|
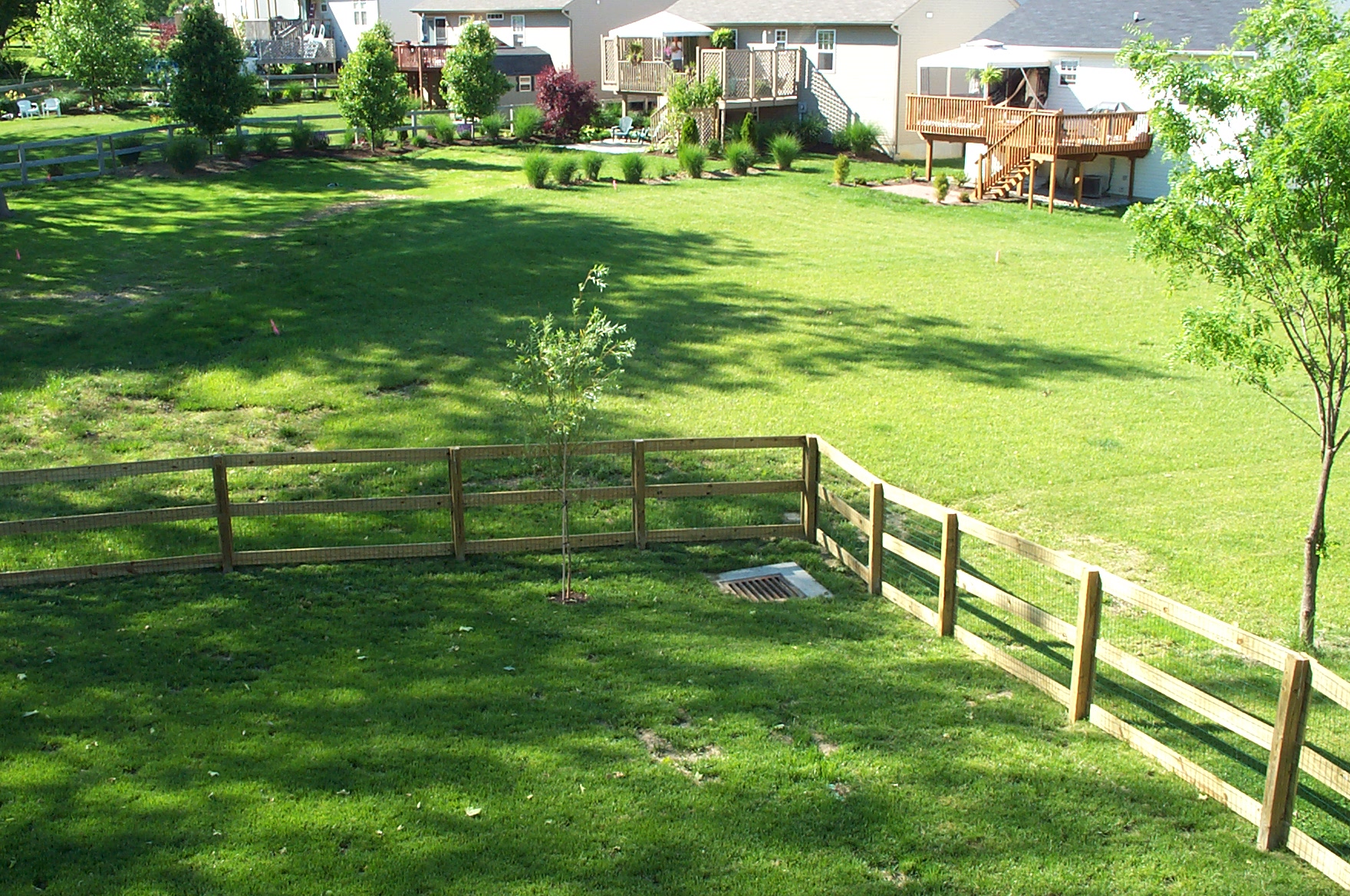
Courtyard
A courtyard or court is a circumscribed area, often surrounded by a building or complex, that is open to the sky. Courtyards are common elements in both Western and Eastern building patterns and have been used by both ancient and contemporary architects as a typical and traditional building feature. Such spaces in inns and public buildings were often the primary meeting places for some purposes, leading to the other meanings of Court (other), court. Both of the words ''court'' and ''yard'' derive from the same root, meaning an enclosed space. See yard (land), yard and garden for the relation of this set of words. In universities courtyards are often known as quadrangle (architecture), quadrangles. Historic use Courtyards—private open spaces surrounded by walls or buildings—have been in use in residential architecture for almost as long as people have lived in constructed dwellings. The courtyard house makes its first appearance –6000 BC (calibrated), in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtyard House
A courtyard house is a type of house—often a large house—where the main part of the building is disposed around a central courtyard. Many houses that have courtyards are not courtyard houses of the type covered by this article. For example, large houses often have small courtyards surrounded by service rooms or corridors, but the main rooms are not disposed around a courtyard. Blenheim Palace in England is an example of such a house. The main rooms of a courtyard house often open onto the courtyard, and the exterior walls may be windowless and/or semi-fortified and/or surrounded by a moat. Courtyard houses of this type occupy an intermediate position between a castle or fortress, where defence is the primary design consideration, and more modern plans in which defence is not a consideration at all. In England the courtyard house was a popular design for large houses in the sixteenth century, after noblemen had stopped building themselves castles, but before thoughts of defenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
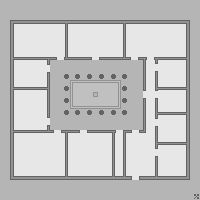
Siheyuan
A ''siheyuan'' (; ɹ̩̂.xɤ̌.ɥɛ̂n is a traditional Chinese architectural style characterized by a courtyard enclosed by buildings on all four sides. This design was prevalent throughout China, notably in Beijing and rural Shanxi. Historically, siheyuan served as the foundational layout for various structures, including residences, palaces, temples, monasteries, family businesses, and government offices In ancient times, a spacious siheyuan would be occupied by a single, usually large and extended family, signifying wealth and prosperity. Today, remaining siheyuan are often still used as subdivided housing complexes, although many lack modern amenities. Names ''Siheyuan'' is a courtyard surrounded by buildings on all four sides. It also appears in English translation as and, less often, as . History Siheyuan dates back as early as the Western Zhou period, and has a history of over 2,000 years. They exhibit outstanding and fundamental characteristics of Chinese archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yard (land)
A yard is an area of land immediately adjacent to one or more buildings. It may be either enclosed or open. The word may come from the same linguistic root as the word ''garden'' (Proto-Indo-European ''gher'' "to grasp, enclose") and has many of the same meanings. A number of derived words exist, usually tied to a particular usage or building type. Some may be archaic or in lesser use now. Examples of such words are: courtyard, barnyard, hops, hopyard, graveyard, churchyard, brickyard, Prison#Common facilities, prison yard, railyard, wrecking yard, junkyard, stableyard, and dooryard. Word origin One possible account of the origin is the Middle English ''yerd'', going back to Old English ''geard'' "fence, enclosure, dwelling, home, district, country," going back to Germanic *''garđa''- (whence also Old Saxon ''gard'' "garden, (compare the French''jardin'') dwelling, world," Middle Dutch ''gaert'' "garden, yard," Old High German ''gart'' "enclosure, circle, enclosed piece of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peristyle
In ancient Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture, a peristyle (; ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. ''Tetrastoön'' () is a rarely used archaic term for this feature. The peristyle in a Greek temple is a ''peristasis (architecture), peristasis'' (). In the Christian Church architecture, ecclesiastical architecture that developed from the Roman basilica, a courtyard peristyle and its garden came to be known as a cloister. Etymology The Greek word περίστυλον ''perístylon'' is composed of περί ''peri'', "around" or "surrounded", and στῦλος ''stylos'', "column" or "pillar", together meaning "surrounded by columns/pillars". It was Latinised into synonyms ''peristylum'' and ''peristylium''. In Greek architecture A peristyle was mostly used as a courtyard in Ancient Greece, but in the homes of people who were in the upper class or if they owned s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impluvium
The ''impluvium'' (: ''impluvia'') is a water-catchment pool system meant to capture rain-water flowing from the ''compluvium'', an area of roof. Often placed in a courtyard, under an opening in the roof, and thus "inside", instead of "outside", a building, it is a notable feature in many architectural traditions. Greco-Roman ''impluvium'' In Greco-Roman architectural studies, the ''impluvium'' refers to the sunken part of the Atrium (architecture), atrium in a Greek or Roman house (''domus''), designed to carry away the rainwater falling from the ''compluvium'' of the roof. It is usually made of marble and placed about 30 cm below the floor of the atrium, and emptied into a subfloor cistern. Construction and use Inspection (without excavation) of ''impluvia'' in Paestum, Pompeii and Rome indicated that the pavement surface in the ''impluvia'' was porous, or that the non-porous stone tiles were separated by gaps significant enough to allow a substantial quantity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooper House (Baltimore, Maryland)
The Hooper House, also known as Hooper House II, located in Bare Hills in Baltimore County, Maryland, was commissioned by philanthropist Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives for the public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material ... Edith Hooper, and designed by architects Marcel Breuer and Herbert Beckhard. Breuer had designed an addition to the Hoopers' prior home in Baltimore in 1948; that home is often referred to as "Hooper House I," which is why this newer residence is often called "Hooper House II." Ground was broken on the project in 1958 and the house was completed in 1959. Design One of the most immediately apparent as well as fundamentally important features of this home is its "binuclear" design: A central courtyard divides the house into living/dining/cooking/entertaining and family/bedroom areas. The fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrangle (architecture)
In architecture, a quadrangle (or colloquially, a quad) is a space or a courtyard, usually rectangular (square or oblong) in plan, the sides of which are entirely or mainly occupied by parts of a large building (or several smaller buildings). The word is probably most closely associated with college or university campus architecture, but quadrangles are also found in other buildings such as palaces. Most quadrangles are open-air, though a few have been roofed over (often with glass), to provide additional space for social meeting areas or coffee shops for students. The word ''quadrangle'' was originally synonymous with ''quadrilateral'', but this usage is now relatively uncommon. Some modern quadrangles resemble cloister gardens of medieval monasteries, called garths, which were usually square or rectangular, enclosed by covered arcades or cloisters. However, it is clear from the oldest examples (such as Mob Quad) which are plain and unadorned with arcades, that the medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
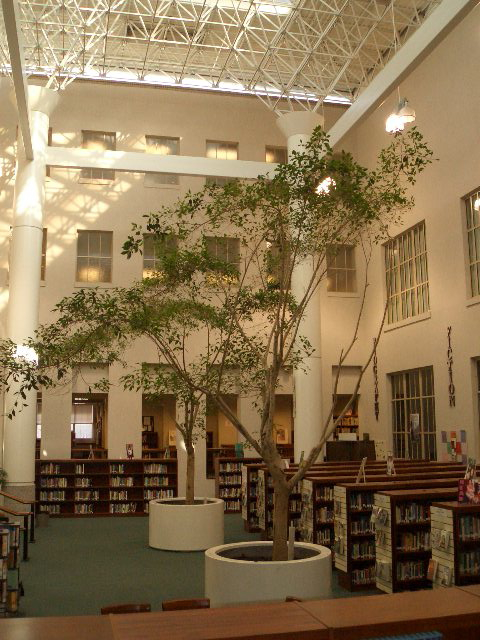
Atrium (architecture)
In architecture, an atrium (: atria or atriums) is a large open-air or skylight-covered space surrounded by a building. Atria were a common feature in Ancient Roman dwellings, providing light and ventilation to the interior. Modern atria, as developed in the late 19th and 20th centuries, are often several stories high, with a glazed roof or large windows, and often located immediately beyond a building's main entrance doors (in the lobby). Atria are a popular design feature because they give their buildings a "feeling of space and light." The atrium has become a key feature of many buildings in recent years. Atria are popular with building users, building designers and building developers. Users like atria because they create a dynamic and stimulating interior that provides shelter from the external environment while maintaining a visual link with that environment. Designers enjoy the opportunity to create new types of spaces in buildings, and developers see atria as prestigi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much architecture, artistic expression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing (building)
A wing is part of a building – or any feature of a building – that is subordinate to the main, central structure.Curl, James Stevens (2006). ''Oxford Dictionary of Architecture and Landscape Architecture'', 2nd ed., OUP, Oxford and New York, p. 853, . The individual wings may directly adjoin the main building or may be built separately and joined to it by a connecting structure such as a colonnade or pergola. New buildings may incorporate wings from the outset or these may be added at a later date as part of an expansion or remodelling. History In Classical (architecture), Classical and Palladian (architecture), Palladian buildings, the wings are smaller buildings either side of the ''corps de logis'' and joined to it by Quadrant (architecture), quadrants or colonnades, partially projecting forward to form a courtyard, court or ''cour d'honneur''. They may also be an integral part of the principal block and be emphasised by any combination of a change in height, profile, colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oak Ridge Apartments (7345691882)
Oak Ridge Apartments is a historic apartment building at 1615-1625 Ridge Avenue in Evanston, Illinois. The three-story brick building was built in 1914. Architect Andrew Sandegren, who also designed several Chicago apartment buildings, designed the building in the Tudor Revival style; Sandegren would go on to live in the building. The building features projecting entrance bays, an open central courtyard, and a crenellated roofline with projecting gables. Each apartment included amenities meant to cater to upper-class residents, such as servants' quarters, sunrooms, and brick fireplaces. The building was added to the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Hist ... on March 15, 1984. References External links Buildings and structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church, Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |