|
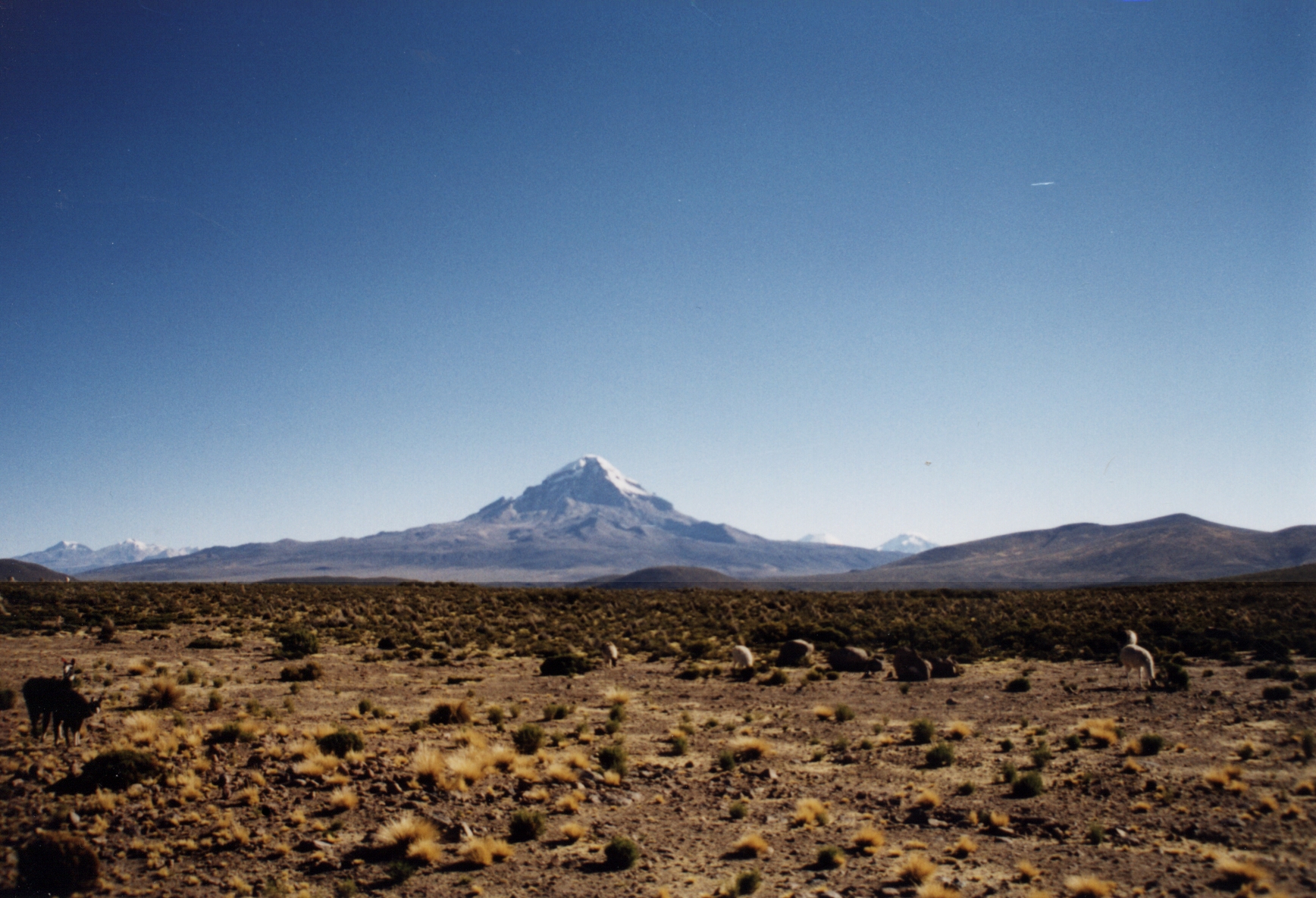
Cordillera Occidental (Bolivia)
Topographic map of Bolivia showing (east to west) plains of Cordill.html" ;"title="Geology of Bolivia#Lowlands and Sub-Andean zone">Sub-Andean Zone in red, Cordillera Oriental (Bolivia)">Eastern Cordillera in white, Altiplano in gray, and Western Cordillera in white The Cordillera Occidental or Western Cordillera of Bolivia is part of the Andes (that is also part of the American Cordillera), a mountain range characterized by volcanic activity, making up the natural border with Chile and starting in the north with Juqhuri and ending in the south at the Licancabur volcano, which is on the southern limit of Bolivia with Chile. The border goes through the innominated point located at two-thirds of elevation of Licancabur's northeastern slope at the southwestermost point of Bolivia at 22° 49' 41" south and 67° 52' 35" west. The climate of the region is cold and inadequate for animal and plant life. Its main feature is its ground, in which are large quantities of metallic minerals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mount Fuji
is an active stratovolcano located on the Japanese island of Honshu, with a summit elevation of . It is the highest mountain in Japan, the second-highest volcano on any Asian island (after Mount Kerinci on the Indonesian island of Sumatra), and List of islands by highest point, seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth. Mount Fuji Hōei eruption, last erupted from 1707 to 1708. It is located about southwest of Tokyo, from where it is visible on clear days. Its exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is snow field, covered in snow for about five months of the year, is a Japanese cultural icon and is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers, hikers and mountain climbers. Mount Fuji is one of Japan's along with Mount Tate and Mount Haku. It is a List of Special Places of Scenic Beauty, Special Historic Sites and Special Natural Monuments, Special Place of Scenic Beauty and one of Japan's Monuments of Japan, Historic Sites. It was added to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
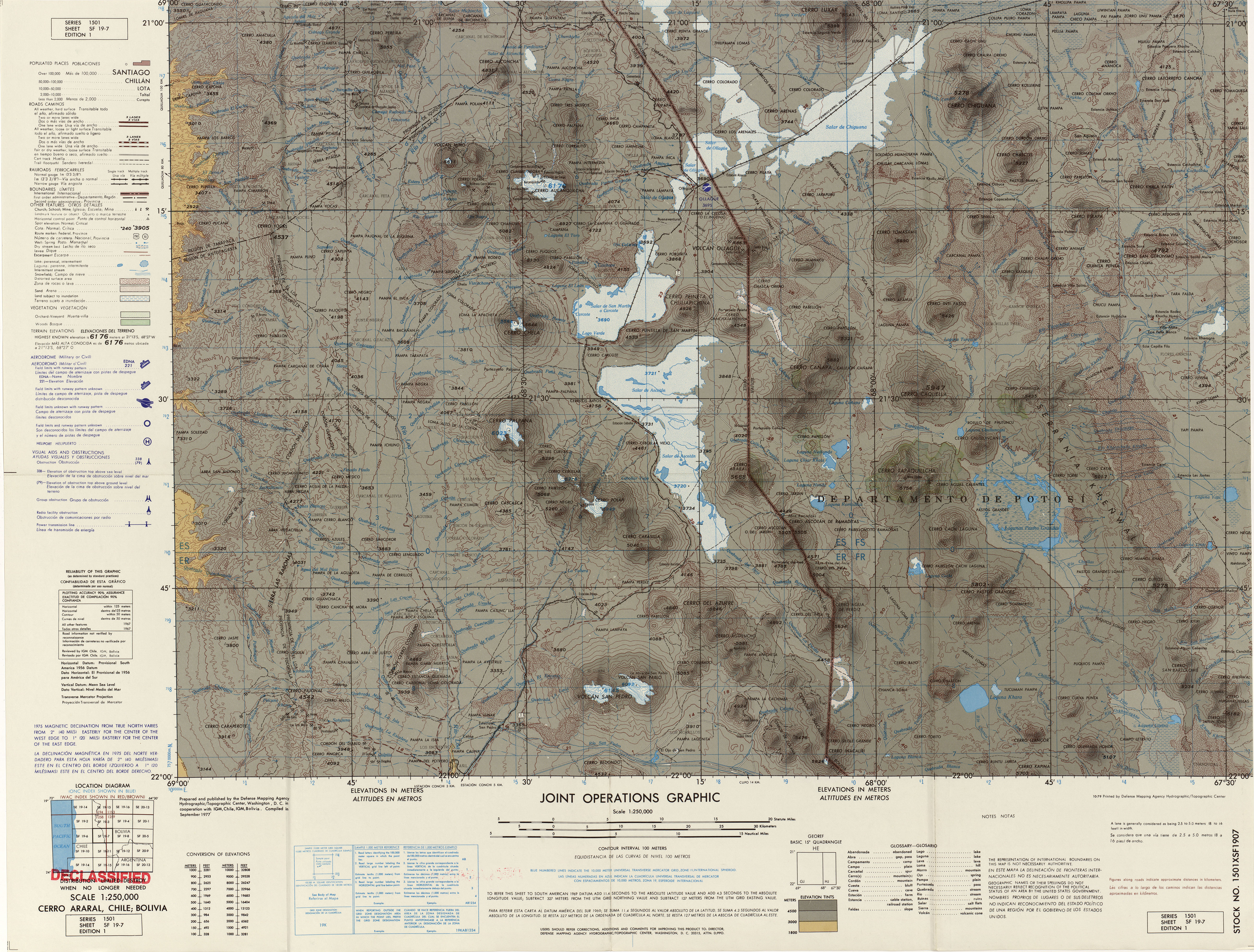
Mountains Of Arica Y Parinacota Region
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cordillera Occidental (other)
Cordillera Occidental is Spanish for "Western mountain". It may refer to: * Cordillera Occidental (Colombia) * Cordillera Occidental (Ecuador) * Cordillera Occidental (Peru) * Cordillera Occidental (Bolivia) See also * Sierra Madre Occidental, the Western mountain range in Mexico * North American Cordillera The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera, or the Pacific Cordillera, is the North American portion of the American Cordillera, the mountain chain system along the Pacifi ..., the Western mountain range in North America * Cordillera Central (other) * Cordillera Oriental (other) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cordillera Oriental (Bolivia)
The Cordillera Oriental or Eastern Cordillera is a set of parallel mountain ranges of the Bolivian Andes, emplaced on the eastern and north eastern margin of the Andes. Large parts of Cordillera Oriental are forested and humid areas rich in agricultural and livestock products. Geologically, the Cordillera Oriental is formed by the Central Andean fold and thrust belt. The Bolivian tin belt lies in the cordillera. Division Topographic map of Bolivia showing (east to west) plains of Sub-Andean Zone in red, Eastern Cordillera in white, Western Cordillera in white">Altiplano in gray, and Cordillera Occidental (Central Andes)">Western Cordillera in white The cordillera can be divided into three sections in Bolivia and one in northwestern Argentina: * The northern section is a continuous mountain range like Eslabón, San Buenaventura, Muchane, Pilón, etc. and between its important summits you can find Astalaya and Cerro Colorado. * The central section was formed entirely by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cordillera Central (Bolivia)
The Cordillera Central is a Bolivian mountain range that divides the three river basins in the country and also has the second highest peaks in Bolivia. It is rich in minerals and starts in the north with Chawpi Urqu and the three Palumanis that were in the south up to Zapaleri, forming a border with Chile and Argentina. The Cordillera Central is divided into three sections: * The northern section or Cordillera Real, with Chawpi Urqu and Palumani, also taking into account the most significant of Bolivia that you find near La Paz, Illimani, Illampu, Janq'u Uma, Mururata, and Huayna Potosí, all of which are more than 6,000 meters high. This section is famous because the highest meteorological observatory in the world can be found on Chacaltaya. Some of the highest ski slopes in the world can be found here also. * The central section contains Sumaq Urqu, with the Potosí mountain range and the ''Paso de Condor'' rail station, both situated at an elevation of 4,288 meters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
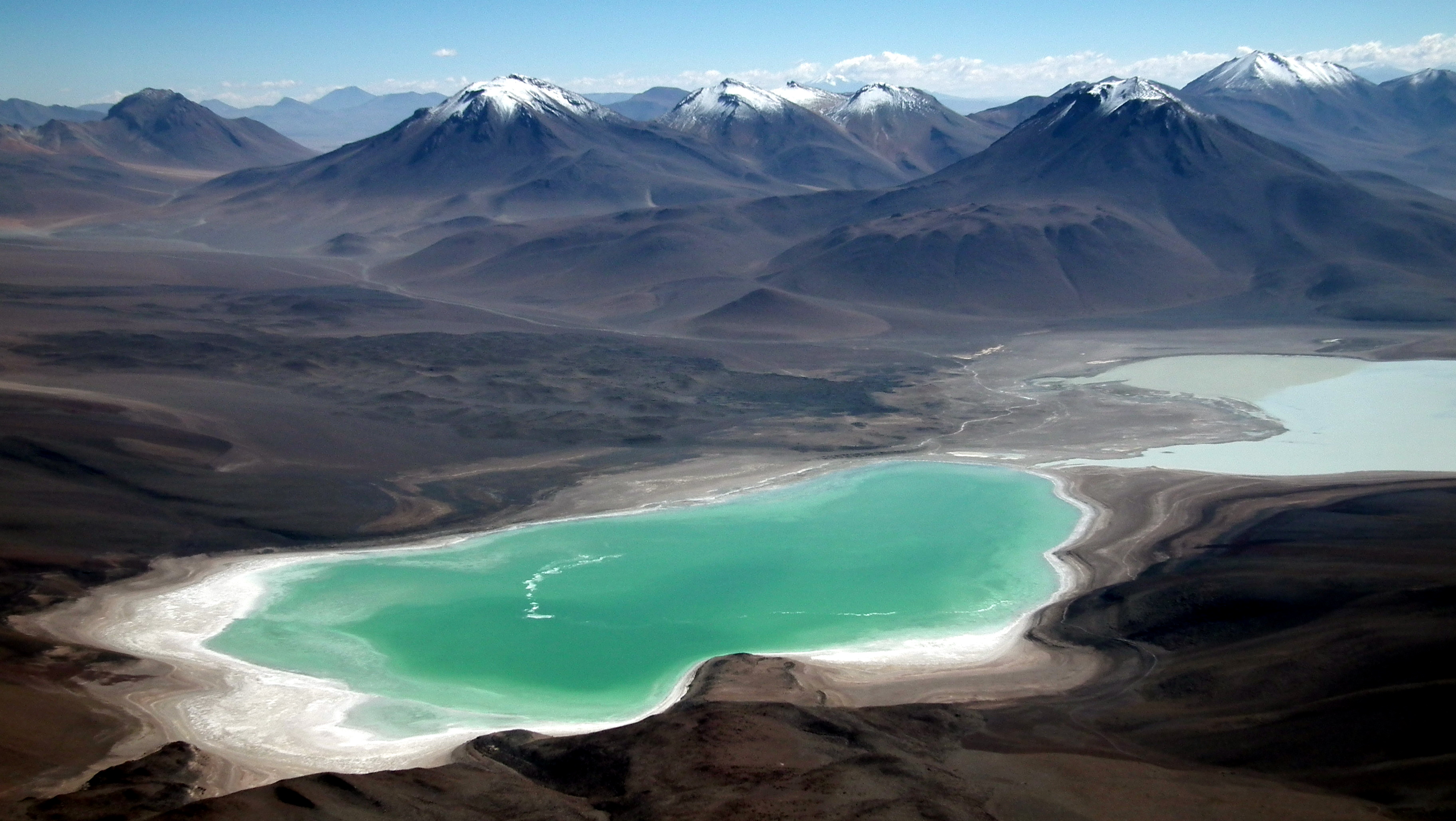
Laguna Verde, Bolivia
__NOTOC__ Laguna Verde (Spanish for "green lake") is a salt lake in an endorheic basin, in the southwestern Altiplano in Bolivia. It is located in the Sur Lípez Province of the Potosí Department. It is close to the Chilean border, at the foot of the volcano Licancabur. Geography The Laguna Verde is a lake at elevation. It covers an area of and has a depth of , and a narrow causeway divides it into two parts. It is at the southwestern extremity of the Eduardo Avaroa Andean Fauna National Reserve and Bolivia itself. It has mineral suspensions of arsenic and other minerals which renders colour to the lake waters. Its color varies from turquoise to dark emerald depending on the disturbance caused to sediments in the lake by winds. In the backdrop of the lake there is the inactive volcano Licancabur of in elevation, which is a nearly perfect cone. The shorelines west and east of the lake have different characteristics, with the western and southern shores eroded into volcanoes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Laguna Colorada
__NOTOC__ Laguna Colorada (''Red Lagoon'') is a shallow salt lake (geography), salt lake in the southwest of the altiplano of Bolivia, within Eduardo Avaroa Andean Fauna National Reserve and close to the border with Chile, notable for the Red, reddish color of its waters. Contents The lake contains borax islands, whose white color contrasts with the reddish color of its waters, which is caused by red sediments and pigmentation of some algae. Geography Laguna Colorada is part of the Los Lípez (formerly Laguna Colorada) Ramsar wetland. It was listed as a "Ramsar list of wetlands of international importance, Ramsar Wetland of International Importance" in 1990. On, July 13, 2009, the site was expanded from 513.18 to to include the surrounding high Andean endorheic, hypersaline and brackish lakes and associated wetlands (known as bofedales). Fauna James's flamingos abound in the area. It is also possible to find Andean flamingo, Andean and Chilean flamingo, Chilean flamingos, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ollagüe
Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the Bolivia–Chile border, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosí Department, Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar. Ollagüe is mostly of Pleistocene age. It started developing more than one million years ago, forming the so-called Vinta Loma and Santa Rosa series mostly of Andesite, andesitic lava flows. A fault (geology), fault bisects the edifice and two large landslides occurred in relation to it. Later two groups of Dacite, dacitic lava domes formed, Ch'aska Urqu (Nor Lípez), Ch'aska Urqu on the southeastern slope and La Celosa on the northwestern. Another centre named La Poruñita formed at that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coipasa
__NOTOC__ Lago Coipasa is a lake in Sabaya Province, Oruro Department, Bolivia. At an elevation of 3657 m, its surface area is 806 km². It is located on the western part of Altiplano, 20 km north of Salar de Uyuni and south of the main road linking Oruro and Huara (Chile). Lake Coipasa is a tectonic saline lake with a depth of 3.5 metres that is surrounded by the Salar de Coipasa ("Coipasa Salt Flats"), and dominated by the volcanic cone of the 4,920 m high Wila Pukarani. Thousands of flamingo Flamingos or flamingoes () are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbe ...s have settled on the shores of Lake Coipasa. Gallery Coipasa lake map of the shape and depth (bathymetry) 2020.jpg, Map of the shape and depth (bathymetry) of the Coipasa lake, 2020 Lago Uru Uru Chipaya 4.jpg, The lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |