|
Contractility
Contractility refers to the ability for self- contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue *Contractile ring in cytokinesis *Contractile vacuole *Muscle contraction **Myocardial contractility *See contractile cell for an overview of cell types in humans. See also *motility Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently using metabolism, metabolic energy. This biological concept encompasses movement at various levels, from whole organisms to cells and subcellular components. Motility is observed in ... {{SIA Cell movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Contractility
Myocardial contractility represents the innate ability of the heart muscle ( cardiac muscle or myocardium) to contract. It is the maximum attainable value for the force of contraction of a given heart. The ability to produce changes in force during contraction result from incremental degrees of binding between different types of tissue, that is, between filaments of myosin (thick) and actin (thin) tissue. The degree of binding depends upon the concentration of calcium ions in the cell. Within an in vivo intact heart, the action/response of the sympathetic nervous system is driven by precisely timed releases of a catecholamine, which is a process that determines the concentration of calcium ions in the cytosol of cardiac muscle cells. The factors causing an increase in contractility work by causing an increase in intracellular calcium ions (Ca++) during contraction. Mechanisms for altering contractility Increasing contractility is done primarily through increasing the influx of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
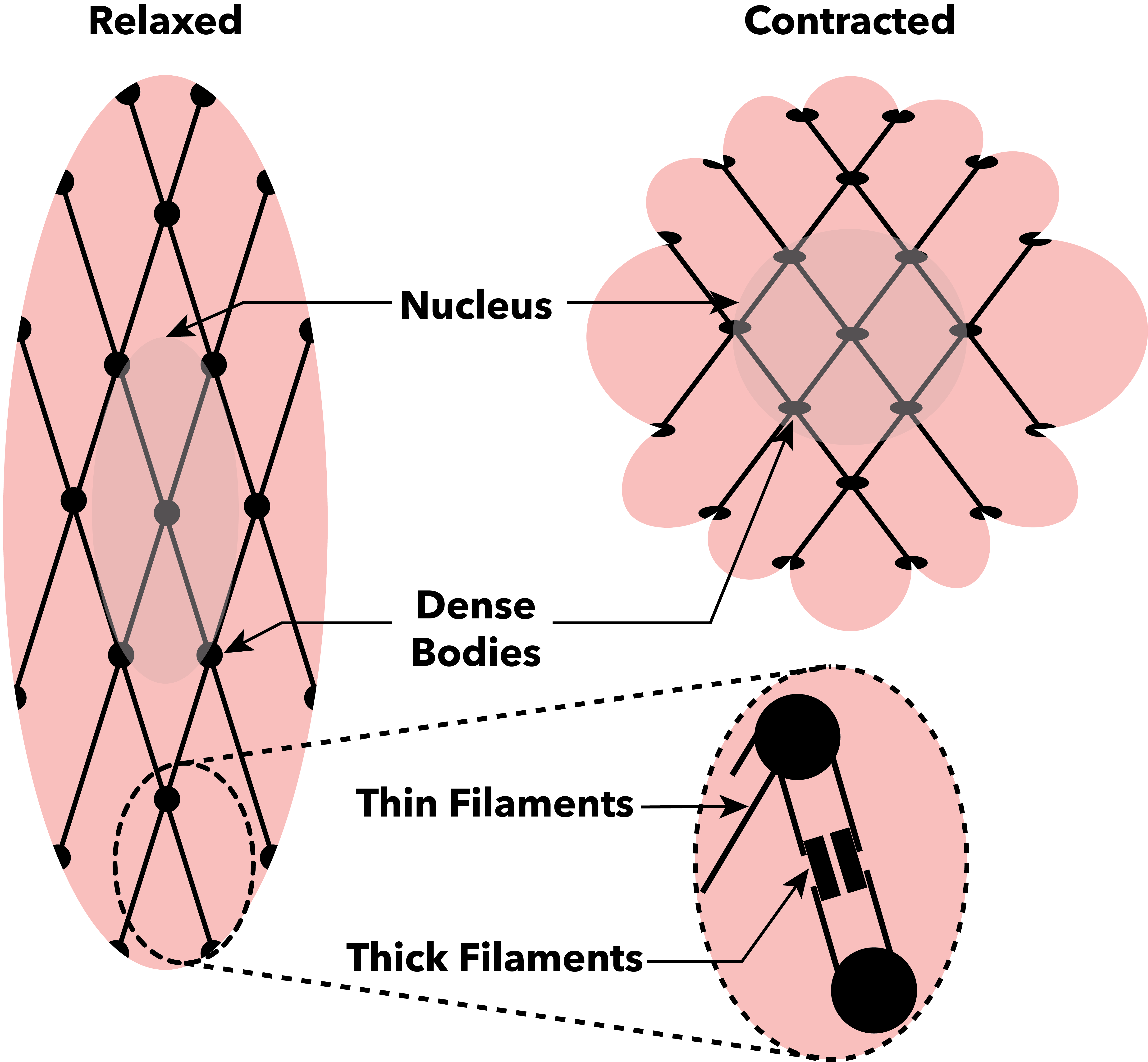
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the change in action of two types of Myofilament, filaments: thin and thick filaments. The major constituent of thin filaments is a chain formed by helical coiling of two strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the Motor protein, motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional organelles in the skeletal muscle system. In vertebrates, Muscle cell#Muscle contraction in striated muscle, skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractile Cell
Contractility refers to the ability for self- contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue * Contractile ring in cytokinesis * Contractile vacuole * Muscle contraction ** Myocardial contractility *See contractile cell for an overview of cell types in humans. See also *motility Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently using metabolism, metabolic energy. This biological concept encompasses movement at various levels, from whole organisms to cells and subcellular components. Motility is observed in ... {{SIA Cell movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction
Contraction may refer to: Linguistics * Contraction (grammar), a shortened word * Poetic contraction, omission of letters for poetic reasons * Elision, omission of sounds ** Syncope (phonology), omission of sounds in a word * Synalepha, merged syllables ** Synaeresis, combined vowels ** Crasis, merged vowels or diphthongs Mathematics and logic * Contraction (operator theory), in operator theory, state of a bounded operator between normed vector spaces after suitable scaling * Contraction hierarchies, in applied mathematics, a technique to speed up shortest-path routing * Contraction mapping, a type of function on a metric space * Edge contraction or vertex contraction, graph operations used in graph theory * Tensor contraction, an operation on one or more tensors that arises from the natural pairing of a finite-dimensional vector space and its dual * Left contraction and right contraction of multivectors in a geometric algebra, extensions of the inner product * One of the rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractile Ring
In molecular biology, an actomyosin ring or contractile ring, is a prominent structure during cytokinesis. It forms perpendicular to the axis of the spindle apparatus towards the end of telophase, in which sister chromatids are identically separated at the opposite sides of the spindle forming nuclei (Figure 1). The actomyosin ring follows an orderly sequence of events: identification of the active division site, formation of the ring, constriction of the ring, and disassembly of the ring. It is composed of actin and myosin II bundles, thus the term actomyosin. The actomyosin ring operates in contractile motion, although the mechanism on how or what triggers the constriction is still an evolving topic. Other cytoskeletal proteins are also involved in maintaining the stability of the ring and driving its constriction. Apart from cytokinesis, in which the ring constricts as the cells divide (Figure 2), actomyosin ring constriction has also been found to activate during wound closu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractile Vacuole
A contractile vacuole (CV) is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists, including unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole. Overview The contractile vacuole is a specialized type of vacuole that regulates the quantity of water inside a cell. In freshwater environments, the concentration of solutes is hypotonic, lower outside than inside the cell. Under these conditions, osmosis causes water to accumulate in the cell from the external environment. The contractile vacuole acts as part of a protective mechanism that prevents the cell from absorbing too much water and possibly lysing (rupturing) through excessive internal pressure. The contractile vacuole, as its name suggests, expels water out of the cell by contracting. The growth (water gathering) and contraction (water expulsion) of the contractile vacuole are periodical. One cycle takes several seconds, depending on the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently using metabolism, metabolic energy. This biological concept encompasses movement at various levels, from whole organisms to cells and subcellular components. Motility is observed in animals, microorganisms, and even some plant structures, playing crucial roles in activities such as foraging, reproduction, and cellular functions. It is genetically determined but can be influenced by environmental factors. In multicellular organisms, motility is facilitated by systems like the Nervous system, nervous and Human musculoskeletal system, musculoskeletal systems, while at the cellular level, it involves mechanisms such as amoeboid movement and flagellar propulsion. These cellular movements can be directed by external stimuli, a phenomenon known as taxis. Examples include chemotaxis (movement along chemical gradients) and phototaxis (movement in response to light). Motility also includes physiological processes like gastroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |