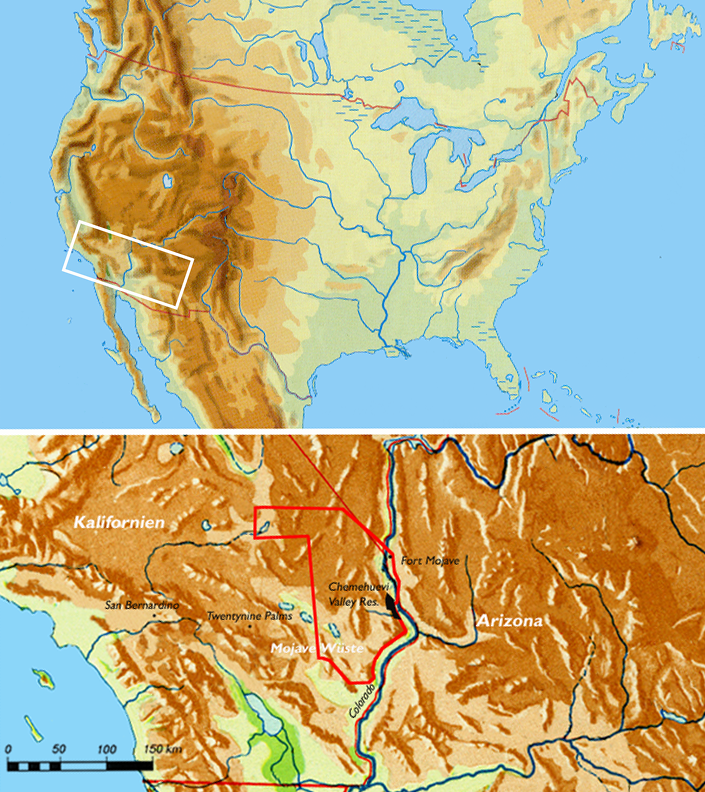
Chemehuevi
The Chemehuevi ( ) are an indigenous people of the Great Basin. They are the southernmost branch of Southern Paiute. Today, Chemehuevi people are enrolled in the following federally recognized tribes: * Colorado River Indian Tribes * Chemehuevi Indian Tribe of the Chemehuevi Reservation * Morongo Band of Mission Indians * Cabazon Band of Mission Indians * Agua Caliente Band of Cahuilla Indians * Torres-Martinez Desert Cahuilla Indians * Twenty-Nine Palms Band of Mission Indians of California Some Chemehuevi are also part of the Soboba Band of Luiseño Indians, whose members are mostly ''Sovovatum'' or ''Soboba band'' members of Cahuilla and Luiseño people. Name "Chemehuevi" has multiple interpretations. It is considered to either be a Mojave term meaning "those who play with fish;" or a Quechan word meaning "nose-in-the-air-like-a- roadrunner."Pritzker 23 The Chemehuevi call themselves ''Nüwüvi'' ("The People", singular ''Nüwü'') or ''Tantáwats'', meaning " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokuts
The Yokuts (previously known as MariposasPowell, 1891:90–91.) are an ethnic group of Native Americans native to central California. Before European contact, the Yokuts consisted of up to 60 tribes speaking several related languages. Yokuts is both plural and singular; Yokut, while common, is erroneous. Yokut should only be used when referring specifically to the Tachi Yokut Tribe of Lemoore. Some of their descendants prefer to refer to themselves by their respective tribal names; they reject the term Yokuts,' saying that it is an exonym invented by English-speaking settlers and historians. Conventional subgroupings include the Foothill Yokuts, Northern Valley Yokuts, and Southern Valley Yokuts.Pritzker, 211 History Another name used to refer to the Yokuts was Mariposans. The endonym "Yokuts" itself means "people." Many stories are told, depending on the tribe, on how the Yokuts and their land came to be, but most follow a similar form. Their creation story is such: Once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yana People
The Yana are a group of Native Americans indigenous to Northern California in the central Sierra Nevada, on the western side of the range. Their lands, prior to encroachment by white settlers, bordered the Pit and Feather rivers. They were nearly destroyed during the California genocide in the latter half of the 19th century. Descendants of the Central and Southern Yana continue to live in California as members of Redding Rancheria. Etymology The Yana-speaking people comprise four groups: the North Yana, the Central Yana, the Southern Yana, and the Yahi, two of which - the Central and Southern - have living descendants. The noun stem ''Ya''- means "person"; the noun suffix is -''na'' in the northern Yana dialects and -''hi'' iin the southern dialects. History Anthropologist Alfred L. Kroeber put the 1770 population of the Yana at 1,500, and Sherburne F. Cook estimated their numbers at 1,900 and 1,850. Other estimates of the total Yana population before the Gold Rush e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wappo
The Wappo (endonym: ''Micewal'') are an Indigenous people of northern California. Their traditional homelands are in Napa Valley, the south shore of Clear Lake, Alexander Valley, and Russian River valley. They are distantly related to the Yuki people, from which they seem to have diverged at least 500 years ago. Their language, Wappo, has been influenced by the neighboring Pomo, who use the term ''A'shochamai'' or ''A'shotenchawi'' (transcribed as ''Ashochimi'' by some authors), meaning "northerners", to refer to the Wappo. Culture Prior to European colonization, the Wappo lived by hunting and gathering, and lived in small groups without centralized political authority, in homes built from branches, leaves and mud. Their woven baskets were so well-crafted that they were able to hold water. History When Mexicans arrived to colonize California, Wappo villages existed near the present-day towns of Yountville, St. Helena and Calistoga. Those on the south shore of Clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
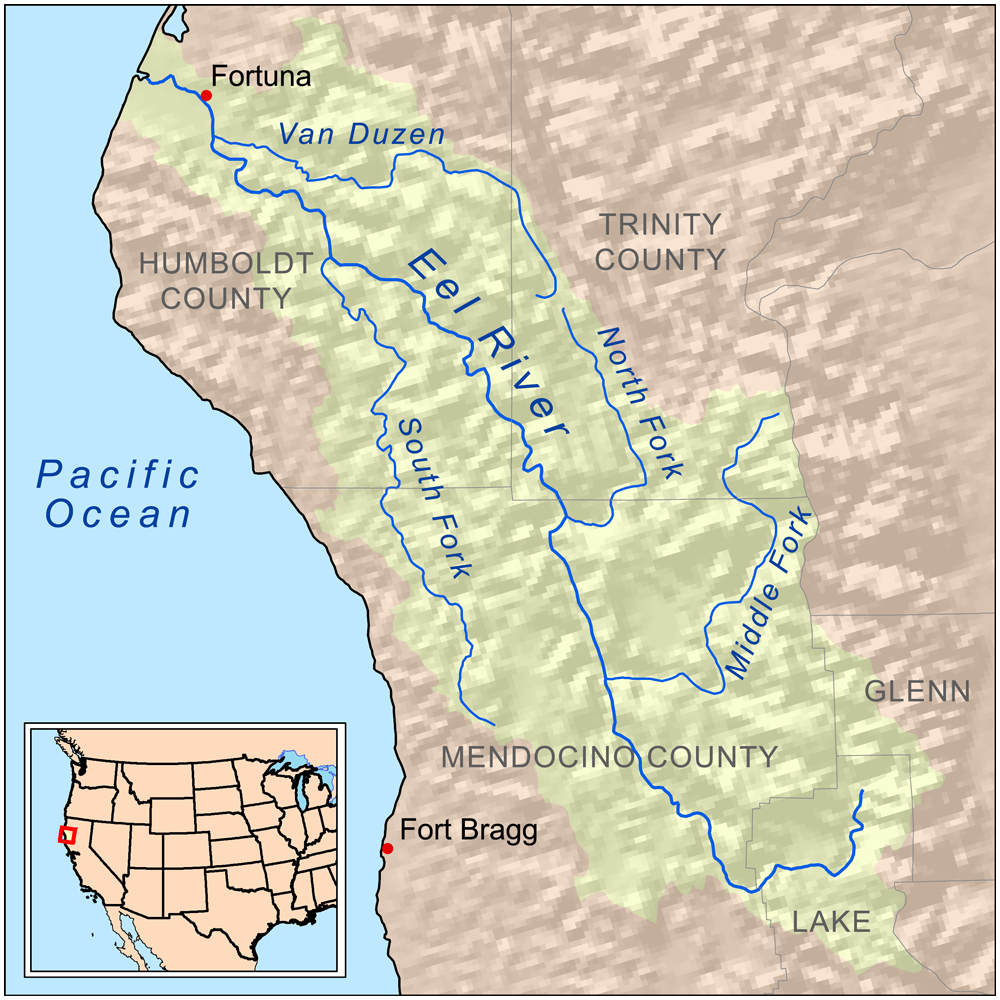
Sinkyone
The Eel River Athapaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or near the Eel River (California), Eel River and Van Duzen River of northwestern California. These groups speak dialects of the Wailaki language belonging to the Pacific Coast Athabaskan, Pacific Coast Athapaskan group of the Athabaskan languages, Athapaskan language family which is prominently represented in Alaska, western Canada, and the southwestern U.S. Other related Athapaskan groups neighboring the Eel River Athapaskans included the Hupa-Whilkut-Chilula to the north, the Mattole on the coast to the west, and the Kato (tribe), Kato to the south. The Whilkut, Nongatl and Lassik were essentially annihilated during the Bald Hills War in the 1860s. Some Wailaki people are registered members of Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |